Windows Vista theme by NaViTo
Download: Vista_NaViTo.p3t

The #1 spot for Playstation themes!
Vortex theme by faps
Download: Vortex.p3t

(1 background, different for HD and SD)



In fluid dynamics, a vortex (pl.: vortices or vortexes)[1][2] is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved.[3][4] Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of a boat, and the winds surrounding a tropical cyclone, tornado or dust devil.
Vortices are a major component of turbulent flow. The distribution of velocity, vorticity (the curl of the flow velocity), as well as the concept of circulation are used to characterise vortices. In most vortices, the fluid flow velocity is greatest next to its axis and decreases in inverse proportion to the distance from the axis.
In the absence of external forces, viscous friction within the fluid tends to organise the flow into a collection of irrotational vortices, possibly superimposed to larger-scale flows, including larger-scale vortices. Once formed, vortices can move, stretch, twist, and interact in complex ways. A moving vortex carries some angular and linear momentum, energy, and mass, with it.
In the dynamics of fluid, a vortex is fluid that revolves around the axis line. This fluid might be curved or straight. Vortices form from stirred fluids: they might be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools, in the wake of a boat or the winds around a tornado or dust devil.
Vortices are an important part of turbulent flow. Vortices can otherwise be known as a circular motion of a liquid. In the cases of the absence of forces, the liquid settles. This makes the water stay still instead of moving.
When they are created, vortices can move, stretch, twist and interact in complicated ways. When a vortex is moving, sometimes, it can affect an angular position.
For an example, if a water bucket is rotated or spun constantly, it will rotate around an invisible line called the axis line. The rotation moves around in circles. In this example the rotation of the bucket creates extra force.
The reason that the vortices can change shape is the fact that they have open particle paths. This can create a moving vortex. Examples of this fact are the shapes of tornadoes and drain whirlpools.
When two or more vortices are close together they can merge to make a vortex. Vortices also hold energy in its rotation of the fluid. If the energy is never removed, it would consist of circular motion forever.

A key concept in the dynamics of vortices is the vorticity, a vector that describes the local rotary motion at a point in the fluid, as would be perceived by an observer that moves along with it. Conceptually, the vorticity could be observed by placing a tiny rough ball at the point in question, free to move with the fluid, and observing how it rotates about its center. The direction of the vorticity vector is defined to be the direction of the axis of rotation of this imaginary ball (according to the right-hand rule) while its length is twice the ball's angular velocity. Mathematically, the vorticity is defined as the curl (or rotational) of the velocity field of the fluid, usually denoted by and expressed by the vector analysis formula , where is the nabla operator and is the local flow velocity.[5]
The local rotation measured by the vorticity must not be confused with the angular velocity vector of that portion of the fluid with respect to the external environment or to any fixed axis. In a vortex, in particular, may be opposite to the mean angular velocity vector of the fluid relative to the vortex's axis.
In theory, the speed u of the particles (and, therefore, the vorticity) in a vortex may vary with the distance r from the axis in many ways. There are two important special cases, however:
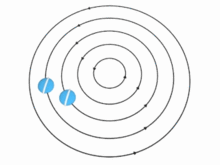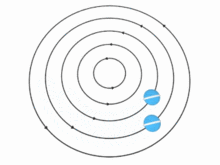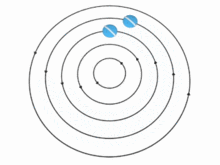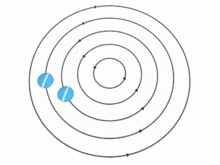
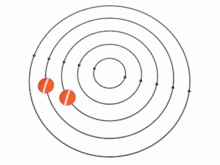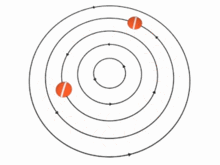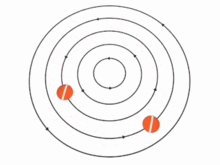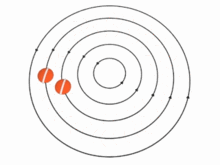

In the absence of external forces, a vortex usually evolves fairly quickly toward the irrotational flow pattern[citation needed], where the flow velocity u is inversely proportional to the distance r. Irrotational vortices are also called free vortices.
For an irrotational vortex, the circulation is zero along any closed contour that does not enclose the vortex axis; and has a fixed value, Γ, for any contour that does enclose the axis once.[6] The tangential component of the particle velocity is then . The angular momentum per unit mass relative to the vortex axis is therefore constant, .
The ideal irrotational vortex flow in free space is not physically realizable, since it would imply that the particle speed (and hence the force needed to keep particles in their circular paths) would grow without bound as one approaches the vortex axis. Indeed, in real vortices there is always a core region surrounding the axis where the particle velocity stops increasing and then decreases to zero as r goes to zero. Within that region, the flow is no longer irrotational: the vorticity becomes non-zero, with direction roughly parallel to the vortex axis. The Rankine vortex is a model that assumes a rigid-body rotational flow where r is less than a fixed distance r0, and irrotational flow outside that core regions.
