Ill Nino theme by Erwiner
Download: IllNino.p3t

(2 backgrounds)
Redirect to:
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:
|

The #1 spot for Playstation themes!
Ill Nino theme by Erwiner
Download: IllNino.p3t

(2 backgrounds)
Redirect to:
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:
|
Avril Lavigne theme by M@rio
Download: AvrilLavigne_2.p3t

(3 backgrounds)
Avril Lavigne | |
|---|---|
 Lavigne in 2019 | |
| Born | Avril Ramona Lavigne September 27, 1984 Belleville, Ontario, Canada |
| Citizenship |
|
| Occupations |
|
| Years active | 1999–present |
| Works | |
| Spouses | |
| Relatives | Ryota Kohama (brother-in-law) |
| Awards | Full list |
| Musical career | |
| Genres | |
| Instruments |
|
| Labels | |
TikTok information | |
| Page | |
| Followers | 5.7 million |
| Likes | 39.2 million |
Last updated: June 28, 2024 | |
| Website | avrillavigne |
| Signature | |
 | |
Avril Ramona Lavigne CM[1] (/ˈævrɪl ləˈviːn/ AV-ril lə-VEEN, French: [avʁil ʁamɔna laviɲ]; born September 27, 1984) is a Canadian singer-songwriter. She is considered a key musician in the development of pop-punk music, as she paved the way for female-driven, punk-influenced pop music in the early 2000s.[2][3] Her accolades include eight Grammy Award nominations.
At age 16, Lavigne signed a two-album recording contract with Arista Records. Her debut studio album, Let Go (2002), is the best-selling album of the 21st century by a Canadian artist. It yielded the successful singles "Complicated" and "Sk8er Boi", which emphasized a skate punk persona and earned her the title "Pop-Punk Queen" from music publications.[4][5] Her second studio album, Under My Skin (2004), became Lavigne's first album to reach the top of the Billboard 200 chart in the United States, going on to sell 10 million copies worldwide.
Lavigne's third studio album, The Best Damn Thing (2007), reached number one in seven countries worldwide and saw the international success of its lead single "Girlfriend", which became her first single to reach the top of the Billboard Hot 100 in the United States. Her next two studio albums, Goodbye Lullaby (2011) and Avril Lavigne (2013), saw continued commercial success and were both certified gold in Canada, the United States, and other territories.[6][7][8] After releasing her sixth studio album, Head Above Water (2019), she returned to her punk roots with her seventh studio album, Love Sux (2022).[9]
Avril Ramona Lavigne was born on September 27, 1984, in Belleville, Ontario. She was named Avril (the French word for April) by her father.[10] He and Lavigne's mother recognized their child's vocal abilities when she was two years old and sang "Jesus Loves Me" on the way home from church.[11] Lavigne has an older brother named Matthew and a younger sister named Michelle,[12] both of whom teased her when she sang. "My brother used to knock on the wall because I used to sing myself to sleep and he thought it was really annoying."[11] She is the sister-in-law of Japanese band One OK Rock bassist Ryota Kohama.[13] Lavigne's paternal grandfather Maurice Yves Lavigne was born in Saint-Jérôme, Quebec.[14] A member of the Royal Canadian Air Force, he married Lucie Dzierzbicki, a French native of Morhange in 1953. Their son, Jean-Claude Lavigne, was born in 1954 at RCAF Station Grostenquin near Grostenquin, Lorraine.[15] When Jean-Claude was a child, the family moved to Ontario, and in 1975, he married Judith-Rosanne "Judy" Loshaw.[16][17]
When Lavigne was 5, the family moved to Napanee (now incorporated as Greater Napanee),[18] a town with a population of approximately 5,000 at the time.[19][20][21] Also when she was 5, she was diagnosed with ADHD, which caused her problems during her school years.[22]
To support her musical interests, her father bought her a microphone, a drum kit, a keyboard, and several guitars, and converted their basement into a studio. Her father often played bass at the church the family attended, the Third Day Worship Centre in Kingston. When Lavigne was 14 years old, her parents took her to karaoke sessions.[23]
Lavigne performed at country fairs, singing songs by Garth Brooks, the Chicks, and Shania Twain, and began writing her own songs. Her first song was called "Can't Stop Thinking About You", about a teenage crush, which she described as "cheesy cute".[24]
Lavigne also played hockey during high school and won MVP twice as a right winger in a boys league.[25]
In 1999, Lavigne won a radio contest to perform with Canadian singer Shania Twain at the Corel Centre in Ottawa, before an audience of 20,000 people.[26][18][19] Twain and Lavigne sang Twain's song, "What Made You Say That",[18] and Lavigne told Twain that she aspired to be "a famous singer".[19] During a performance with the Lennox Community Theatre, Lavigne was spotted by local folksinger Stephen Medd. He invited her to contribute vocals on his song, "Touch the Sky", for his 1999 album, Quinte Spirit. She later sang on "Temple of Life" and "Two Rivers" for his follow-up album, My Window to You, in 2000.
In December 1999, Lavigne was discovered by her first professional manager, Cliff Fabri, while singing country covers at a Chapters bookstore in Kingston.[18][19] Fabri sent out VHS tapes of Lavigne's home performances to several industry prospects, and Lavigne was visited by several executives.[27] Mark Jowett, co-founder of a Canadian management firm, Nettwerk, received a copy of Lavigne's karaoke performances recorded in her parents' basement.[28] Jowett arranged for Lavigne to work with producer Peter Zizzo during the summer of 2000 in New York, where she wrote the song "Why". Lavigne was noticed by Arista Records during a trip to New York.[27]
In November 2000,[20] Ken Krongard, an A&R representative, invited Antonio "L.A." Reid, then head of Arista Records, to Zizzo's Manhattan studio to hear Lavigne sing. Her 15-minute audition "so impressed" Reid that he immediately signed her to Arista with a deal worth $1.25 million for two albums and an extra $900,000 for a publishing advance.[21][18] By this time, Lavigne had found that she fit in naturally with her hometown high school's skater clique, an image that carried through to her first album, but although she enjoyed skateboarding, school left her feeling insecure. Having signed a record deal, and with support from her parents, she left school to focus on her music career.[20][29][24] Lavigne's band, which were mostly the members of Closet Monster, was chosen by Nettwerk, as they wanted young performers who were up and coming from the Canadian punk rock scene who would fit with Lavigne's personality.[30]

Reid gave A&R Joshua Sarubin the responsibility of overseeing Lavigne's development and the recording of her debut album. They spent several months in New York working with different co-writers, trying to forge an individual sound for her. Sarubin told HitQuarters that they initially struggled; although early collaborations with songwriter-producers including Sabelle Breer, Curt Frasca and Peter Zizzo resulted in some good songs, they did not match her or her voice. It was only when Lavigne went to Los Angeles in May 2001 and created two songs with the Matrix production team—including "Complicated", later released as her debut single—that the record company felt she had made a major breakthrough. Lavigne worked further with the Matrix and also with singer-songwriter Clif Magness. Recording of Lavigne's debut album, Let Go, finished in January 2002.[31]
Lavigne released Let Go in June 2002 in the US, where it reached number two on the Billboard 200 albums chart. It peaked at number one in Australia, Canada, and the UK—this made Lavigne, at 17 years old, the youngest female soloist to have a number-one album on the UK Albums Chart at that time.[32] By the end of 2002, the album was certified four-times Platinum by the RIAA, making her the bestselling female artist of 2002 and Let Go the top-selling debut of the year.[33] By May 2003, Let Go had accumulated over 1 million sales in Canada, receiving a diamond certification from the Canadian Recording Industry Association.[34] By 2009, the album had sold over 16 million units worldwide.[35] By March 2018, the RIAA certified the album seven-times Platinum, denoting shipments of over seven million units in the US.[36]
Lavigne's debut single, "Complicated", peaked at number one in Australia and number two in the US. "Complicated" was one of the bestselling Canadian singles of 2002, and one of the decade's biggest hits in the US,[37] where subsequent singles "Sk8er Boi" and "I'm with You" reached the top ten.[38] With these three singles, Lavigne became the second artist in history to have three top-ten songs from a debut album on Billboard's Mainstream Top 40 chart.[39] Lavigne was named Best New Artist (for "Complicated") at the 2002 MTV Video Music Awards,[40] won four Juno Awards in 2003 out of six nominations,[41] received a World Music Award for "World's Bestselling Canadian Singer", and was nominated for eight Grammy Awards, including Best New Artist and Song of the Year for "Complicated".[42]
In 2002, Lavigne made a cameo appearance in the music video for "Hundred Million" by the pop punk band Treble Charger.[43] In March 2003, Lavigne posed for the cover of Rolling Stone magazine,[16] and in May she performed "Fuel" during MTV's Icon tribute to Metallica.[44][45] During her first headlining tour, the Try to Shut Me Up Tour, Lavigne covered Green Day's "Basket Case".[46]

