Xbox 360 theme by Sygal
Download: Xbox360_2.p3t
(3 backgrounds)
  
| |
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Flextronics, Wistron, Celestica, Foxconn[1][2] |
| Product family | Xbox |
| Type | Home video game console |
| Generation | Seventh |
| Release date | November 22, 2005[5]
|
| Introductory price | |
| Discontinued |
|
| Units sold | Worldwide: 84 million (as of June 9, 2014[update])[8] (details) |
| Media | DVD, CD, digital distribution Add-on: HD DVD (discontinued) |
| Operating system | Xbox 360 system software |
| System on a chip | XCGPU (Xbox 360 S and E models only) |
| CPU | 3.2 GHz PowerPC Tri-Core Xenon |
| Memory | |
| Storage | Storage media
|
| Display | Video output formats
|
| Graphics | 500 MHz ATI/AMD Xenos, 240 GFLOPS |
| Sound |
|
| Controller input | 4 maximum* (any combination):
|
| Connectivity |
|
| Current firmware | 2.0.17559.0[12] |
| Online services | Xbox Live |
| Best-selling game | Kinect Adventures! (24 million as pack-in game for Kinect)[13][14] |
| Backward compatibility | Selected Xbox games[15][16] (requires hard drive and the latest update) |
| Predecessor | Xbox |
| Successor | Xbox One |
| Website | xbox |
The Xbox 360 is a home video game console developed by Microsoft. As the successor to the original Xbox, it is the second console in the Xbox series. It was officially unveiled on MTV on May 12, 2005, with detailed launch and game information announced later that month at the 2005 Electronic Entertainment Expo (E3).[17][18][19][20] As a seventh-generation console, it primarily competed with Sony's PlayStation 3 and Nintendo's Wii.
The Xbox 360 features an online service, Xbox Live, which was expanded from its previous iteration on the original Xbox and received regular updates during the console's lifetime. Available in free and subscription-based varieties, Xbox Live allows users to play games online; download games (through Xbox Live Arcade) and game demos; purchase and stream music, television programs, and films through the Xbox Music and Xbox Video portals; and access third-party content services through media streaming applications. In addition to online multimedia features, it allows users to stream media from local PCs. Several peripherals have been released, including wireless controllers, expanded hard drive storage, and the Kinect motion sensing camera. The release of these additional services and peripherals helped the Xbox brand grow from gaming-only to encompassing all multimedia, turning it into a hub for living-room computing entertainment.[21][22][23][24]
Launched worldwide across 2005–2006, the Xbox 360 was initially in short supply in many regions, including North America and Europe. The earliest versions of the console suffered from a high failure rate, indicated by the so-called "Red Ring of Death", necessitating an extension of the device's warranty period. Microsoft released two redesigned models of the console: the Xbox 360 S in 2010,[25] and the Xbox 360 E in 2013.[26] Xbox 360 is the ninth-highest-selling home video game console in history, and the highest-selling console made by an American company. Although not the best-selling console of its generation, the Xbox 360 was deemed by TechRadar to be the most influential through its emphasis on digital media distribution and multiplayer gaming on Xbox Live.[24][27]
The Xbox 360's successor, the Xbox One, was released on November 22, 2013.[28] On April 20, 2016, Microsoft announced that it would end the production of new Xbox 360 hardware, although the company will continue to support the platform.[7] On August 17, 2023, Microsoft announced that on July 29, 2024, the Xbox 360 game marketplace will stop offering new purchases and Microsoft Movies & TV app will no longer function (the console will still be able to download previously purchased content, run it, and enter multiplayer sessions).[29][30]
History[edit]
Development[edit]
Known during development as Xbox Next, Xenon, Xbox 2, Xbox FS or NextBox,[31] the Xbox 360 was conceived in early 2003.[32] In February 2003, planning for the Xenon software platform began, and was headed by Microsoft's Vice President J Allard.[32] That month, Microsoft held an event for 400 developers in Bellevue, Washington to recruit support for the system.[32] Also that month, Peter Moore, former president of Sega of America, joined Microsoft. On August 12, 2003, ATI signed on to produce the graphics processing unit for the new console, a deal that was publicly announced two days later.[33] Before the launch of the Xbox 360, several Alpha development kits were spotted using Apple's Power Mac G5 hardware. This was because the system's PowerPC 970 processor was running the same PowerPC architecture that the Xbox 360 would eventually run under IBM's Xenon processor. The cores of the Xenon processor were developed using a slightly modified version of the PlayStation 3's Cell Processor PPE architecture. According to David Shippy and Mickie Phipps, the IBM employees were "hiding" their work from Sony and Toshiba, IBM's partners in developing the Cell Processor.[34] Jeff Minter created the music visualization program Neon which is included with the Xbox 360.[35]