In a viscous fluid, irrotational flow contains viscous dissipation everywhere, yet there are no net viscous forces, only viscous stresses.[7] Due to the dissipation, this means that sustaining an irrotational viscous vortex requires continuous input of work at the core (for example, by steadily turning a cylinder at the core). In free space there is no energy input at the core, and thus the compact vorticity held in the core will naturally diffuse outwards, converting the core to a gradually-slowing and gradually-growing rigid-body flow, surrounded by the original irrotational flow. Such a decaying irrotational vortex has an exact solution of the viscous Navier–Stokes equations, known as a Lamb–Oseen vortex.

A rotational vortex – a vortex that rotates in the same way as a rigid body – cannot exist indefinitely in that state except through the application of some extra force, that is not generated by the fluid motion itself. It has non-zero vorticity everywhere outside the core. Rotational vortices are also called rigid-body vortices or forced vortices.
For example, if a water bucket is spun at constant angular speed w about its vertical axis, the water will eventually rotate in rigid-body fashion. The particles will then move along circles, with velocity u equal to wr.[6] In that case, the free surface of the water will assume a parabolic shape.
In this situation, the rigid rotating enclosure provides an extra force, namely an extra pressure gradient in the water, directed inwards, that prevents transition of the rigid-body flow to the irrotational state.
Vortex structures are defined by their vorticity, the local rotation rate of fluid particles. They can be formed via the phenomenon known as boundary layer separation which can occur when a fluid moves over a surface and experiences a rapid acceleration from the fluid velocity to zero due to the no-slip condition. This rapid negative acceleration creates a boundary layer which causes a local rotation of fluid at the wall (i.e. vorticity) which is referred to as the wall shear rate. The thickness of this boundary layer is proportional to (where v is the free stream fluid velocity and t is time).
If the diameter or thickness of the vessel or fluid is less than the boundary layer thickness then the boundary layer will not separate and vortices will not form. However, when the boundary layer does grow beyond this critical boundary layer thickness then separation will occur which will generate vortices.
This boundary layer separation can also occur in the presence of combatting pressure gradients (i.e. a pressure that develops downstream). This is present in curved surfaces and general geometry changes like a convex surface. A unique example of severe geometric changes is at the trailing edge of a bluff body where the fluid flow deceleration, and therefore boundary layer and vortex formation, is located.
Another form of vortex formation on a boundary is when fluid flows perpendicularly into a wall and creates a splash effect. The velocity streamlines are immediately deflected and decelerated so that the boundary layer separates and forms a toroidal vortex ring.[8]
In a stationary vortex, the typical streamline (a line that is everywhere tangent to the flow velocity vector) is a closed loop surrounding the axis; and each vortex line (a line that is everywhere tangent to the vorticity vector) is roughly parallel to the axis. A surface that is everywhere tangent to both flow velocity and vorticity is called a vortex tube. In general, vortex tubes are nested around the axis of rotation. The axis itself is one of the vortex lines, a limiting case of a vortex tube with zero diameter.
According to Helmholtz's theorems, a vortex line cannot start or end in the fluid – except momentarily, in non-steady flow, while the vortex is forming or dissipating. In general, vortex lines (in particular, the axis line) are either closed loops or end at the boundary of the fluid. A whirlpool is an example of the latter, namely a vortex in a body of water whose axis ends at the free surface. A vortex tube whose vortex lines are all closed will be a closed torus-like surface.
A newly created vortex will promptly extend and bend so as to eliminate any open-ended vortex lines. For example, when an airplane engine is started, a vortex usually forms ahead of each propeller, or the turbofan of each jet engine. One end of the vortex line is attached to the engine, while the other end usually stretches out and bends until it reaches the ground.
When vortices are made visible by smoke or ink trails, they may seem to have spiral pathlines or streamlines. However, this appearance is often an illusion and the fluid particles are moving in closed paths. The spiral streaks that are taken to be streamlines are in fact clouds of the marker fluid that originally spanned several vortex tubes and were stretched into spiral shapes by the non-uniform flow velocity distribution.

The fluid motion in a vortex creates a dynamic pressure (in addition to any hydrostatic pressure) that is lowest in the core region, closest to the axis, and increases as one moves away from it, in accordance with Bernoulli's principle. One can say that it is the gradient of this pressure that forces the fluid to follow a curved path around the axis.
In a rigid-body vortex flow of a fluid with constant density, the dynamic pressure is proportional to the square of the distance r from the axis. In a constant gravity field, the free surface of the liquid, if present, is a concave paraboloid.
In an irrotational vortex flow with constant fluid density and cylindrical symmetry, the dynamic pressure varies as P∞ − K/r2, where P∞ is the limiting pressure infinitely far from the axis. This formula provides another constraint for the extent of the core, since the pressure cannot be negative. The free surface (if present) dips sharply near the axis line, with depth inversely proportional to r2. The shape formed by the free surface is called a hyperboloid, or "Gabriel's Horn" (by Evangelista Torricelli).