Lavigne's second studio album, Under My Skin, was released in May 2004 and debuted at number one in Australia, Canada, Japan, the UK, and the US.[47] The album was certified five-times Platinum in Canada[48] and has sold 10 million copies,[49] including 3.2 million in the US.[50] Lavigne wrote most of the album's tracks with Canadian singer-songwriter Chantal Kreviazuk, and Kreviazuk's husband, Our Lady Peace front man Raine Maida, co-produced the album with Butch Walker and Don Gilmore. Lavigne said that Under My Skin proved her credentials as a songwriter, saying that "each song comes from a personal experience of mine, and there are so much [sic] emotions in those songs".[51] "Don't Tell Me", the lead single off the album, reached the top five in the UK and Canada and the top ten in Australia. "My Happy Ending", the album's second single, was a top five hit in the UK and Australia. In the US, it was a top ten entry on the Billboard Hot 100 and became a number-one pop radio hit. The third single, "Nobody's Home", did not manage to make the top 40 in the US and performed moderately elsewhere.
During early 2004 Lavigne went on the 'Live and By Surprise' acoustic mall tour in the US and Canada to promote Under My Skin, accompanied by her guitarist Evan Taubenfeld. In September 2004, Lavigne embarked on her first world tour, the year-long Bonez Tour. Lavigne won two World Music Awards in 2004, for 'World's Best Pop/Rock Artist' and 'World's Bestselling Canadian Artist' and won three Juno Awards from five nominations in 2005, including 'Artist of the Year'.[52] She also won in the category of 'Favorite Female Singer' at the eighteenth annual Nickelodeon Kids' Choice Awards.[53]
Lavigne co-wrote the song "Breakaway", which was recorded by Kelly Clarkson for the soundtrack to the 2004 film The Princess Diaries 2: Royal Engagement.[54] "Breakaway" was released as a single in mid 2004 and subsequently included as the title track on Clarkson's second album, Breakaway. Lavigne performed the Goo Goo Dolls song "Iris" with the band's lead singer John Rzeznik at Fashion Rocks in September 2004,[55] and she posed for the cover of Maxim in October 2004.[56] She recorded the theme song for The SpongeBob SquarePants Movie (released in November 2004) with producer Butch Walker.[57]
In February 2006, Lavigne represented Canada at the closing ceremony of the 2006 Winter Olympics.[58] Fox Entertainment Group approached Lavigne to write a song for the soundtrack to the 2006 fantasy-adventure film Eragon; her contribution, "Keep Holding On", was released as a single to promote the film and its soundtrack.[59][60][61]

Lavigne's third album, The Best Damn Thing, was released in April 2007 and debuted at number one on the U.S. Billboard 200,[62] and subsequently achieved Platinum status in Canada.[48] The album sold more than 2 million copies in the US.[36] Its lead single, "Girlfriend", became Lavigne's first number-one single on the U.S. Billboard Hot 100 and one of the decade's biggest singles.[62][63] The single also peaked at number one in Australia, Canada, and Japan, and reached number two in the UK and France. As well as English, "Girlfriend" was recorded in Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese, German, Japanese, and Mandarin. The International Federation of the Phonographic Industry ranked "Girlfriend" as the most-downloaded track worldwide in 2007, selling 7.3 million copies, including the versions recorded in eight different languages.[64][65] "When You're Gone", the album's second single, reached the top five in Australia and the United Kingdom, the top ten in Canada, and the top forty in the US. "Hot" was the third single and charted only at number 95 in the US, although it reached the top 10 in Canada and the top 20 in Australia.
Lavigne won two World Music Awards in 2007, for 'World's Bestselling Canadian Artist' and 'World's Best Pop/Rock Female Artist'. She won her first two MTV Europe Music Awards, received a Teen Choice Award for 'Best Summer Single', and was nominated for five Juno Awards.[52] In December 2007, Lavigne was ranked number eight in Forbes magazine's list of 'Top 20 Earners Under 25', with annual earnings of $12 million.[66] In March 2008, Lavigne undertook a world tour, The Best Damn World Tour, and appeared on the cover of Maxim for the second time.[67] In mid-August, Malaysia's Islamic opposition party, the Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party, attempted to ban Lavigne's tour show in Kuala Lumpur, judging her stage moves "too sexy". It was thought that her concert on August 29 would promote wrong values ahead of Malaysia's Independence Day on August 31.[68] On August 21, 2008, MTV reported that the concert had been approved by the Malaysian government.[69]
In January 2010, Lavigne worked with Disney to create clothing designs inspired by Tim Burton's feature film Alice in Wonderland. She recorded a song for its soundtrack, "Alice", which was played over the end credits and included on the soundtrack album Almost Alice.[70][71][72] In February, Lavigne performed at the Vancouver 2010 Winter Olympics closing ceremony.[73] Lavigne's song "I'm with You" was sampled by Rihanna on the track "Cheers (Drink to That)", which is featured on Rihanna's fifth studio album, Loud (2010).[74][75] "Cheers (Drink to That)" was released as a single the following year, and Lavigne appeared in its music video.[76] In December 2010, American singer Miranda Cosgrove released "Dancing Crazy", a song written by Lavigne, Max Martin and Shellback. It was also produced by Martin.[77]
Lavigne began recording for her fourth studio album, Goodbye Lullaby, in her home studio in November 2008. Its opening track, "Black Star", was written to help promote her first fragrance of the same name.[78][79] Lavigne described the album as being about her life experiences rather than focusing on relationships, and its style as less pop rock than her previous material, reflecting her age.[79][80] The release date for Goodbye Lullaby was delayed several times, which Lavigne said was because of her label.[81][82] Goodbye Lullaby was released in March 2011,[83][80] and its lead single, "What the Hell", premiered in December 2010, ahead of the album's release.[83] Goodbye Lullaby received Juno Award nominations for Album of the Year and Pop Album of the Year.[52] By March 2018, Goodbye Lullaby sold more than 500,000 copies in the US, and it was certified Gold by the RIAA.[36]

Three months after the release of Goodbye Lullaby, Lavigne announced that work on her fifth studio album had already begun, describing it as the musical opposite of Goodbye Lullaby[84] and "pop and more fun again".
Amiga theme by Maff Mace
Download: Amiga.p3t