Launch[edit]
The Xbox 360 was released on November 22, 2005, in the United States and Canada;[5] December 2, 2005, in Europe and December 10, 2005, in Japan. It was later launched in Mexico, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, India, and Russia. In its first year in the market, the system was launched in 36 countries, more countries than any other console has launched in a single year.[36]
Critical reception[edit]
In 2009, IGN named the Xbox 360 the sixth-greatest video game console of all time, out of a field of 25.[37] Although not the best-selling console of the seventh generation, the Xbox 360 was deemed by TechRadar to be the most influential, by emphasizing digital media distribution and online gaming through Xbox Live, and by popularizing game achievement awards.[24] PC Magazine considered the Xbox 360 the prototype for online gaming as it "proved that online gaming communities could thrive in the console space".[21] Five years after the Xbox 360's debut, the well-received Kinect motion capture camera was released, which set the record of being the fastest selling consumer electronic device in history, and extended the life of the console.[38] Edge ranked Xbox 360 the second-best console of the 1993–2013 period, stating "It had its own social network, cross-game chat, new indie games every week, and the best version of just about every multiformat game ... Killzone is no Halo and nowadays Gran Turismo is no Forza, but it's not about the exclusives—there's nothing to trump Naughty Dog's PS3 output, after all. Rather, it's about the choices Microsoft made back in the original Xbox's lifetime. The PC-like architecture meant the early EA Sports games ran at 60fps compared to only 30 on PS3, Xbox Live meant every dedicated player had an existing friends list, and Halo meant Microsoft had the killer next-generation exclusive. And when developers demo games on PC now they do it with a 360 pad—another industry benchmark, and a critical one."[39]
Sales[edit]
| Region | Units sold | First available |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 38.8 million as of June 27, 2013[update][40] | November 22, 2005 |
| EMEA region(Europe, Middle East and Africa) | 13.7 million as of March 31, 2011[update][41](includes UK sales) | December 2, 2005 |
| United Kingdom | 9 million (lifetime sales)[42][43] | |
| Japan | 1.62 million (lifetime sales)[44] | December 10, 2005 |
| Australia & New Zealand | 1 million as of April 19, 2010[update][45] | March 23, 2006 |
| Worldwide | 84 million as of June 9, 2014[update][8] | (more...) |
The Xbox 360 began production only 69 days before launch, on September 14, 2005,[46][47] and Microsoft was not able to supply enough systems to meet initial consumer demand in Europe or North America, selling out completely upon release in all regions except in Japan.[48][49][50][51] Forty thousand units were offered for sale on auction site eBay during the initial week of release, 10% of the total supply.[52] By year's end, Microsoft had shipped 1.5 million units, including 900,000 in North America, 500,000 in Europe, and 100,000 in Japan.[53]
In May 2008, Microsoft announced that 10 million Xbox 360s had been sold and that it was the "first current generation gaming console" to surpass the 10 million figure in the US.[54] In the US, the Xbox 360 was the leader in current-generation home console sales until June 2008, when it was surpassed by the Wii.[55][56][57] By the end of March 2011, Xbox 360 sales in the US had reached 25.4 million units.[41] Between January 2011 and October 2013, the Xbox 360 was the best-selling console in the United States for these 32 consecutive months.[58] By the end of 2014, Xbox 360 sales had surpassed sales of the Wii, making the Xbox 360 the best-selling 7th-generation console in the US once again.[59] In Canada, the Xbox 360 has sold a total of 870,000 units as of August 1, 2008.[60]