The core of a vortex in air is sometimes visible because water vapor condenses as the low pressure of the core causes adiabatic cooling; the funnel of a tornado is an example. When a vortex line ends at a boundary surface, the reduced pressure may also draw matter from that surface into the core. For example, a dust devil is a column of dust picked up by the core of an air vortex attached to the ground. A vortex that ends at the free surface of a body of water (like the whirlpool that often forms over a bathtub drain) may draw a column of air down the core. The forward vortex extending from a jet engine of a parked airplane can suck water and small stones into the core and then into the engine.
Vortices need not be steady-state features; they can move and change shape. In a moving vortex, the particle paths are not closed, but are open, loopy curves like helices and cycloids. A vortex flow might also be combined with a radial or axial flow pattern. In that case the streamlines and pathlines are not closed curves but spirals or helices, respectively. This is the case in tornadoes and in drain whirlpools. A vortex with helical streamlines is said to be solenoidal.
As long as the effects of viscosity and diffusion are negligible, the fluid in a moving vortex is carried along with it. In particular, the fluid in the core (and matter trapped by it) tends to remain in the core as the vortex moves about. This is a consequence of Helmholtz's second theorem. Thus vortices (unlike surface waves and pressure waves) can transport mass, energy and momentum over considerable distances compared to their size, with surprisingly little dispersion. This effect is demonstrated by smoke rings and exploited in vortex ring toys and guns.
Two or more vortices that are approximately parallel and circulating in the same direction will attract and eventually merge to form a single vortex, whose circulation will equal the sum of the circulations of the constituent vortices. For example, an airplane wing that is developing lift will create a sheet of small vortices at its trailing edge. These small vortices merge to form a single wingtip vortex, less than one wing chord downstream of that edge. This phenomenon also occurs with other active airfoils, such as propeller blades. On the other hand, two parallel vortices with opposite circulations (such as the two wingtip vortices of an airplane) tend to remain separate.
Vortices contain substantial energy in the circular motion of the fluid. In an ideal fluid this energy can never be dissipated and the vortex would persist forever. However, real fluids exhibit viscosity and this dissipates energy very slowly from the core of the vortex. It is only through dissipation of a vortex due to viscosity that a vortex line can end in the fluid, rather than at the boundary of the fluid.


Windows Vista theme by rsebes
Download: Vista_rsebes.p3t

(9 backgrounds)
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
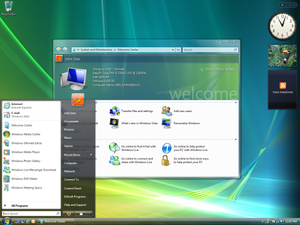 Screenshot of Windows Vista Ultimate, showing its desktop, taskbar, Start menu, Windows Sidebar, Welcome Center, and glass effects of Windows Aero | |
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model | |
| Released to manufacturing | November 8, 2006[2] |
| General availability | January 30, 2007[3] |
| Final release | Service Pack 2[4] (6.0.6002.24170) / July 21, 2017[5] |
| Marketing target | Consumer and Business |
| Update method | |
| Platforms | IA-32 and x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| Userland | Windows API, NTVDM, SUA |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows XP (2001) |
| Succeeded by | Windows 7 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Vista (archived at the Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on April 10, 2012[6] Extended support ended on April 11, 2017[6] | |
| Part of a series of articles on |
| Windows Vista |
|---|
| New features |
| Siblings |
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows. It was released to manufacturing on November 8, 2006, and over the following two months, it was released in stages to business customers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; it is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform.[7]
Development of Windows Vista began in 2001 when it was codenamed "Longhorn"; originally envisioned as a minor successor to Windows XP, it gradually included numerous new features from the then-next major release of Windows codenamed "Blackcomb", after which it was repositioned as a major release of Windows, and it consequently underwent a protracted development that was unprecedented for Microsoft. Most new features were prominently based on a new presentation layer codenamed Avalon, a new communications architecture codenamed Indigo, and a relational storage platform codenamed WinFS — all built on the premature .NET Framework; however, this proved to be untenable due to incompleteness of technologies and ways in which new features were added, and Microsoft changed the project in 2004. Many new features were eventually reimplemented during development, but Microsoft ceased using managed code to develop the operating system.[8]
New features of Windows Vista include a graphical user interface and visual style referred to as Windows Aero; a content index and desktop search platform called Windows Search; new peer-to-peer technologies to simplify sharing files and media between computers and devices on a home network; and new multimedia tools such as Windows DVD Maker. Windows Vista included version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, allowing software developers to write applications without traditional Windows APIs. There are major architectural overhauls to audio, display, network, and print sub-systems; deployment, installation, servicing, and startup procedures are also revised. It is the first release of Windows built on Microsoft's Trustworthy Computing initiative and emphasized security with the introduction of many new security and safety features such as BitLocker and User Account Control.