(2 backgrounds)
 | |
 The 1987 Amiga 500 was the bestselling model. | |
| Manufacturer | Commodore International |
|---|---|
| Product family | Amiga |
| Type | Personal computer Game console (CD32) |
| Release date | July 23, 1985 (Amiga 1000) |
| Introductory price | Amiga 1000: US$1,295 (equivalent to $3,670 in 2023) Monitor: US$300 (equivalent to $850 in 2023) |
| Discontinued | 1996 (Amiga 1200 & 4000T) |
| Units sold | 4.85 million[1] |
| Operating system | AmigaOS on Kickstart |
| CPU | Motorola 680x0 @ ≈7+ MHz |
| Memory | 256 KB and up, expandable |
| Predecessor | |
Amiga is a family of personal computers introduced by Commodore in 1985. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16- or 16/32-bit processors, 256 KB or more of RAM, mouse-based GUIs, and significantly improved graphics and audio compared to previous 8-bit systems. These systems include the Atari ST—released earlier the same year—as well as the Macintosh and Acorn Archimedes. Based on the Motorola 68000 microprocessor, the Amiga differs from its contemporaries through the inclusion of custom hardware to accelerate graphics and sound, including sprites and a blitter, and a pre-emptive multitasking operating system called AmigaOS.
The Amiga 1000 was released in July 1985, but production problems kept it from becoming widely available until early 1986. The best-selling model, the Amiga 500, was introduced in 1987 along with the more expandable Amiga 2000. The Amiga 3000 was introduced in 1990, followed by the Amiga 500 Plus, and Amiga 600 in March 1992. Finally, the Amiga 1200 and Amiga 4000 were released in late 1992. The Amiga line sold an estimated 4.85 million units.
Although early advertisements cast the computer as an all-purpose business machine,[2][3][4][5][6][7] especially when outfitted with the Sidecar IBM PC compatibility add-on, the Amiga was most commercially successful as a home computer, with a wide range of games and creative software. It also found a niche in video production with the Video Toaster hardware and software, and Amiga's audio hardware made it a popular platform for music tracker software. The processor and memory capacity enabled 3D rendering packages, including LightWave 3D, Imagine, and Traces, a predecessor to Blender.
Poor marketing and the failure of later models to repeat the technological advances of the first systems resulted in Commodore quickly losing market share to the rapidly dropping prices of IBM PC compatibles, which gained 256 color graphics in 1987,[8] as well as the fourth generation of video game consoles.
Commodore ultimately went bankrupt in April 1994 after a version of the Amiga packaged as a game console, the Amiga CD32, failed in the marketplace. Since the demise of Commodore, various groups have marketed successors to the original Amiga line, including Genesi, Eyetech, ACube Systems Srl and A-EON Technology. AmigaOS has influenced replacements, clones, and compatible systems such as MorphOS and AROS. Currently Belgian company Hyperion Entertainment maintains and develops AmigaOS 4, which is an official and direct descendant of AmigaOS 3.1 – the last system made by Commodore for the original Amiga Computers.
Jay Miner joined Atari, Inc. in the 1970s to develop custom integrated circuits, and led development of the Atari Video Computer System's TIA.[9] When complete, the team began developing a much more sophisticated set of chips, CTIA, ANTIC and POKEY, that formed the basis of the Atari 8-bit computers.[10]
With the 8-bit line's launch in 1979, the team once again started looking at a next generation chipset. Nolan Bushnell had sold the company to Warner Communications in 1978, and the new management was much more interested in the existing lines than development of new products that might cut into their sales. Miner wanted to start work with the new Motorola 68000, but management was only interested in another 6502 based system. Miner left the company, and, for a time, the industry.[10]
In 1979, Larry Kaplan left Atari and founded Activision. In 1982, Kaplan was approached by a number of investors who wanted to develop a new game platform. Kaplan hired Miner to run the hardware side of the newly formed company, "Hi-Toro". The system was code-named "Lorraine" in keeping with Miner's policy of giving systems female names, in this case the company president's wife, Lorraine Morse.[11] When Kaplan left the company late in 1982, Miner was promoted to head engineer[10] and the company relaunched as Amiga Corporation.[12]

The Amiga hardware was designed by Miner, RJ Mical, and Dale Luck.[13] A breadboard prototype for testing and development was largely completed by late 1983, and shown at the January 1984 Consumer Electronics Show (CES). At the time, the operating system was not ready, so the machine was demonstrated with the "Boing Ball" demo, a real-time animation showing a red-and-white spinning ball bouncing and casting a shadow; this bouncing ball later became the official logo of Escom subsidiary Amiga Technologies. CES attendees had trouble believing the computer being demonstrated had the power to display such a demo and searched in vain for the "real" computer behind it.[14][failed verification]
A further developed version of the system was demonstrated at the June 1984 CES and shown to many companies in hopes of garnering further funding, but found little interest in a market that was in the final stages of the video game crash of 1983.[11][15]
In March, Atari expressed a tepid interest in Lorraine for its potential use in a games console or home computer tentatively known as the 1850XLD. The talks were progressing slowly,[16] and Amiga was running out of money. A temporary arrangement in June led to a $500,000 loan from Atari to Amiga to keep the company going. The terms required the loan to be repaid at the end of the month, otherwise Amiga would forfeit the Lorraine design to Atari.[17]
During 1983, Atari lost over $1 million a week, due to the combined effects of the crash and the ongoing price war in the home computer market. By the end of the year, Warner was desperate to sell the company. In January 1984, Jack Tramiel resigned from Commodore due to internal battles over the future direction of the company. A number of Commodore employees followed him to his new company, Tramel Technology. This included a number of the senior technical staff, where they began development of a 68000-based machine of their own. In June, Tramiel arranged a no-cash deal to take over Atari, reforming Tramel Technology as Atari Corporation.
As many Commodore technical staff had moved to Atari, Commodore was left with no workable path to design their own next-generation computer. The company approached Amiga offering to fund development as a home computer system. They quickly arranged to repay the Atari loan, ending that threat. The two companies were initially arranging a $4 million license agreement before Commodore offered $24 million to purchase Amiga outright.[17]
By late 1984, the prototype breadboard chipset had successfully been turned into integrated circuits, and the system hardware was being readied for production. At this time the operating system (OS) was not as ready, and led to a deal to port an OS known as TRIPOS to the platform. TRIPOS was a multitasking system that had been written in BCPL during the 1970s for the PDP-11 minicomputer, but later experimentally ported to the 68000. This early version was known as AmigaDOS and the GUI as Workbench. The BCPL parts were later rewritten in the C language, and the entire system became AmigaOS.
The system was enclosed in a pizza box form factor case; a late change was the introduction of vertical supports on either side of the case to provide a "garage" under the main section of the system where the keyboard could be stored.[18]
The first model was announced in 1985 as simply "The Amiga from Commodore", later to be retroactively dubbed the Amiga 1000.[a] They were first offered for sale in August, but by October only 50 had been built, all of which were used by Commodore. Machines only began to arrive in quantity in mid-November, meaning they missed the Christmas buying rush.[19] By the end of the year, they had sold 35,000 machines, and severe cashflow problems made the company pull out of the January 1986 CES.[20] Bad or entirely missing marketing, forcing the development team to move to the east coast, notorious stability problems and other blunders limited sales in early 1986 to between 10,000 and 15,000 units a month.[18] 120,000 units were reported as having been sold from the machine's launch up to the end of 1986.[21]
In late 1985, Thomas Rattigan was promoted to COO of Commodore, and then to CEO in February 1986. He immediately implemented an ambitious plan that covered almost all of the company's operations. Among these was the long-overdue cancellation of the now outdated PET and VIC-20 lines, as well as a variety of poorly selling Commodore 64 offshoots and the Commodore 900 workstation effort.[22]
Another one of the changes was to split the Amiga into two products, a new high-end version of the Amiga aimed at the creative market, and a cost-reduced version that would take over for the Commodore 64 in the low-end market.[22] These new designs were released in 1987 as the Amiga 2000 and Amiga 500, the latter of which went on to widespread success and became their best selling model.
Similar high-end/low-end models would make up the Amiga line for the rest of its history; follow-on designs included the Amiga 3000/Amiga 500 Plus/Amiga 600, and the Amiga 4000/Amiga 1200. These models incorporated a series of technical upgrades known as the ECS and AGA, which added higher resolution displays among many other improvements and simplifications.[23]
The Amiga line sold an estimated 4,850,000 machines over its lifetime.[1] The machines were most popular in the UK and Germany, with about 1.5 million sold in each country, and sales in the high hundreds of thousands in other European nations. The machine was less popular in North America, where an estimated 700,000 were sold.[1][24] In the United States, the Amiga found a niche with enthusiasts and in vertical markets for video processing and editing.[25] In Europe, it was more broadly popular as a home computer and often used for video games.[13] Beginning in 1988 it overlapped with the 16-bit Mega Drive, then the Super Nintendo Entertainment System in the early 1990s. Commodore UK's Kelly Sumner did not see Sega or Nintendo as competitors, but instead credited their marketing campaigns which spent over £40 million or $60,000,000 (equivalent to $130,000,000 in 2023) for promoting video games as a whole and thus helping to boost Amiga sales.[24]
In spite of his successes in making the company profitable and bringing the Amiga line to market, Rattigan was soon forced out in a power struggle with majority shareholder, Irving Gould. This is widely regarded as the turning point, as further improvements to the Amiga were eroded by rapid improvements in other platforms.[26]
Commodore shut down the Amiga division on April 26, 1994, and filed for bankruptcy three days later. Commodore's assets were purchased by Escom, a German PC manufacturer, who created the subsidiary company Amiga Technologies. They re-released the A1200 and A4000T, and introduced a new 68060 version of the A4000T. In 1996, it was reported that Escom had sold the Amiga intellectual property to VIScorp for $40m (equivalent to $71,750,000 in 2023).[13] Amiga Technologies researched and developed the Amiga Walker prototype. They presented the machine publicly at CeBit,[27][28] but this deal fell through, and Escom, in turn, went bankrupt in 1997.[29][30]
A U.S. Wintel PC manufacturer, Gateway 2000, then purchased the Amiga branch and technology.[13] In 2000, Gateway sold the Amiga brand to Amiga, Inc., without having released any products. Amiga, Inc. licensed the rights to sell hardware using the AmigaOne brand to Eyetech Group and Hyperion Entertainment. In 2019, Amiga, Inc. sold its intellectual property to Amiga Corporation.[31][32]