In Europe, the Xbox 360 has sold seven million units as of November 20, 2008.[61] The Xbox 360 took 110 weeks to reach 2 million units sold in the UK, generating £507m in revenue.[42] Sales in the United Kingdom would reach 3.2 million units by January 2009, per GfK Chart-Track.[62] The 8 million unit mark was crossed in the UK by February 2013.[63] Sales of the Xbox 360 would overtake the Wii later that year, topping 9 million units, making the Xbox 360 the best-selling 7th-generation console in the UK, as well as making it the third best-selling console of all time in the region, behind the PS2 and Nintendo DS.[64][42][43] Over 1 million units were sold in Spain across the console's lifecycle.[65]
The Xbox 360 crossed the 1 million units sold in Japan in March 2009,[66] and the 1.5 million units sold in June 2011.[67] Lifetime sales of the Xbox 360 in Japan stand at 1,616,218 million units. While the Xbox 360 has sold poorly in Japan, it improved upon the sales of the original Xbox, which had total sales of 474,992 units.[44] Furthermore, the Xbox 360 managed to outsell both the PlayStation 3 and Wii the week ending September 14, 2008, as well as the week ending February 22, 2009, when the Japanese Xbox 360 exclusives Infinite Undiscovery[68] and Star Ocean: The Last Hope,[69] were released those weeks, respectively. Ultimately, Edge magazine would report that Microsoft had been unable to make serious inroads into the dominance of domestic rivals Sony and Nintendo; adding that lackluster sales in Japan had led to retailers scaling down and in some cases, discontinuing sales of the Xbox 360 completely.[70] The significance of Japan's poor sales might be overstated in the media in comparison to overall international sales.[71]
Legacy[edit]
The Xbox 360 sold much better than its predecessor, and although not the best-selling console of the seventh generation, it is regarded as a success since it strengthened Microsoft as a major force in the console market at the expense of well-established rivals.[27] The inexpensive Wii did sell the most console units but eventually saw a collapse of third-party software support in its later years, and it has been viewed by some as a fad since the succeeding Wii U had a poor debut in 2012.[24][72][73][74][75] The PlayStation 3 struggled for a time due to being too expensive and initially lacking quality games,[76] making it far less dominant than its predecessor, the PlayStation 2, and it took until late in the PlayStation 3's lifespan for its sales and games to reach parity with the Xbox 360. TechRadar proclaimed that "Xbox 360 passes the baton as the king of the hill – a position that puts all the more pressure on its successor, Xbox One".[24]
The Xbox 360's advantage over its competitors was due to the release of high-profile games from both first party and third-party developers. The 2007 Game Critics Awards honored the platform with 38 nominations and 12 wins – more than any other platform.[77][78] By March 2008, the Xbox 360 had reached a software attach rate of 7.5 games per console in the US; the rate was 7.0 in Europe, while its competitors were 3.8 (PS3) and 3.5 (Wii), according to Microsoft.[79] At the 2008 Game Developers Conference, Microsoft announced that it expected over 1,000 games available for Xbox 360 by the end of the year.[80] As well as enjoying exclusives such as additions to the Halo franchise and Gears of War, the Xbox 360 has managed to gain a simultaneous release of games that were initially planned to be PS3 exclusives, including Devil May Cry 4,[81] Ace Combat 6,[82] Virtua Fighter 5,[83] Grand Theft Auto IV,[84] Final Fantasy XIII,[85] Tekken 6,[86] Metal Gear Rising: Revengeance,[87] and L.A. Noire.[88] In addition, Xbox 360 versions of cross-platform games were generally considered superior to their PS3 counterparts in 2006 and 2007, due in part to the difficulties of programming for the PS3.[89]
TechRadar deemed the Xbox 360 as the most influential game system through its emphasis of digital media distribution, Xbox Live online gaming service, and game achievement feature.[24] During the console's lifetime, the Xbox brand has grown from gaming-only to encompassing all multimedia, turning it into a hub for "living-room computing environment".[90][22][23]
Microsoft announced the successor to the Xbox 360, the Xbox One, on May 21, 2013.[91] On April 20, 2016, Microsoft announced the end of production of new Xbox 360 hardware, though the company will continue to provide hardware and software support for the platform as selected Xbox 360 games are playable on Xbox One.[92] The Xbox 360 continued to be supported by major publishers with new games well into the Xbox One's lifecycle. New titles were still being released in 2018.[93] The Xbox 360 continues to have an active player base years after the system's discontinuation. Speaking to Engadget at E3 2019 after the announcement of Project Scarlett, the next-generation of Xbox consoles after the Xbox One, Phil Spencer stated that there were still "millions and millions of players" act