The ambitiousness and scope of these changes, and the abundance of new features earned positive reviews, but Windows Vista was the subject of frequent negative press and significant criticism. Criticism of Windows Vista focused on driver, peripheral, and program incompatibility; digital rights management; excessive authorization from the new User Account Control; inordinately high system requirements when contrasted with Windows XP; its protracted development; longer boot time; and more restrictive product licensing. Windows Vista deployment and satisfaction rates were consequently lower than those of Windows XP, and it is considered a market failure;[9][10] however, its use surpassed Microsoft's pre-launch two-year-out expectations of achieving 200 million users[11] (with an estimated 330 million users by 2009).[12] On October 22, 2010, Microsoft ceased retail distribution of Windows Vista; OEM supply ceased a year later.[13] Windows Vista was succeeded by Windows 7 in 2009.
Mainstream support for Windows Vista ended on April 10, 2012 and extended support ended on April 11, 2017.[6]
Microsoft began work on Windows Vista, known at the time by its codename "Longhorn", in May 2001,[14] five months before the release of Windows XP. It was originally expected to ship in October 2003 as a minor step between Windows XP and "Blackcomb", which was planned to be the company's next major operating system release. Gradually, "Longhorn" assimilated many of the important new features and technologies slated for Blackcomb, resulting in the release date being pushed back several times in three years. In some builds of Longhorn, their license agreement said "For the Microsoft product codenamed 'Whistler'". Many of Microsoft's developers were also re-tasked to build updates to Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to strengthen security. Faced with ongoing delays and concerns about feature creep, Microsoft announced on August 27, 2004, that it had revised its plans. For this reason, Longhorn was reset to start work on componentizing the Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 codebase, and over time re-incorporating the features that would be intended for an actual operating system release. However, some previously announced features such as WinFS were dropped or postponed, and a new software development methodology called the Security Development Lifecycle was incorporated to address concerns with the security of the Windows codebase, which is programmed in C, C++ and assembly. Longhorn became known as Vista in 2005. Vista in Spanish means view.[15][16]
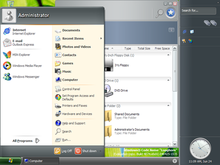
The early development stages of Longhorn were generally characterized by incremental improvements and updates to Windows XP. During this period, Microsoft was fairly quiet about what was being worked on, as their marketing and public relations efforts were more strongly focused on Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003, which was released in April 2003. Occasional builds of Longhorn were leaked onto popular file sharing networks such as IRC, BitTorrent, eDonkey and various newsgroups, and so most of what is known about builds before the first sanctioned development release of Longhorn in May 2003 is derived from these builds.
After several months of relatively little news or activity from Microsoft with Longhorn, Microsoft released Build 4008, which had made an appearance on the Internet around February 28, 2003.[17] It was also privately handed out to a select group of software developers. As an evolutionary release over build 3683, it contained several small improvements, including a modified blue "Plex" theme and a new, simplified Windows Image-based installer that operates in graphical mode from the outset, and completed an install of the operating system in approximately one third the time of Windows XP on the same hardware. An optional "new taskbar" was introduced that was thinner than the previous build and displayed the time differently. The most notable visual and functional difference, however, came with Windows Explorer. The incorporation of the Plex theme made blue the dominant color of the entire application. The Windows XP-style task pane was almost completely replaced with a large horizontal pane that appeared under the toolbars. A new search interface allowed for filtering of results, searching for Windows help, and natural-language queries that would be used to integrate with WinFS. The animated search characters were also removed. The "view modes" were also replaced with a single slider that would resize the icons in real-time, in the list, thumbnail, or details mode, depending on where the slider was. File metadata was also made more visible and more easily editable, with more active encouragement to fill out missing pieces of information. Also of note was the conversion of Windows Explorer to being a .NET application.
Most builds of Longhorn and Vista were identified by a label that was always displayed in the bottom-right corner of the desktop. A typical build label would look like "Longhorn Build 3683.Lab06_N.020923-1821". Higher build numbers did not automatically mean that the latest features from every development team at Microsoft was included. Typically, a team working on a certain feature or subsystem would generate their working builds which developers would test with, and when the code was deemed stable, all the changes would be incorporated back into the main development tree at once. At Microsoft, several "Build labs" exist where the compilation of the entirety of Windows can be performed by a team. The name of the lab in which any given build originated is shown as part of the build label, and the date and time of the build follow that. Some builds (such as Beta 1 and Beta 2) only display the build label in the version information dialog (Winver). The icons used in these builds are from Windows XP.