The Amiga has a custom chipset consisting of several coprocessors which handle audio, video, and direct memory access independently of the Central Processing Unit (CPU). This architecture gave the Amiga a performance edge over its competitors, particularly for graphics-intensive applications and games.[33]
The architecture uses two distinct bus subsystems: the chipset bus and the CPU bus. The chipset bus allows the coprocessors and CPU to address "Chip RAM". The CPU bus provides addressing to conventional RAM, ROM and the Zorro II or Zorro III expansion subsystems. This enables independent operation of the subsystems. The CPU bus can be much faster than the chipset bus. CPU expansion boards may provide additional custom buses. Additionally, "busboards" or "bridgeboards" may provide ISA or PCI buses.[33]
The most popular models from Commodore, including the Amiga 1000, Amiga 500, and Amiga 2000, use the Motorola 68000 as the CPU. From a developer's point of view, the 68000 provides a full suite of 32-bit operations, but the chip can address only 16 MB of physical memory and is implemented using a 16-bit arithmetic logic unit and has a 16-bit external data bus, so 32-bit computations are transparently handled as multiple 16-bit values at a performance cost.[34][35] The later Amiga 2500 and the Amiga 3000 models use fully 32-bit, 68000 compatible, processors from Motorola improved performance and larger addressing capability.
CPU upgrades were offered by both Commodore and third-party manufacturers. Most Amiga models can be upgraded either by direct CPU replacement or through expansion boards. Such boards often included faster and higher capacity memory interfaces and hard disk controllers.
Towards the end of Commodore's time in charge of Amiga development, there were suggestions that Commodore intended to move away from the 68000 series to higher performance RISC processors, such as the PA-RISC.[36][37] Those ideas were never developed before Commodore filed for bankruptcy. Despite this, third-party manufacturers designed upgrades featuring a combination of 68000 series and PowerPC processors along with a PowerPC native microkernel and software.[38][39] Later Amiga clones featured PowerPC processors only.
The custom chipset at the core of the Amiga design appeared in three distinct generations, with a large degree of backward-compatibility. The Original Chip Set (OCS) appeared with the launch of the A1000 in 1985. OCS was eventually followed by the modestly improved Enhanced Chip Set (ECS) in 1990 and finally by the partly 32-bit Advanced Graphics Architecture (AGA) in 1992. Each chipset consists of several coprocessors that handle graphics acceleration, digital audio, direct memory access and communication between various peripherals (e.g., CPU, memory and floppy disks). In addition, some models featured auxiliary custom chips that performed tasks such as SCSI control and display de-interlacing.


All Amiga systems can display full-screen animated planar graphics with 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 (EHB Mode), or 4096 colors (HAM Mode). Models with the AGA chipset (A1200 and A4000) also have non-EHB 64, 128, 256, and 262144 (HAM8 Mode) color modes and a palette expanded from 4096 to 16.8 million colors.
The Amiga chipset can genlock, which is the ability to adjust its own screen refresh timing to match an incoming NTSC or PAL video signal. When combined with setting transparency, this allows an Amiga to overlay an external video source with graphics. This ability made the Amiga popular for many applications, and provides the ability to do character generation and CGI effects far more cheaply than earlier systems. This ability has been frequently utilized by wedding videographers, TV stations and their weather forecasting divisions (for weather graphics and radar), advertising channels, music video production, and desktop videographers. The NewTek Video Toaster was made possible by the genlock ability of the Amiga.
In 1988, the release of the Amiga A2024 fixed-frequency monochrome monitor with built-in framebuffer and flicker fixer hardware provided the Amiga with a choice of high-resolution graphic modes (1024×800 for NTSC and 1024×1024 for PAL).[40]
ReTargetable Graphics is an API for device drivers mainly used by 3rd party graphics hardware to interface with AmigaOS via a set of libraries. The software libraries may include software tools to adjust resolution, screen colors, pointers and screenmodes. The standard Intuition interface is limited to display depths of 8 bits, while RTG makes it possible to handle higher depths like 24-bits.
The sound chip, named Paula, supports four PCM sound channels (two for the left speaker and two for the right) with 8-bit resolution for each channel and a 6-bit volume control per channel. The analog output is connected to a low-pass filter, which filters out high-frequency aliasing when the Amiga is using a lower sampling rate (see Nyquist frequency). The brightness of the Amiga's power LED is used to indicate the status of the Amiga's low-pass filter. The filter is active when the LED is at normal brightness, and deactivated when dimmed (or off on older A500 Amigas). On Amiga 1000 (and first Amiga 500 and Amiga 2000 model), the power LED had no relation to the filter's status, and a wire needed to be manually soldered between pins on the sound chip to disable the filter. Paula can read arbitrary waveforms at arbitrary rates and amplitudes directly from the system's RAM, using direct memory access (DMA), making sound playback without CPU intervention possible.
Although the hardware is limited to four separate sound channels, software such as OctaMED uses software mixing to allow eight or more virtual channels, and it was possible for software to mix two hardware channels to achieve a single 14-bit resolution channel by playing with the volumes of the channels in such a way that one of the source channels contributes the most significant bits and the other the least.
The quality of the Amiga's sound output, and the fact that sound hardware is part of the standard chipset and easily addressed by software, were standout features of Amiga hardware unavailable on PC platforms for years[b]. Third-party sound cards exist that provide DSP functions[citation needed], multi-track direct-to-disk recording[citation needed], multiple hardware sound channels and 16-bit and beyond resolutions. A retargetable sound API called AHI was developed allowing these cards to be used transparently by the OS and software.[41]
Kickstart is the firmware upon which AmigaOS is bootstrapped. Its purpose is to initialize the Amiga hardware and core components of AmigaOS and then attempt to boot from a bootable volume, such as a floppy disk or hard disk drive. Most models (excluding the Amiga 1000) come equipped with Kickstart on an embedded ROM-chip.