Mac V2.00
Mac V2.00 theme by SilentTiger
Download: MacV2.00.p3t
(3 backgrounds)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
PS3 Vista
PS3 Vista theme by Wizer238
Download: PS3Vista.p3t

(1 background)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Vista for PS3 XMB Style v1.1
Vista for PS3 XMB Style version 1.1 theme by zsdg07
Download: VistaForPS3XMBv1.1.p3t

(3 backgrounds)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Windows Vista #6
Windows Vista theme by rmc08
Download: WindowsVista_6.p3t

(6 backgrounds)
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
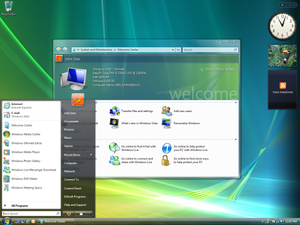 Screenshot of Windows Vista Ultimate, showing its desktop, taskbar, Start menu, Windows Sidebar, Welcome Center, and glass effects of Windows Aero | |
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model | |
| Released to manufacturing | November 8, 2006[2] |
| General availability | January 30, 2007[3] |
| Final release | Service Pack 2[4] (6.0.6002.24170) / July 21, 2017[5] |
| Marketing target | Consumer and Business |
| Update method | |
| Platforms | IA-32 and x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| Userland | Windows API, NTVDM, SUA |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows XP (2001) |
| Succeeded by | Windows 7 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Vista (archived at the Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on April 10, 2012[6] Extended support ended on April 11, 2017[6] | |
| Part of a series of articles on |
| Windows Vista |
|---|
| New features |
| Siblings |
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows. It was released to manufacturing on November 8, 2006, and over the following two months, it was released in stages to business customers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; it is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform.[7]
Development of Windows Vista began in 2001 when it was codenamed "Longhorn"; originally envisioned as a minor successor to Windows XP, it gradually included numerous new features from the then-next major release of Windows codenamed "Blackcomb", after which it was repositioned as a major release of Windows, and it consequently underwent a protracted development that was unprecedented for Microsoft. Most new features were prominently based on a new presentation layer codenamed Avalon, a new communications architecture codenamed Indigo, and a relational storage platform codenamed WinFS — all built on the premature .NET Framework; however, this proved to be untenable due to incompleteness of technologies and ways in which new features were added, and Microsoft changed the project in 2004. Many new features were eventually reimplemented during development, but Microsoft ceased using managed code to develop the operating system.[8]
New features of Windows Vista include a graphical user interface and visual style referred to as Windows Aero; a content index and desktop search platform called Windows Search; new peer-to-peer technologies to simplify sharing files and media between computers and devices on a home network; and new multimedia tools such as Windows DVD Maker. Windows Vista included version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, allowing software developers to write applications without traditional Windows APIs. There are major architectural overhauls to audio, display, network, and print sub-systems; deployment, installation, servicing, and startup procedures are also revised. It is the first release of Windows built on Microsoft's Trustworthy Computing initiative and emphasized security with the introduction of many new security and safety features such as BitLocker and User Account Control.
The ambitiousness and scope of these changes, and the abundance of new features earned positive reviews, but Windows Vista was the subject of frequent negative press and significant criticism. Criticism of Windows Vista focused on driver, peripheral, and program incompatibility; digital rights management; excessive authorization from the new User Account Control; inordinately high system requirements when contrasted with Windows XP; its protracted development; longer boot time; and more restrictive product licensing. Windows Vista deployment and satisfaction rates were consequently lower than those of Windows XP, and it is considered a market failure;[9][10] however, its use surpassed Microsoft's pre-launch two-year-out expectations of achieving 200 million users[11] (with an estimated 330 million users by 2009).[12] On October 22, 2010, Microsoft ceased retail distribution of Windows Vista; OEM supply ceased a year later.[13] Windows Vista was succeeded by Windows 7 in 2009.