At the Windows Hardware Engineering Conference (WinHEC) in May 2003, Microsoft gave their first public demonstrations of the new Desktop Window Manager and Aero. The demonstrations were done on a revised build 4015 which was never released. Several sessions for developers and hardware engineers at the conference focused on these new features, as well as the Next-Generation Secure Computing Base (previously known as "Palladium"), which at the time was Microsoft's proposed solution for creating a secure computing environment whereby any given component of the system could be deemed "trusted". Also at this conference, Microsoft reiterated their roadmap for delivering Longhorn, pointing to an "early 2005" release date.[18]
By 2004, it had become obvious to the Windows team at Microsoft that they were losing sight of what needed to be done to complete the next version of Windows and ship it to customers. Internally, some Microsoft employees were describing the Longhorn project as "another Cairo" or "Cairo.NET", referring to the Cairo development project that the company embarked on through the first half of the 1990s, which never resulted in a shipping operating system (though nearly all the technologies developed in that time did end up in Windows 95 and Windows NT[19]). Microsoft was shocked in 2005 by Apple's release of Mac OS X Tiger. It offered only a limited subset of features planned for Longhorn, in particular fast file searching and integrated graphics and sound processing, but appeared to have impressive reliability and performance compared to contemporary Longhorn builds.[20] Most Longhorn builds had major Windows Explorer system leaks which prevented the OS from performing well, and added more confusion to the development teams in later builds with more and more code being developed which failed to reach stability.
In a September 23, 2005 front-page article in The Wall Street Journal,[21] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin, who had overall responsibility for the development and delivery of Windows, explained how development of Longhorn had been "crashing into the ground" due in large part to the haphazard methods by which features were introduced and integrated into the core of the operating system, without a clear focus on an end-product. Allchin went on to explain how in December 2003, he enlisted the help of two other senior executives, Brian Valentine and Amitabh Srivastava, the former being experienced with shipping software at Microsoft, most notably Windows Server 2003,[22] and the latter having spent his career at Microsoft researching and developing methods of producing high-quality testing systems.[23] Srivastava employed a team of core architects to visually map out the entirety of the Windows operating system, and to proactively work towards a development process that would enforce high levels of code quality, reduce interdependencies between components, and in general, "not make things worse with Vista".[24] Since Microsoft decided that Longhorn needed to be further componentized, work started on builds (known as the Omega-13 builds, named after a time travel device in the film Galaxy Quest[25]) that would componentize existing Windows Server 2003 source code, and over time add back functionality as development progressed. Future Longhorn builds would start from Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 and continue from there.
This change, announced internally to Microsoft employees on August 26, 2004, began in earnest in September, though it would take several more months before the new development process and build methodology would be used by all of the development teams. A number of complaints came from individual developers, and Bill Gates himself, that the new development process was going to be prohibitively difficult to work within.
By approximately November 2004, the company had considered several names for the final release, ranging from simple to fanciful and inventive. In the end, Microsoft chose Windows Vista as confirmed on July 22, 2005, believing it to be a "wonderful intersection of what the product really does, what Windows stands for, and what resonates with customers, and their needs". Group Project Manager Greg Sullivan told Paul Thurrott "You want the PC to adapt to you and help you cut through the clutter to focus on what's important to you. That's what Windows Vista is all about: "bringing clarity to your world" (a reference to the three marketing points of Vista—Clear, Connected, Confident), so you can focus on what matters to you".[26] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin also loved the name, saying that "Vista creates the right imagery for the new product capabilities and inspires the imagination with all the possibilities of what can be done with Windows—making people's passions come alive."[27]
After Longhorn was named Windows Vista in July 2005, an unprecedented beta-test program was started, involving hundreds of thousands of volunteers and companies. In September of that year, Microsoft started releasing regular Community Technology Previews (CTP) to beta testers from July 2005 to February 2006. The first of these was distributed at the 2005 Microsoft Professional Developers Conference, and was subsequently released to beta testers and Microsoft Developer Network subscribers. The builds that followed incorporated most of the planned features for the final product, as well as a number of changes to the user interface, based largely on feedback from beta testers. Windows Vista was deemed feature-complete with the release of the "February CTP", released on February 22, 2006, and much of the remainder of the work between that build and the final release of the product focused on stability, performance, application and driver compatibility, and documentation. Beta 2, released in late May, was the first build to be made available to the general public through Microsoft's Customer Preview Program. It was downloaded over 5 million times. Two release candidates followed in September and October, both of which were made available to a large number of users.[28]
At the Intel Developer Forum on March 9, 2006, Microsoft announced a change in their plans to support EFI in Windows Vista. The UEFI 2.0 specification (which replaced EFI 1.10) was not completed until early 2006, and at the time of Microsoft's announcement, no firmware manufacturers had completed a production implementation which could be used for testing. As a result, the decision was made to postpone the introduction of UEFI support to Windows; support for UEFI on 64-bit platforms was postponed until Vista Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2008 and 32-bit UEFI would not be supported, as Microsoft did not expect many such systems to be built because the market was quickly moving to 64-bit processors.[29][30]
While Microsoft had originally hoped to have the consumer versions of the operating system available worldwide in time for the 2006 holiday shopping season, it announced in March 2006 that the release date would be pushed back to January 2007 in order to give the company—and the hardware and software companies that Microsoft depends on for providing device drivers—additional time to prepare. Because a release to manufacturing (RTM) build is the final version of code shipped to retailers and other distributors, the purpose of a pre-RTM build is to eliminate any last "show-stopper" bugs that may prevent the code from responsibly being shipped to customers, as well as anything else that consumers may find troublesome. Thus, it is unlikely that any major new features would be introduced; instead, work would focus on Vista's fit and finish. In just a few days, developers had managed to drop Vista's bug count from over 2470 on September 22 to just over 1400 by the time RC2 shipped in early October. However, they still had a way to go before Vista was ready to RTM. Microsoft's internal processes required Vista's bug count to drop to 500 or fewer before the product could go into escrow for RTM.[31] For most of the pre-RTM builds, only 32-bit editions were released.