The keyboard on Amiga computers is similar to that found on a mid-80s IBM PC: Ten function keys, a numeric keypad, and four separate directional arrow keys. Caps Lock and Control share space to the left of A. Absent are Home, End, Page Up, and Page Down keys: These functions are accomplished on Amigas by pressing shift and the appropriate arrow key. The Amiga keyboard adds a Help key, which a function key usually acts as on PCs (usually F1). In addition to the Control and Alt modifier keys, the Amiga has 2 "Amiga" keys, rendered as "Open Amiga" and "Closed Amiga" similar to the Open/Closed Apple logo keys on Apple II keyboards. The left is used to manipulate the operating system (moving screens and the like) and the right delivers commands to the application. The absence of Num lock frees space for more mathematical symbols around the numeric pad.
Like IBM-compatible computers, the mouse has two buttons, but in AmigaOS, pressing and holding the right button replaces the system status line at the top of the screen with a Maclike menu bar. As with Apple's Mac OS prior to Mac OS 8, menu options are selected by releasing the button over that option, not by left clicking. Menu items that have a Boolean toggle state can be left clicked whilst the menu is kept open with the right button, which allows the user – for example – to set some selected text to bold, underline and italics in one visit to the menus.
The mouse plugs into one of two Atari joystick ports used for joysticks, game paddles, and graphics tablets. Although compatible with analog joysticks, Atari-style digital joysticks became standard.[42] Unusually, two independent mice can be connected to the joystick ports; some games, such as Lemmings, were designed to take advantage of this.[43]
Bug-02 theme by BUG
Download: Bug-02.p3t

(1 background)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Bug-01 theme by BUG
Download: Bug-01.p3t

(1 background)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Darkness Blue – Burning Version theme by André Mello
Download: DarknessBlueBurningVersion.p3t
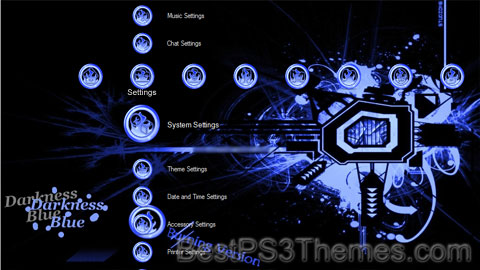
(5 backgrounds)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Assassin’s Creed theme by Paja
Download: AssassinsCreed_7.p3t

(1 background)
| Assassin's Creed | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Genre(s) | |
| Developer(s) | |
| Publisher(s) | Ubisoft |
| Creator(s) | |
| First release | Assassin's Creed November 13, 2007 |
| Latest release | Assassin's Creed Nexus VR November 16, 2023 |
Assassin's Creed is a historical action-adventure video game series and media franchise published by Ubisoft and developed mainly by its studio Ubisoft Montreal using the game engine Anvil and its more advanced derivatives. Created by Patrice Désilets, Jade Raymond, and Corey May, the Assassin's Creed video game series depicts a fictional millennia-old struggle between the Order of Assassins, who fight for peace and free will, and the Knights Templar, who desire peace through order and control. The series features historical fiction, science fiction, and fictional characters intertwined with real-world historical events and historical figures. In most games, players control a historical Assassin while also playing as an Assassin Initiate or someone caught in the Assassin–Templar conflict in the present-day framing story. Considered a spiritual successor to the Prince of Persia series, Assassin's Creed took inspiration from the novel Alamut by the Slovenian writer Vladimir Bartol, based on the historical Hashashin sect of the medieval Middle East.
The first Assassin's Creed game was released in 2007, and the series has featured thirteen main installments in total, the most recent being Assassin's Creed Mirage in 2023. Main games in the Assassin's Creed series are set in an open world and played from the third-person view. Gameplay revolves around combat, stealth, and exploration, including the use of parkour to navigate the environment. The games feature both main and side missions, and some titles also include competitive and cooperative multiplayer game modes.
A new story and occasionally new time periods are introduced in each entry, with the gameplay elements also evolving. There are three overarching story arcs in the series. The first five main games follow Desmond Miles, a descendant of several important Assassins throughout history, who uses a machine called the Animus to relive his ancestors' memories and find powerful artifacts called Pieces of Eden in an attempt to prevent a catastrophic event, referencing the 2012 phenomenon. From Assassin's Creed IV: Black Flag to Assassin's Creed Syndicate, Assassin initiates and employees of Abstergo (a company used as a front by the modern-day Templars) record genetic memories using the Helix software, helping the Templars and Assassins find new Pieces of Eden in the modern world. The next three games, Assassin's Creed Origins, Odyssey, and Valhalla, follow ex-Abstergo employee Layla Hassan on her own quest to save humanity from another disaster.
The main games in the Assassin's Creed franchise have received generally positive reviews for their ambition in visuals, game design, and narratives, with criticism for the yearly release cycle and frequent bugs, as well as the prioritising of role-playing mechanics in later titles. The series has received multiple awards and nominations, including multiple Game of the Year awards. It is commercially successful, selling over 200 million copies as of September 2022[update], becoming Ubisoft's best-selling franchise and one of the highest selling video game franchises of all time. While main titles are produced for major consoles and desktop platforms, multiple spin-off games have been released for consoles, mobiles, and handheld platforms. A series of art books, encyclopedias, comics, and novels have also been published. A live-action film adaptation of the series, titled Assassin's Creed, was released in 2016.
While the games in the series have had several narrative arcs, Ubisoft views the series as currently having three periods of development and design philosophy. Until 2015's Assassin's Creed Syndicate, the franchise was structured around single-player content, and while centering on open world spaces and several role-playing elements, were more action-adventure and stealth-oriented. Period two, covering from Assassin's Creed Origins to Assassin's Creed Mirage, brought in more role-playing elements and live-service features to increase player engagement. Period three will launch with Assassin's Creed Shadows, using lessons from the second period of development to make engrossing single-player games similar to the original titles but with features to allow players to share achievements and content with others, all to be backed by the Infinity hub system.[1]
The first Assassin's Creed game originated out of ideas for a sequel for Ubisoft's video game Prince of Persia: The Sands of Time, aiming for the seventh generation of video game consoles. The Ubisoft Montreal team decided to take the gameplay from The Sands of Time into an open-world approach, taking advantage of the improved processing power to render larger spaces and crowds. Narratively, the team wanted to move away from the Prince being someone next in line for the throne but to have to work for it; combined with research into secret societies led them to focus on the Order of Assassins, based upon the historical Hashashin sect of Ismaili, who were followers of Shia Islam, heavily borrowing from the novel Alamut.[2][3] Ubisoft developed a narrative where the player would control an Assassin escorting a non-playable Prince, leading them to call this game Prince of Persia: Assassin,[4] or Prince of Persia: Assassins.[5] Ubisoft was apprehensive to a Prince of Persia game without the Prince as the playable character, but this led the marketing division to suggest the name Assassin's Creed, playing off the creed of the Assassins, "nothing is true; everything is permitted". Ubisoft Montreal ran with this in creating a new intellectual property, eliminating the Prince, and basing it around the Assassins and the Knights Templar in the Holy Land during the 12th century. Additionally, in postulating what other assassinations they could account for throughout history, they came onto the idea of genetic memory and created the Animus device and modern storyline elements. This further allowed them to explain certain facets of gameplay, such as accounting for when the player character is killed, similar to The Sands of Time.[5]
After Assassin's Creed was released in 2007, Ubisoft Montreal said they looked to "rework the global structure" in developing the sequel, Assassin's Creed II. They felt that parkour was underutilized in the first game and designed the world in the sequel to feature freerun highways to make it easier to enter into parkour moves, for example using rooftops to escape pursuits.[6] The change in setting meant that the game would feature a new cast of characters, including a new protagonist, Ezio Auditore da Firenze. Assassin's Creed II also brought in more use of crowds to hide in plain sight that the developers had seen used in Hitman: Blood Money, adding more to the concept of social stealth as a gameplay option.[6] Finally, Ubisoft Montreal completely reworked the repetitive mission structure from the first game through numerous side activities, collectibles, and secrets. These additions became a central part of the series going forward as well as other Ubisoft games like Watch Dogs, Far Cry, and Tom Clancy's Ghost Recon.[6] Assassin's Creed II was followed by two sequels, Assassin's Creed: Brotherhood and Assassin's Creed: Revelations, which also featured Ezio as the main protagonist and introduced the ability for players to recruit NPCs as Assassins and manage them in missions.[6]
Assassin's Creed III originated from both Ubisoft Montreal, who wanted to progress the series' narrative forward in time, and to an unattached project that had been developed at Ubisoft Singapore and featured naval ship combat. As the main team had settled into the American Revolution period for the game, they found the ship-to-ship combat system fitted with the story and redesigned the setting to incorporate it further. Another major change in Assassin's Creed III was transitioning the parkour and freerun systems to work in the natural woodlands of 18th-century Massachusetts and New York. This further allowed the adding of trees and other vegetation within the city areas themselves, not just as part of the parkour systems, but to add more varied environments, which would continue as part of the series' ongoing design.[6]
For Assassin's Creed III's sequel, Assassin's Creed IV: Black Flag, the Ubisoft team built upon the foundation of its predecessor, particularly with regards to the naval gameplay, merging it seamlessly with the land-based gameplay.[6] The team also used the game as a chance to address aspects of the series' storyline. Choosing to focus on an outsider's perspective to the Assassin–Templar conflict, they set the game around the Golden Age of Piracy, with the protagonist, Edward Kenway, starting out as a pirate who initially becomes involved in the conflict with the prospect of wealth. Similarly, after the conclusion of Desmond Miles' story arc in Assassin's Creed III, the modern-day segments put players in the role of a nameless individual controlled from a first-person perspective. The team chose this approach because they believed it allowed players to more easily identify themselves in their character.[6] This trend would continue in the series until Assassin's Creed Syndicate.[6]
Development of Assassin's Creed Unity began shortly after the completion of Brotherhood in 2010,[7] with the core development team splitting off during the early stages of development on Assassin's Creed III.[8] As the first game in the series to be released exclusively for the eighth generation of video game consoles, Unity featured a graphical and gameplay overhaul. The setting chosen for the game was Paris during the early years of the French Revolution, with players taking control of a new Assassin named Arno Dorian.[7][8] After Unity, Ubisoft released Assassin's Creed Syndicate in 2015.[6]
After Syndicate, Ubisoft decided that the series needed a major reinvention across both gameplay and narrative. It was decided to make the next game, Assassin's Creed Origins, closer to a role-playing video game than a stealth-action game, which would also bring a game with many more hours of play than previous titles. Some long-standing features of the series were eliminated for this purpose, such as the social stealth mechanic. This changed how missions were presented — rather than being linearly directed through the Animus, the player character could meet various quest givers in the game's world to receive missions.[6] From the narrative side, Ubisoft placed the game before the formation of the Assassin Brotherhood in Ancient Egypt to make the player character, Bayek of Siwa, a medjay that people would respect and seek the help of.[6] The modern-day storyline also shifted back to a single character, Layla Hassan. The developers limited the number of playable sequences for her character compared to previous games but gave them more meaning, such as allowing the player to explore Layla's laptop with background information on the game's universe.[6]
Origins was followed in 2018 by Assassin's Creed Odyssey, which shifted the setting to Classical Greece and followed a similar approach to its predecessor but with more emphasis on the role-playing elements.[6] 2020's Assassin's Creed Valhalla, set in Medieval England and Norway during the Viking Age, continued the same style as Origins and Odyssey. The developers recognized feedback from the previous two games and brought back the social stealth elements, as well as the concept of a customizable home base that was first introduced in Assassin's Creed II.[6]
In 2023, Ubisoft released Assassin's Creed Mirage, a smaller title which sought to pay tribute to the franchise's earlier installments by focusing on stealth and assassinations over its predecessors' role-playing elements. The game started development as an expansion for Valhalla before being turned into a standalone release, and was set in 9th-century Baghdad during the Islamic Golden Age, a decade before the events of Valhalla, to which it served as a prequel.[9][10]
In 2022, Ubisoft announced several additional games for the series. Assassin's Creed Infinity has been described by its executive producer, Marc-Alexis Côté, as a "new design philosophy" for the series,[1][11] as well as a hub that will provide the releases of future games.[12] The first two games to be included in Infinity will be Assassin's Creed Shadows, set in Japan during the Sengoku period,[9] and Assassin's Creed: Codename Hexe, rumoured to be set in Central Europe during the 16th century.[13]