Mainstream support for Windows Vista ended on April 10, 2012 and extended support ended on April 11, 2017.[6]
Development[edit]
Microsoft began work on Windows Vista, known at the time by its codename "Longhorn", in May 2001,[14] five months before the release of Windows XP. It was originally expected to ship in October 2003 as a minor step between Windows XP and "Blackcomb", which was planned to be the company's next major operating system release. Gradually, "Longhorn" assimilated many of the important new features and technologies slated for Blackcomb, resulting in the release date being pushed back several times in three years. In some builds of Longhorn, their license agreement said "For the Microsoft product codenamed 'Whistler'". Many of Microsoft's developers were also re-tasked to build updates to Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to strengthen security. Faced with ongoing delays and concerns about feature creep, Microsoft announced on August 27, 2004, that it had revised its plans. For this reason, Longhorn was reset to start work on componentizing the Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 codebase, and over time re-incorporating the features that would be intended for an actual operating system release. However, some previously announced features such as WinFS were dropped or postponed, and a new software development methodology called the Security Development Lifecycle was incorporated to address concerns with the security of the Windows codebase, which is programmed in C, C++ and assembly. Longhorn became known as Vista in 2005. Vista in Spanish means view.[15][16]
Longhorn[edit]
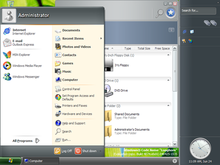
The early development stages of Longhorn were generally characterized by incremental improvements and updates to Windows XP. During this period, Microsoft was fairly quiet about what was being worked on, as their marketing and public relations efforts were more strongly focused on Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003, which was released in April 2003. Occasional builds of Longhorn were leaked onto popular file sharing networks such as IRC, BitTorrent, eDonkey and various newsgroups, and so most of what is known about builds before the first sanctioned development release of Longhorn in May 2003 is derived from these builds.
After several months of relatively little news or activity from Microsoft with Longhorn, Microsoft released Build 4008, which had made an appearance on the Internet around February 28, 2003.[17] It was also privately handed out to a select group of software developers. As an evolutionary release over build 3683, it contained several small improvements, including a modified blue "Plex" theme and a new, simplified Windows Image-based installer that operates in graphical mode from the outset, and completed an install of the operating system in approximately one third the time of Windows XP on the same hardware. An optional "new taskbar" was introduced that was thinner than the previous build and displayed the time differently. The most notable visual and functional difference, however, came with Windows Explorer. The incorporation of the Plex theme made blue the dominant color of the entire application. The Windows XP-style task pane was almost completely replaced with a large horizontal pane that appeared under the toolbars. A new search interface allowed for filtering of results, searching for Windows help, and natural-language queries that would be used to integrate with WinFS. The animated search characters were also removed. The "view modes" were also replaced with a single slider that would resize the icons in real-time, in the list, thumbnail, or details mode, depending on where the slider was. File metadata was also made more visible and more easily editable, with more active encouragement to fill out missing pieces of information. Also of note was the conversion of Windows Explorer to being a .NET application.
Most builds of Longhorn and Vista were identified by a label that was always displayed in the bottom-right corner of the desktop. A typical build label would look like "Longhorn Build 3683.Lab06_N.020923-1821". Higher build numbers did not automatically mean that the latest features from every development team at Microsoft was included. Typically, a team working on a certain feature or subsystem would generate their working builds which developers would test with, and when the code was deemed stable, all the changes would be incorporated back into the main development tree at once. At Microsoft, several "Build labs" exist where the compilation of the entirety of Windows can be performed by a team. The name of the lab in which any given build originated is shown as part of the build label, and the date and time of the build follow that. Some builds (such as Beta 1 and Beta 2) only display the build label in the version information dialog (Winver). The icons used in these builds are from Windows XP.