On June 14, 2006, Windows developer Philip Su posted a blog entry which decried the development process of Windows Vista, stating that "The code is way too complicated, and that the pace of coding has been tremendously slowed down by overbearing process."[32] The same post also described Windows Vista as having approximately 50 million lines of code, with about 2,000 developers working on the product. During a demonstration of the speech recognition feature new to Windows Vista at Microsoft's Financial Analyst Meeting on July 27, 2006, the software recognized the phrase "Dear mom" as "Dear aunt". After several failed attempts to correct the error, the sentence eventually became "Dear aunt, let's set so double the killer delete select all".[33] A developer with Vista's speech recognition team later explained that there was a bug with the build of Vista that was causing the microphone gain level to be set very high, resulting in the audio being received by the speech recognition software being "incredibly distorted".[34]
Windows Vista build 5824 (October 17, 2006) was supposed to be the RTM release, but a bug, where the OOBE hangs at the start of the WinSAT Assessment (if upgraded from Windows XP), requiring the user to terminate msoobe.exe by pressing Shift+F10 to open Command Prompt using either command-line tools or Task Manager prevented this, damaging development and lowering the chance that it would hit its January 2007 deadline.[35]
Development of Windows Vista came to an end when Microsoft announced that it had been finalized on November 8, 2006, and was concluded by co-president of Windows development, Jim Allchin.[36] The RTM's build number had also jumped to 6000 to reflect Vista's internal version number, NT 6.0.[37] Jumping RTM build numbers is common practice among consumer-oriented Windows versions, like Windows 98 (build 1998), Windows 98 SE (build 2222), Windows Me (build 3000) or Windows XP (build 2600), as compared to the business-oriented versions like Windows 2000 (build 2195) or Server 2003 (build 3790). On November 16, 2006, Microsoft made the final build available to MSDN and Technet Plus subscribers.[38] A business-oriented Enterprise edition was made available to volume license customers on November 30, 2006.[39] Windows Vista was launched for general customer availability on January 30, 2007.[3]
New features introduced by Windows Vista are very numerous, encompassing significant functionality not available in its predecessors.
Lil Monsters theme by xBiG_BOSSx
Download: LilMonsters.p3t
(1 background)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Kubrick Tribute theme by YASAI
Download: KubrickTribute.p3t

(1 background)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Star Wars Vader Time theme by PenguinRage and EVILEMPIRE
Download: VaderTime_by_PenguinRage.p3t

(1 background)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Kingdom Hearts theme by Septimus
Download: kingdomhearts.p3t

(1 background)
| Kingdom Hearts | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Genre(s) | |
| Developer(s) |
|
| Publisher(s) |
|
| Creator(s) | |
| Composer(s) | Yoko Shimomura |
| Platform(s) | |
| First release | Kingdom Hearts March 28, 2002 |
| Latest release | Kingdom Hearts: Melody of Memory November 11, 2020 |
| Parent series | Final Fantasy |
Kingdom Hearts[a] is a series of action role-playing games created by Japanese game designers Tetsuya Nomura and Shinji Hashimoto, being developed and published by Square Enix (originally by Square). It is a collaboration between Square Enix and The Walt Disney Company, and is under the leadership of Nomura, a longtime Square Enix employee.
Kingdom Hearts is a crossover of various Disney properties based in an original fictional universe. The series centers on the main character, Sora, and his journey and experiences with various Disney characters, as well as some from Square Enix properties, such as Final Fantasy, The World Ends with You, and Einhänder, in addition to original characters and locations created specifically for the series.