The Assassin's Creed games are centered around one or more fictional members of the Order of the Assassins. Their memories are experienced by an in-game character in the modern-day period through a device called the Animus and its derivations. The Animus allows the user to explore these memories passed down via genetics. Within the context of the game, this provides a diegetic interface to the real-world player of the game, showing them elements like health bars, a mini-map, and target objectives as if presented by the Animus. Additionally, should the player cause the historical character to die or fail a mission, this is rectified as desynchronization of the genetic memory, allowing the player to try the mission again. Through the Animus interface, the player can retry any past mission already completed; for example, in Assassin's Creed: Brotherhood, the player achieves better synchronization results by performing the mission in a specific manner, such as by only killing the mission's target. The Animus also imparts special abilities to the modern-day character that helps them to see their target in a crowd or other unique points of interest.[14][15]
While playing as the Assassin characters, the games are generally presented from a third-person view in an open world environment, focusing on stealth and parkour. The games use a mission structure to follow the main story, assigning the player to complete an assassination of public figureheads or a covert mission. Alternatively, several side missions are available, such as mapping out the expansive cities from a high perch followed by performing a leap of faith into a haystack below, collecting treasures hidden across the cities, exploring ruins for relics, building a brotherhood of assassins to perform other tasks, or funding the rebuilding of a city through purchasing and upgrading of shops and other features. At times, the player is in direct control of the modern-day character who, by nature of the Animus use, has learned Assassin techniques through the bleeding effect, as well as their genetic ability of Eagle Vision, which separates friend, foe, and assassination targets by illuminating people in different colors.[16][17]
The games use the concept of active versus passive moves, with active moves, such as running, climbing the sides of buildings, or jumping between rooftops, more likely to alert the attention of nearby guards. When the guards become alerted, the player must either fight them or break their line of sight and locate a hiding place, such as a haystack or a well, and wait until the guards' alert is reduced. The combat system allows for a number of unique weapons, armor, and moves, including the use of a hidden blade set in a bracer on the Assassin's arm, which can be used to perform surreptitious assassinations.[18]