At the Windows Hardware Engineering Conference (WinHEC) in May 2003, Microsoft gave their first public demonstrations of the new Desktop Window Manager and Aero. The demonstrations were done on a revised build 4015 which was never released. Several sessions for developers and hardware engineers at the conference focused on these new features, as well as the Next-Generation Secure Computing Base (previously known as "Palladium"), which at the time was Microsoft's proposed solution for creating a secure computing environment whereby any given component of the system could be deemed "trusted". Also at this conference, Microsoft reiterated their roadmap for delivering Longhorn, pointing to an "early 2005" release date.[18]
Development reset[edit]
By 2004, it had become obvious to the Windows team at Microsoft that they were losing sight of what needed to be done to complete the next version of Windows and ship it to customers. Internally, some Microsoft employees were describing the Longhorn project as "another Cairo" or "Cairo.NET", referring to the Cairo development project that the company embarked on through the first half of the 1990s, which never resulted in a shipping operating system (though nearly all the technologies developed in that time did end up in Windows 95 and Windows NT[19]). Microsoft was shocked in 2005 by Apple's release of Mac OS X Tiger. It offered only a limited subset of features planned for Longhorn, in particular fast file searching and integrated graphics and sound processing, but appeared to have impressive reliability and performance compared to contemporary Longhorn builds.[20] Most Longhorn builds had major Windows Explorer system leaks which prevented the OS from performing well, and added more confusion to the development teams in later builds with more and more code being developed which failed to reach stability.
In a September 23, 2005 front-page article in The Wall Street Journal,[21] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin, who had overall responsibility for the development and delivery of Windows, explained how development of Longhorn had been "crashing into the ground" due in large part to the haphazard methods by which features were introduced and integrated into the core of the operating system, without a clear focus on an end-product. Allchin went on to explain how in December 2003, he enlisted the help of two other senior executives, Brian Valentine and Amitabh Srivastava, the former being experienced with shipping software at Microsoft, most notably Windows Server 2003,[22] and the latter having spent his career at Microsoft researching and developing methods of producing high-quality testing systems.[23] Srivastava employed a team of core architects to visually map out the entirety of the Windows operating system, and to proactively work towards a development process that would enforce high levels of code quality, reduce interdependencies between components, and in general, "not make things worse with Vista".[24] Since Microsoft decided that Longhorn needed to be further componentized, work started on builds (known as the Omega-13 builds, named after a time travel device in the film Galaxy Quest[25]) that would componentize existing Windows Server 2003 source code, and over time add back functionality as development progressed. Future Longhorn builds would start from Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 and continue from there.
This change, announced internally to Microsoft employees on August 26, 2004, began in earnest in September, though it would take several more months before the new development process and build methodology would be used by all of the development teams. A number of complaints came from individual developers, and Bill Gates himself, that the new development process was going to be prohibitively difficult to work within.
As Windows Vista[edit]
By approximately November 2004, the company had considered several names for the final release, ranging from simple to fanciful and inventive. In the end, Microsoft chose Windows Vista as confirmed on July 22, 2005, believing it to be a "wonderful intersection of what the product really does, what Windows stands for, and what resonates with customers, and their needs". Group Project Manager Greg Sullivan told Paul Thurrott "You want the PC to adapt to you and help you cut through the clutter to focus on what's important to you. That's what Windows Vista is all about: "bringing clarity to your world" (a reference to the three marketing points of Vista—Clear, Connected, Confident), so you can focus on what matters to you".[26] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin also loved the name, saying that "Vista creates the right imagery for the new product capabilities and inspires the imagination with all the possibilities of what can be done with Windows—making people's passions come alive."[27]
After Longhorn was named Windows Vista in July 2005, an unprecedented beta-test program was started, involving hundreds of thousands of volunteers and companies. In September of that year, Microsoft started releasing regular Community Technology Previews (CTP) to beta testers from July 2005 to February 2006. The first of these was distributed at the 2005 Microsoft Professional Developers Conference, and was subsequently released to beta testers and Microsoft Developer Network subscribers. The builds that followed incorporated most of the planned features for the final product, as well as a number of changes to the user interface, based largely on feedback from beta testers. Windows Vista was deemed feature-complete with the release of the "February CTP", released on February 22, 2006, and much of the remainder of the work between that build and the final release of the product focused on stability, performance, application and driver compatibility, and documentation. Beta 2, released in late May, was the first build to be made available to the general public through Microsoft's Customer Preview Program. It was downloaded over 5 million times. Two release candidates followed in September and October, both of which were made available to a large number of users.[28]
At the Intel Developer Forum on March 9, 2006, Microsoft announced a change in their plans to support EFI in Windows Vista. The UEFI 2.0 specification (which replaced EFI 1.10) was not completed until early 2006, and at the time of Microsoft's announcement, no firmware manufacturers had completed a production implementation which could be used for testing. As a result, the decision was made to postpone the introduction of UEFI support to Windows; support for UEFI on 64-bit platforms was postponed until Vista Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2008 and 32-bit UEFI would not be supported, as Microsoft did not expect many such systems to be built because the market was quickly moving to 64-bit processors.[29][30]
While Microsoft had originally hoped to have the consumer versions of the operating system available worldwide in time for the 2006 holiday shopping season, it announced in March 2006 that the release date would be pushed back to January 2007 in order to give the company—and the hardware and software companies that Microsoft depends on for providing device drivers—additional time to prepare. Because a release to manufacturing (RTM) build is the final version of code shipped to retailers and other distributors, the purpose of a pre-RTM build is to eliminate any last "show-stopper" bugs that may prevent the code from responsibly being shipped to customers, as well as anything else that consumers may find troublesome. Thus, it is unlikely that any major new features would be introduced; instead, work would focus on Vista's fit and finish. In just a few days, developers had managed to drop Vista's bug count from over 2470 on September 22 to just over 1400 by the time RC2 shipped in early October. However, they still had a way to go before Vista was ready to RTM. Microsoft's internal processes required Vista's bug count to drop to 500 or fewer before the product could go into escrow for RTM.[31] For most of the pre-RTM builds, only 32-bit editions were released.