The series consists of thirteen games available for multiple platforms, and future games are planned. Most of the games in the series have been positively received and commercially successful. As of March 2022, the Kingdom Hearts series has shipped more than 36 million copies worldwide. A wide variety of related merchandise has been released along with the games, including soundtracks, action figures, companion books, light novels, a collectible card game, and a manga series.
| 2002 | Kingdom Hearts |
|---|---|
| 2003 | |
| 2004 | Chain of Memories |
| 2005 | Kingdom Hearts II |
| 2006 | |
| 2007 | Re:Chain of Memories |
| 2008 | Coded |
| 2009 | 358/2 Days |
| 2010 | Birth by Sleep |
| Re:coded | |
| 2011 | |
| 2012 | Dream Drop Distance |
| 2013 | 1.5 Remix |
| χ | |
| 2014 | 2.5 Remix |
| 2015 | (Unchained / Union) χ |
| 2016 | |
| 2017 | 2.8 Final Chapter Prologue |
| 2018 | |
| 2019 | Kingdom Hearts III |
| 2020 | Dark Road |
| Melody of Memory | |
| 2021 | |
| 2022 | |
| 2023 | |
| 2024 | Missing-Link |
| TBA | Kingdom Hearts IV |
Kingdom Hearts features a mixture of familiar Disney and Square Enix characters, as well as several new characters designed and created by Nomura.[77] In addition to original locations, the Kingdom Hearts series features many worlds from Disney films. Sora must visit these worlds and interact with various Disney characters to protect them from enemies. Often, his actions in these worlds closely follow the storylines of their respective Disney films. The main characters try not to interfere with the affairs of other worlds, as it could negatively affect the universe's order.[78][79] Various Final Fantasy characters also make appearances within several worlds throughout the series. This includes Moogles, small creatures who are another common element in the games. They provide the player with a synthesis shop in order to create and purchase items used in the game. The main cast from The World Ends with You also makes an appearance in the series in Dream Drop Distance, and Kingdom Hearts III features characters from Pixar films such as the Toy Story series and Monsters, Inc., as well as Schwarzgeist, one of the bosses from Einhänder.[80][81][82] Nevertheless, the usage of Disney characters is not without restrictions. For example, Nomura had requested the use of Oswald the Lucky Rabbit in Kingdom Hearts III, but the response from Disney was that the character would be "too difficult" to use, with no further clarification or details from Disney.[83]
This article's plot summary may be too long or excessively detailed. (April 2022) |
 | |
Type of site | Internet forum |
|---|---|
| Available in | English |
| Owner | NeoGaf LLC (100% — Tyler Malka) |
| Created by | Jim Cordeira |
| URL | neogaf.com |
| Commercial | Yes |
| Registration | Optional[α] |
| Launched | 1999 (as Gaming-Age Forums) |
| Current status | Active |
| Written in | PHP, MySQL (powered by XenForo 2.2) |
NeoGAF is an Internet forum primarily dedicated to the discussion of video games. Founded as an adjunct to a video game news site under the name Gaming-Age Forums, on April 4, 2006 it changed its name to NeoGAF and became independently hosted and administered.
In 2017, site owner Tyler "Evilore" Malka was accused of sexual harassment. The allegations resulted in moderator resignations, mass exodus off the site and later site policy changes. Former members and moderators would later launch the new forum ResetEra.
NeoGAF began as "The Gaming-Age Forums", a forum for gaming website Gaming-Age. As Gaming-Age outgrew its hosting, IGN took over hosting of Gaming-Age's forums. After IGN ceased hosting of GAF in mid-2001, GAF moved to ezboard, and the administration of GAF became more estranged from Gaming Age.[1]
As the Gaming-Age staff became gradually more divorced from the day-to-day operation of GAF, problems with the new Gamesquad hosting cropped up. As software bugs in vBulletin 2, the version GAF was using at the time, continued to worsen, the Gamesquad hosting became increasingly more impractical, until the forums' database became corrupted, forcing a move to new hosting in order to change software and salvage what was left of the forums' database. In the spring of 2004, a fundraiser was held to move GAF to new hosting. On June 6, 2004, GAF took its newest form (known as NeoGAF to long-time posters) and moved to new hosting and new software, vBulletin 3.
On April 4, 2006, the forums were relaunched as NeoGAF, the former in-moniker, by its administrators. NeoGAF also features its own front page, an upfront admission that the forum's audience had drifted from that of its birthing news site, but yet mandated a single portal to represent the forum's members.