The Assassin's Creed games primarily revolve around the rivalry and conflict between two ancient secret societies: the Order of Assassins, who represent freedom, and the Knights Templar, who represent order. Versions of these societies have existed for centuries, with the Assassins seeking to stop the Templars from gaining control of Pieces of Eden, artifacts that can override free will to control people.[19]
These artifacts are remnants of an ancient species pre-dating humanity called the Isu, or Precursors, which created humanity to live in peace alongside them. The Isu ensured humans could not rise against them by creating the Pieces of Eden to control them. When the first hybrid Isu-human beings emerged, named Adam and Eve, they were immune to the effects of the Pieces of Eden. They stole the Pieces of Eden, which led to a great war that ended when a massive solar flare devastated the surface of the Earth. The Isu began to die out while humanity thrived. Three Isu—Minerva, Juno, and Jupiter—attempted to prepare humanity for a solar flare they knew would come centuries later. Minerva and Jupiter prepared vaults from which humanity could activate a protective shield around Earth with the Pieces of Eden and the Eye, a means to communicate how to find and use these vaults; however, Juno saw humanity as a threat and attempted to sabotage Minerva and Jupiter's plan. Minerva and Jupiter were forced to destroy Juno, unaware she had hidden her consciousness to wake upon activation of the Eye. All that remained of the Isu were the traces of their memories in the world's mythologies, and religions, while the Pieces of Eden were lost to time.[19]
The series takes place in the modern era, in which the Templars have established the mega-corporation Abstergo Industries. Abstergo has developed a device, the Animus, whose user can relive the memories of their ancestors through their genetic material. Abstergo has kidnapped people who are descendants of past Assassins to locate the missing Pieces of Eden via the Animus.[19] A user of the Animus can move about in simulated memories as their ancestor, but performing actions outside the bounds of what their ancestor did can lead to desynchronization of the memory.[14][15] Extended use of the Animus creates a bleeding effect that gives users some of the skills and capabilities they experienced with their ancestor.[20]
The first five main games in the series focus on Desmond Miles, a bartender who learns he is a descendant of several important Assassins throughout history, including Altaïr Ibn-LaʼAhad from the Middle East during the Third Crusade; Ezio Auditore da Firenze from the Italian Renaissance during the late 15th and early 16th centuries; and Ratonhnhaké:ton (better known as Connor), a half-Mohawk, half-British Assassin during the American Revolution. Desmond is used by Abstergo to find Pieces of Eden but is freed by Lucy Stillman, an undercover agent for the Assassins. Lucy takes Desmond to meet Shaun Hastings and Rebecca Crane, two other members of the modern-day Assassins. The group is joined later by William Miles, Desmond's father. They continue to explore Desmond's memories and eventually discover the Eye and Minerva's warning of another possible solar flare. They also inadvertently free Juno, who then kills Lucy, revealed to be a double agent for the Templars. The group continues to find the vaults across the globe via Desmond's memories, and Desmond ultimately activates them in time to block the solar flare, at the cost of his own life.[19]
Starting with Assassin's Creed IV: Black Flag, William goes into exile, while Shaun and Rebecca continue to monitor Abstergo by posing as employees of one of their spin-off companies, Abstergo Entertainment. Abstergo has refined the Animus technology to allow anyone to experience genetic memories from the DNA material of another person, allowing Abstergo to continue their search for the Pieces of Eden under the guise of creating entertainment products. In Black Flag, the player assumes the role of an unnamed Abstergo employee tasked with scanning the memories of Edward Kenway, a privateer-turned-pirate during the Golden Age of Piracy and Connor's grandfather. During their investigation, the player is blackmailed into helping a fellow employee, John Standish, recover sensitive information and deliver it to the Assassins. John is later revealed to be a Sage, a human reincarnation of Juno's husband Aita, who is trying to resurrect her, though he is killed by Abstergo before his plan can come to fruition.[19] In Assassin's Creed Rogue, the player controls another Abstergo employee who is recruited by the Templars to clean their servers after the Assassins breach them and recover data on the life of Shay Patrick Cormac, an Assassin-turned-Templar from the 18th century. The Assassins are ultimately forced to go underground once more, and the player character is invited to join the Templars.[19]
By the time of Assassin's Creed Unity, Abstergo distributes its Animus product via a video game console named Helix, tapping into an extensive, unaware player base to help them locate more Pieces of Eden and determine the fates of various Sages as part of the Phoenix Project, an attempt to recreate the genetic structure of the Isu. The game's opening has players control an unnamed Templar during the downfall of the Templar Order, while the different "time anomalies" take them to Paris during the Belle Époque, World War II, and the Hundred Years' War. The Assassins locate select players and bring them in as Initiates to help their cause. In Unity, the player character is contacted by an Assassin named Bishop and asked to experience the memories of Arno Dorian, an Assassin active during the French Revolution, so that the modern-day Assassins can locate the body of a Sage and hide it from Abstergo.[19] Despite the Assassins' efforts, Abstergo collects enough samples of other Sages by the start of Assassin's Creed Syndicate to move forward with the Phoenix Project. Again, Bishop contacts the Initiate and asks them to explore the memories of Jacob and Evie Frye, twin Assassins from Victorian England, to locate a Piece of Eden known as the Shroud, which Abstergo needs to complete the process of recreating the Isu genetic structure. Although the Initiate manages to locate the Shroud, the Templars beat the Assassins to it.[19]
A new storyline is introduced in Assassin's Creed Origins focusing on Abstergo researcher Layla Hassan. Initially tasked with locating historical artifacts in Egypt, Layla stumbles upon the mummified corpses of the medjay Bayek and his wife Aya, co-founders of the Hidden Ones, the precursor organizati
Bitta Somethin’ Extra theme by Ross Sneddon
Download: BsE.p3t
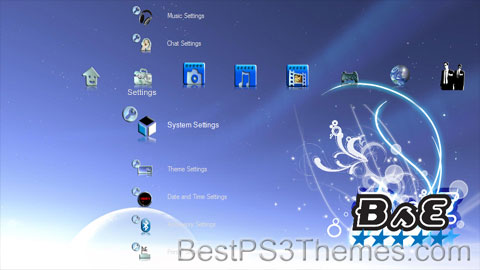
(2 backgrounds)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Psych theme by appleman
Download: Psych.p3t

(7 backgrounds)
| Psych | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Genre | |
| Created by | Steve Franks |
| Starring | |
| Opening theme | "I Know You Know" by The Friendly Indians |
| Ending theme | "I Know You Know" by The Friendly Indians |
| Country of origin | United States |
| Original language | English |
| No. of seasons | 8 |
| No. of episodes | 120 (list of episodes) |
| Production | |
| Executive producers |
|
| Producers |
|
| Production locations | White Rock, British Columbia, Canada |
| Camera setup | Single-camera |
| Running time | 42 minutes |
| Production companies |
|
| Original release | |
| Network | USA Network |
| Release | July 7, 2006 – March 26, 2014 |
| Related | |
| |
Psych is an American detective comedy-drama television series created by Steve Franks for USA Network.[1] The series stars James Roday as Shawn Spencer, a young crime consultant for the Santa Barbara Police Department whose "heightened observational skills"[2] and impressive eidetic memory allow him to convince people that he solves cases with psychic abilities. The program also stars Dulé Hill as Shawn's intelligent best friend and reluctant partner Burton "Gus" Guster, as well as Corbin Bernsen as Shawn's father Henry, a former detective with the Santa Barbara Police Department.[3]
Psych premiered on July 7, 2006, following the fifth-season premiere of Monk, and continued to be paired with the series until Monk's conclusion on December 4, 2009. During the second season, an animated segment titled "The Big Adventures of Little Shawn and Gus" was added to the series. Psych was the highest-rated US basic cable television premiere of 2006.[4] USA Network renewed the series for an eighth season on December 19, 2012, to include eight episodes, and ordered two more episodes on June 25, 2013, bringing the episode order to ten.[5][6] On February 5, 2014, USA Network confirmed that the eighth season of Psych would be its last, with the series finale airing on March 26, 2014.[7]
Psych: The Movie, a two-hour television film, aired on USA Network on December 7, 2017, launching the Psych film series,[8] with Franks' hope being to make five more Psych movies following Psych: The Movie.[9] On February 14, 2019, it was announced Psych: The Movie 2 was greenlit and set to premiere in late 2019, for which the main cast would return, but the premiere thereof was subsequently delayed to 2020, with the film renamed Psych 2: Lassie Come Home, and released on NBCUniversal's streaming service, Peacock, July 15, 2020, the day the service officially launched.[10][11][12] On May 13, 2021, Peacock announced a third film, Psych 3: This Is Gus, which premiered on November 18, 2021.[13][14] Three further Psych films are in development.[9]
Most episodes begin with a cold open in the form of a flashback to Shawn and Gus' childhoods. The flashbacks usually involve Shawn and Gus being taught a lesson by a young Henry Spencer (Shawn's father) (Corbin Bernsen), who wishes that his son would follow in his footsteps and become a law enforcement officer. These lessons often play a role for the climax of the episode. As a child, Shawn was taught by Henry to hone his powers of observation and deduction, often using games and challenges to test him. Each flashback also sets the theme for the episode.
Shawn originally becomes known as a psychic when, after calling in tips on dozens of crimes covered on the news which help the police to close the case, the police become suspicious of his knowledge, theorizing that such knowledge could only come from the "inside" and unwilling to believe that it is merely Shawn having honed his observational skills. To avoid being sent to jail, Shawn uses those skills to convince the police that he is psychic; though the interim police chief warns Shawn that if his "powers" are fake, he will be prosecuted. With no choice but to keep up the act, and having proven himself an effective aid to the police in solving crimes, he establishes a psychic detective agency, Psych, and becomes an outside consultant to the police. Pretending to have psychic powers allows him to engage in strange and comic behavior as he turns real clues into hunches and otherworldly visitations. He enjoys teasing lifelong friend Burton Guster (Gus), a pharmaceutical sales representative, about Gus' eclectic interests as they drive around in a blue Toyota Echo nicknamed "The Blueberry"[15] solving crimes.
Head detective Carlton Lassiter (Timothy Omundson), playfully nicknamed "Lassie" by Shawn and Gus, quietly comes to respect Shawn's crime-solving skills despite doubting his psychic abilities; Lassiter is constantly exasperated by Shawn keeping investigations ongoing and/or infuriated by Shawn's antics. However, junior detective Juliet "Jules" O'Hara (Maggie Lawson) and Chief Vick (Kirsten Nelson) are far less antagonistic – with O'Hara expressing belief in Shawn's abilities while Vick is mum on the subject – and usually willing to give Shawn the leeway he needs to solve cases. Henry and Shawn have a difficult relationship, but despite this, Henry reluctantly helps Shawn on various occasions.