On June 14, 2006, Windows developer Philip Su posted a blog entry which decried the development process of Windows Vista, stating that "The code is way too complicated, and that the pace of coding has been tremendously slowed down by overbearing process."[32] The same post also described Windows Vista as having approximately 50 million lines of code, with about 2,000 developers working on the product. During a demonstration of the speech recognition feature new to Windows Vista at Microsoft's Financial Analyst Meeting on July 27, 2006, the software recognized the phrase "Dear mom" as "Dear aunt". After several failed attempts to correct the error, the sentence eventually became "Dear aunt, let's set so double the killer delete select all".[33] A developer with Vista's speech recognition team later explained that there was a bug with the build of Vista that was causing the microphone gain level to be set very high, resulting in the audio being received by the speech recognition software being "incredibly distorted".[34]
Windows Vista build 5824 (October 17, 2006) was supposed to be the RTM release, but a bug, where the OOBE hangs at the start of the WinSAT Assessment (if upgraded from Windows XP), requiring the user to terminate msoobe.exe by pressing Shift+F10 to open Command Prompt using either command-line tools or Task Manager prevented this, damaging development and lowering the chance that it would hit its January 2007 deadline.[35]
Development of Windows Vista came to an end when Microsoft announced that it had been finalized on November 8, 2006, and was concluded by co-president of Windows development, Jim Allchin.[36] The RTM's build number had also jumped to 6000 to reflect Vista's internal version number, NT 6.0.[37] Jumping RTM build numbers is common practice among consumer-oriented Windows versions, like Windows 98 (build 1998), Windows 98 SE (build 2222), Windows Me (build 3000) or Windows XP (build 2600), as compared to the business-oriented versions like Windows 2000 (build 2195) or Server 2003 (build 3790). On November 16, 2006, Microsoft made the final build available to MSDN and Technet Plus subscribers.[38] A business-oriented Enterprise edition was made available to volume license customers on November 30, 2006.[39] Windows Vista was launched for general customer availability on January 30, 2007.[3]
New or changed features[edit]
New features introduced by Windows Vista are very numerous, encompassing significant functionality not available in its predecessors.
End-user[edit]
- Windows Aero is the new graphical user interface, which Jim Allchin stated is an acronym for Authentic, Energetic, Reflective, and Open.[40] Microsoft intended the new interface to be cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing than those of previous Windows versions, and it features advanced visual effects such as blurred glass translucencies and dynamic glass reflections and smooth window animations.[41] Laptop users report, however, that enabling Aero reduces battery life[42][43] and reduces performance. Windows Aero requires a compositing window manager called Desktop Window Manager.