In an interview with VG247 in 2013, Tyler Malka claimed that he was offered $5 million to sell the website, turning down the offer.[2] One year later he stated in a forum post that the offer doubled, later saying he also turned down the deal.[3]
On October 21, 2017, film director Ima Leupp described in a Facebook post, as part of the #MeToo phenomenon, a trip she took with NeoGAF owner Tyler "Evilore" Malka two years before. She said that while she and Malka were drinking together in a New Orleans hotel room in April 2015, she became very sick. While cleaning up in the shower, she said he approached her "fully naked" from behind without her consent.[4][5][6][7][8]
Following the sexual harassment scandal, half of the site's moderation staff resigned, and many users posted "suicide threads" wherein they demanded to be banned from the forum. The website went offline soon after.[9][10] Afterwards, NeoGAF was restored, suspending the off-topic sections of the board, and announcing that politics would henceforth be a prohibited subject of discussion and that moderation would become anonymous.[11]
Members of the video games industry have been known to be members of the website, such as David Jaffe and Cliff Bleszinski.[12]
In 2007, in a thread discussing the resignation of Peter Moore from Microsoft, one user making fun of Microsoft's vice president of global marketing Jeff Bell received a personal message asking them "And your contribution to society is ... what?" The account was later found to be Jeff Bell's.[13] Malka later said he saw a shift on the forums with people in the games industry being more careful of what they post.[14]
In a 2009 thread post on NeoGAF dedicated to the game Scribblenauts, user "Feep" relayed the experience of discovering during E3 that he was able to go back in time with a time machine to collect a dinosaur in order to defeat an army of robot zombies that could not be defeated with regular weapons.[15][16][17] The story, memorialized as "Post 217", led to the games artist Edison Yan creating a desktop wallpaper image of the story, in appreciation of the positive fan response to the game, and the terms "Post Two One Seven", "Feep", and "Neogaf" were included as summonable objects in the game.[18] Scribblenauts' director Jeremiah Slaczka credited the word-of-mouth popularity of "Post 217" for part of the game's success at E3, and noted that he had contacted Feep to gain his permission to include "Feep" (appearing as a robot zombie) within the game.[19]
Describing the development struggles of 2017's Rime, Tequila Works co-founder Raúl Rubio Munárriz said that reading the forum's reactions reduced him to tears for two days and that if he had read them early on in development, the game would have been cancelled. "Partly because I just don't understand the cruelty, but more importantly because I could see those years over those two days, and I began to understand that maybe people can love something so much that they can hate it."[20]
One of the biggest critics of NeoGAF was game designer and former Silicon Knights president Denis Dyack. In June 2008, he issued a challenge to forum users. He asked users to say whether they were for or against the then upcoming Silicon Knights game Too Human. Once the game was released, if the game received negative reception, Dyack would have "Owned by GAF" under his forum name. If positive reception, users who voted against the game would have had "Owned by Too Human."[21] Dyack would later go on the 1UP Yours podcast, explaining his challenge was an experiment to expose the lack of accountability on online forums, adding that NeoGAF would crumble if it doesn't reform itself.[22] He was later permanently banned from the site in August that same year after calling it the worst online forum.[23][24]
Circa 2017, NeoGAF was criticized for biased moderation and banning political dissidents. Tyler "Evilore" Malka made a post admitting biased moderation by at least one former member of the moderation staff. Malka stated that the ex-moderator banned hundreds of members without justification. Malka also made the declaration that discussion should be encouraged with different points of view, saying that people on the website have been "driven out, character assassinated, labeled traitor for not sounding angry enough, or for not being entirely on board with ostracizing someone else for the same reasons."[25]
In 2007, the website partnered up with The Get-Well Gamers Foundation to launch a donation campaign to bring video games to children in hospitals. NeoGAF raised $5,600 in cash and inventory donations over the October to December period.[26]
An exchange on the forum inspired members to start the development of Dudebro II in 2010. The game was intended to be a satirical take on the machismo found in some modern titles and was planned to feature Jon St. John, the voice of Duke Nukem, as the lead.[27] The team's last statement, in late 2017, disassociated the game from NeoGAF due to the sexual harassment controversy, claiming a new and unrelated team would be created to continue development.[28]
In June 2015, a Reddit sub-community devoted towards mocking NeoGAF became one of five communities shut down by the site.[29][30] Reddit argued the ban hit groups "that allow their communities to use the subreddit as a platform to harass individuals when moderators don’t take action."[31]
Vice News noted the site was one of the largest drivers of traffic to Hillary Clinton's website during the 2016 U.S. presidential election.[32]
Several former NeoGAF members established ResetEra on October 24, 2017, after NeoGAF's owner, Tyler Malka faced sexual misconduct accusations.[33][34]
From November 2017 to March 2018, ResetEra hosted Q&A sessions with Insomniac Games, Chucklefish, LizardCube, DotEmu, and Tom Happ and Dan Adelman, the creators of Axiom Verge.[35]
ResetEra moderators enacted the site's first game ban by barring all promotion of the game Hogwarts Legacy, citing a "far-right" YouTube channel run by then-lead designer Troy Leavitt, and comments criticized for transphobia made by author J. K. Rowling.[36] In January 2023, the ban was extended to include any discussion of the game.[37][38]
In October 2021, ResetEra was purchased for 4.5 million dollars by MOBA Network,[39] a Swedish company that focuses on managing web-based forums for video games and esports. In a statement, MOBA Network claimed that it wants to "increase advertising revenue through a higher share of direct sales, implementation of new ad formats, and a long-term product development strategy."[40]
ResetEra is cited for hat tips by PCGamesN and other publications.[41] Game developers and journalists have visited the forums, including journalist Geoff Keighley; Cory Barlog, Creative Director at Santa Monica Studio; James Stevenson, the Community Director for Insomniac Games; and Thomas Mahler, director of Moon Studios; among others.[42][43][44]
Spiderman Black theme by mikeyrawr
Download: SpidermanBlack.p3t

(1 background)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.