| Season | Episodes | Originally aired | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First aired | Last aired | Network | |||
| 1 | 15 | July 7, 2006 | March 2, 2007 | USA | |
| 2 | 16 | July 13, 2007 | February 15, 2008 | ||
| 3 | 16 | July 18, 2008 | February 20, 2009 | ||
| 4 | 16 | August 7, 2009 | March 10, 2010 | ||
| 5 | 16 | July 14, 2010 | December 22, 2010 | ||
| 6 | 16 | October 12, 2011 | April 11, 2012 | ||
| 7 | 14 | February 27, 2013 | May 29, 2013 | ||
| Psych: The Musical | December 15, 2013 | ||||
| 8 | 10 | January 8, 2014 | March 26, 2014 | ||
| Psych: The Movie | December 7, 2017 | ||||
| Psych 2: Lassie Come Home | July 15, 2020 | Peacock | |||
| Psych 3: This Is Gus | November 18, 2021 | ||||
The show uses White Rock, British Columbia, Canada for its Santa Barbara, California setting.[16]
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2021) |
Anne Dudek's character was written out of the series after the character generated a negative test audience reaction with Lassiter due to their relationship. Maggie Lawson was cast as Juliet O'Hara to serve as a replacement.[17][18]
The theme song for Psych is "I Know You Know" by The Friendly Indians, series creator Steve Franks's band. Some episodes in seasons three through eight use an extended version of "I Know You Know" consisting of the first verse and the chorus,[19] but most episodes use a shortened version consisting of mostly the chorus. In some episodes, the theme song is changed, usually as a tie-in to the theme of the episode to come.
Variations of the theme song include:
In the "pilot", Roday improvised by picking up a pineapple and saying, "Should I slice this up for the road?" Since then, pineapples have appeared in every episode as a running gag, whether just one in the background or the actual mention of it. It is Shawn's go-to housewarming gift. The pineapple is a major marketing point for items related to the show on the USA website.[20] Fan movements, such as fan-made websites, have also been dedicated to finding a pineapple or pineapple-related object in each episode.[21]
Following the series finale on March 26, 2014, USA Network aired a live aftershow entitled "Psych After Pshow." The hour-long special was hosted by Kevin Pereira and featured series stars and creator/executive producer Steve Franks.[22]
In July 2011, Ion Television announced that Psych would become part of its 2012 broadcast in syndication.[23] During 2012, reruns of the show mostly ran on Saturdays as a marathon. In 2013, Ion Television announced the acquisition option pick-up of season seven of Psych. It no longer airs on Ion Television. The deal with NBC Universal Cable & New Media Distribution adds all 16 new episodes of season seven to Ion's existing library of seasons one–six of Psych and includes rights to future seasons.[24] As of January 2023, Psych started airing on Hallmark Movies and Mysteries.
| Title | Ep # | Region 1 | Region 2 | Region 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Complete First Season | 15 | June 26, 2007 | April 24, 2008 | April 30, 2008 |
| The Complete Second Season | 16 | July 8, 2008 | June 7, 2010 | March 3, 2010 |
| The Complete Third Season | 16 | July 21, 2009 | February 21, 2011 | March 2, 2011 |
| The Complete Fourth Season | 16 | July 13, 2010 | July 18, 2011 | August 22, 2012 |
| The Complete Fifth Season | 16 | May 31, 2011 | May 21, 2012 | September 5, 2013 |
| The Psych-O-Ween Collection | 4 | September 11, 2012[25] | TBA | TBA |
| The Complete Sixth Season | 16 | October 16, 2012 | July 26, 2013 | August 14, 2014 |
| The Complete Seventh Season | 14 | October 8, 2013 | July 11, 2016 | TBA |
| Psych: The Musical | 4 | December 17, 2013[26] | TBA | TBA |
| The Eighth and Final Season | 10 | April 1, 2014[27] | TBA | TBA |
| The Complete Series | 120 | October 7, 2014[28] | TBA | TBA |
| The Complete Collection | 120, 1 Movie | July 3, 2018[29] | TBA | TBA |
| The Complete Collection (Blu-ray version) | 120, 3 Movies | October 17, 2023[30] | TBA | TBA |
Psych scored a 4.51 rating and an average of 6.1 million total viewers at its premiere, which made it the highest-rated scripted series premiere on basic cable in 2006 in all key demographics (households, P18-49, P25-54, and total viewers), according to a USA Network press release, quoted from the Futon Critic.[4]
| Season | Timeslot (ET) | Episodes | Premiered | Ended | TV season | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Premiere Viewers (in millions) |
Date | Finale Viewers (in millions) | ||||
| 1 | Friday 10:00 pm (July 7, 2006 – February 20, 2009) | 15 | July 7, 2006
|
6.06[31] | March 2, 2007
|
4.48[32] | 2006–2007 |
| 2 | 16 | July 13, 2007
|
4.33[33] | February 15, 2008
|
4.70[34] | 2007–2008 | |
| 3 | 16 | July 18, 2008
|
4.89[35] | February 20, 2009
|
4.83[36] | 2008–2009 | |
| 4 | Friday 10:00 pm (August 7, 2009 – October 16, 2009)
Wednesday 10:00 pm (January 27, 2010 – March 10, 2010) |
16 | August 7, 2009
|
3.98[37] | March 10, 2010
|
2.95[38] | 2009–2010 |
| 5 | Wednesday 10:00 pm (July 14, 2010 – May 29, 2013)[b]
|
16 | July 14, 2010
|
3.69[39] | December 22, 2010
|
2.90[40] | 2010 |
| 6 | 16 | October 12, 2011
|
3.00[41] | April
CubbiesCubbies theme by Eli Download: Cubbies.p3t
Redirect to:
| |||