- Windows Shell offers a new range of organization, navigation, and search capabilities: Task Panes in Windows Explorer are removed, with the relevant tasks moved to a new command bar. The navigation pane can now be displayed when tasks are available, and it has been updated to include a new "Favorite Links" that houses shortcuts to common locations. An incremental search search box now appears at all times in Windows Explorer. The address bar has been replaced with a breadcrumb navigation bar, which means that multiple locations in a hierarchy can be navigated without needing to go back and forth between locations. Icons now display thumbnails depicting contents of items and can be dynamically scaled in size (up to 256 × 256 pixels). A new preview pane allows users to see thumbnails of items and play tracks, read contents of documents, and view photos when they are selected. Groups of items are now selectable and display the number of items in each group. A new details pane allows users to manage metadata. There are several new sharing features, including the ability to directly share files. The Start menu also now includes an incremental search box — allowing the user to press the ⊞ Win key and start typing to instantly find an item or launch a program — and the All Programs list uses a vertical scroll bar instead of the cascading flyout menu of Windows XP.[41]
- Windows Search is a new content index desktop search platform that replaces the Indexing Service of previous Windows versions to enable incremental searches for files and non-file items — documents, emails, folders, programs, photos, tracks, and videos — and contents or details such as attributes, extensions, and filenames across compatible applications.[41]
- Windows Sidebar is a translucent panel that hosts gadgets that display details such as feeds and sports scores on the Windows desktop; the Sidebar can be hidden and gadgets can also be placed on the desktop itself.[41]
- Internet Explorer 7 is a significant revision over Internet Explorer 6 with a new user interface comprising additional address bar features, a new search box, enhanced page zoom, RSS feed functionality, and support for tabbed browsing (with an optional "quick tabs" feature that shows thumbnails of each open tab). Anti-phishing software is introduced that combines client-side scanning with an optional online service; it checks with Microsoft the address being visited to determine its legitimacy, compares the address with a locally stored list of legitimate addresses, and uses heuristics to determine whether an address's characteristics are indicative of phishing attempts. In Windows Vista, it runs in isolation from other applications (protected mode); exploits and malicious software are restricted from writing to any location beyond Temporary Internet Files without explicit user consent.
- Windows Media Player 11 is a significant update to Microsoft's Windows Media Player for playing and organizing photos, tracks, and videos. New features include an updated GUI for the media library, disc spanning, enhanced audio fingerprinting, instant search capabilities, item organization features, synchronization features, the ability to share the media library over a network with other Windows Vista machines, Xbox 360 integration, and
iWikky’s Vista
iWikky’s Vista theme by iWikky
Download: iWikkysVista.p3t

(4 backgrounds)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop MenonThis program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.Playstation 3
Playstation 3 theme by TKC-Muzzer
Download: Playstation3.p3t
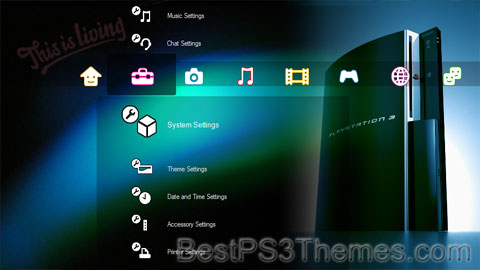
(6 backgrounds)
Redirect to:
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:- Fully protected: This is a redirect from a title that is fully protected from editing for any of several possible reasons. It may have been protected by an administrator, or it may be on the Cascade-protected list, or both.
- Please do not replace these redirected links with links directly to the target page unless expressly advised to do so below or elsewhere on this page, or if the change is supported by a policy or guideline.
When appropriate, protection levels are automatically sensed, described and categorized.- From a miscapitalisation: This is a redirect from a capitalisation error. The correct form is given by the target of the redirect.
- This redirect is made available to aid searches or to maintain links. Pages that use this link should be updated to link directly to the correct form without using a piped link hiding the correct details.
- This template tags redirects with the Redirects from miscapitalisations category, a subcategory of Redirects from incorrect names, so template {{R from incorrect name}} should not be used with this template.
XMB3YOND
XMB3YOND theme by P.D. Latour
Download: XMB3YOND.p3t

(5 backgrounds)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop MenonThis program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.Litho #2
PS3xmbOs_pro
PS3xmbOs_pro theme by P.D. Latour
Download: PS3xmbOs_pro.p3t

(3 backgrounds)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop MenonThis program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename. - Fully protected: This is a redirect from a title that is fully protected from editing for any of several possible reasons. It may have been protected by an administrator, or it may be on the Cascade-protected list, or both.

