Battlefield 2 theme by dieharder
Download: Battlefield2.p3t

(3 backgrounds)
| Battlefield 2 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Developer(s) | Digital Illusions CE |
| Publisher(s) | Electronic Arts |
| Designer(s) | Lars Gustavsson Linus Josephson Erik Sjövold |
| Programmer(s) | Andreas Fredriksson Jonas Kjellström Mats Dal |
| Artist(s) | Mårten Lundsten Riccard Linde |
| Composer(s) |
|
| Series | Battlefield |
| Platform(s) | Microsoft Windows |
| Release |
|
| Genre(s) | First-person shooter |
| Mode(s) | Single-player, multiplayer |
Battlefield 2 is a first-person shooter video game developed by Digital Illusions CE and published by Electronic Arts for Microsoft Windows. It was released in June 2005 as the third game in the Battlefield franchise.[1]
Players fight in a modern battlefield, using modern weapon systems.[2] Battlefield 2 is a first-person shooter with strategy and tactical shooter elements.[3]
The single-player aspect features missions that involve clashes between U.S. Marines, China and the fictional Middle Eastern Coalition. The multiplayer aspect of the game allows players to organize into squads that come under the leadership of a single commander to promote teamwork.[4] The story takes place in the early 21st century during a fictional world war between various power blocs: China, the European Union, the fictional Middle Eastern Coalition (MEC), Russia and the United States. The game takes place in different fronts, as the Middle East and China are being invaded by US and EU forces, and the United States is being invaded by Chinese and MEC forces. A sequel, Battlefield 3, was released in October 2011.
On June 30, 2014, the multiplayer master server was shut down alongside other GameSpy-powered titles,[5][6] although it can still be played online throughout fan-created mods with alternative servers. In 2017, Electronic Arts demanded the takedown of the modified versions of Battlefield 2 on alternate servers, distributed by a group known as "Revive Network", as infringement of their copyrights.[7][8][9]
Gameplay[edit]

Battlefield 2 is a sequel to Battlefield Vietnam, with many changes to the popular gameplay of the original. Many of these new gameplay features were added to the game with teamwork and collaboration in mind. The new game engine includes improved physics, dynamic lighting, and more realistic material penetration.
Battlefield 2 is a multiplayer video game played via the Internet or on a local area network. A single-player mode with three difficulty levels is included. Both player modes use the same maps and use Battlefield's conquest game mode. Single-player mode allows 16 computer-controlled players[10] while Internet mode allows up to 64 players. Players can choose to play as the United States Marine Corps, the People's Liberation Army, or the "Middle Eastern Coalition". Additional factions are playable through the expansion packs, such as the European Union. Progress in the game is made via promotions which allow additional weapons to be unlocked. By playing the game on ranked servers, players are able to add to their global player statistics. These statistics are used to award promotions and other achievements.
In Battlefield 2, players are divided into two opposing teams (which factions they represent is dependent upon the map). The key objective in Battlefield 2 is to reduce the opposing teams tickets. Tickets represent an army's ability to reinforce their position on the battlefield; each team has only a limited supply of tickets, and each casualty on the battlefield reduces the number of available tickets. Control points represent key points on the map, and are represented by flags. Control points are Battlefield 2's spawn points, and one team possessing a significant majority of the control points causes the other teams tickets to gradually decrease, regardless of casualties. A round ends when one team's tickets gone, the round's timer ends, or if at any point a team holds no control points, and has no soldiers alive on the battlefield (meaning they are not present in any way on the battlefield).
Battlefield 2's two game modes are Conquest and Cooperative. The only difference between the two modes is that Cooperative includes computer-controlled players, whilst Conquest allows only human players. Results from Cooperative mode do not count toward global player statistics.
Infantry classes[edit]
In Battlefield 2, as with previous Battlefield titles, players are able to select from a variety of infantry classes. Each class of soldier is equipped with different weaponry appropriate to their role in the battle. Assault soldiers, for example, are general-purpose infantry with grenade-launcher equipped assault-rifles and extra armor, Medics carry first-aid equipment such as a field defibrillator, and Anti-Tank troopers are equipped with missiles which are effective against heavy armor.
Players are able to choose a class at the start of a match, or between dying and respawn. Players can also change their class by picking up a "kit" from the body of an incapacitated soldier, friendly or otherwise. Hence, an Assault soldier can become a Medic if they come across a fallen Medic. Player classes are divided in 'Heavy' (with reduced damage done to the torso, but lower stamina) and 'Light' (with standard multipliers, but higher stamina, thus able to sprint for a longer time).
Within the infantry class, there are four support classes with special abilities. The Engineer can repair with his wrench, the Medic can revive with his defibrillator paddles and heal, the Support can resupply ammunition with his ammunition bags and the sniper can place claymores and engage long distance targets. When one of these three classes occupies a vehicle (with the exception of the recon), nearby personnel and vehicles can be replenished, repaired or healed by being in close proximity.
- Assault - Primary role is to engage in combat with enemies at medium range.
- Medic - Primary role is to revive and heal teammates
- Anti-Tank - Primary role is to undertake anti-tank warfare
- Engineer - Primary role is to repair or destroy vehicles
- Support - Primary role is to provide suppressive fire against enemies and resupply teammates
- Special Forces - Primary role is carry out stealth and sabotage missions
- Sniper - Primary role is to engage targets at long distances.
Vehicles[edit]
The various forces still use the trademark feature of the Battlefield series – the large stable of vehicles that any player can climb into and control.[11] There are many different types of vehicles playable in Battlefield 2, all based on real-life vehicles used by the militaries of different countries.[12]
In contrast to Battlefield 1942, Battlefield 2 has only one purely water-based vehicle, the rigid-inflatable boat; however, the BTR-90, the MEC APC, can travel in water as well as the LAV-25 and the WZ 551, the USMC and PLA equivalents, respectively. The developers tried to design the game so that every vehicle would be weak to another type of vehicle, intending to create a situation similar to a game of rock-paper-scissors.[13] For example, mobile anti-air was intended to effectively destroy helicopters, but are vulnerable against opposing tanks. Included within this relationship are stationary defenses such as light machine guns and anti-aircraft/TOW emplacements. The availability and number of certain vehicles are dependent on the map and its size as well as control points captured. Also, more vehicles become available to be used on the maps of expansion/booster packs. (see Maps). The USS Essex is the only naval ship featured in BF2, featuring two spawn points and aircraft spawn points, and is not drivable or destroyable, except for its Phalanx turrets.
Squads[edit]
Players are able to form squads of up to six soldiers in order to more effectively work as a team. Up to nine squads are permitted per team; each squad has a number (automatically assigned) and name (usually a phonetic alphabet letter) for identification. Members of a squad have the ability to communicate with one another via Battlefield 2's integrated voice over IP (VoIP) system.
Squad leaders may assign their squad a variety of objectives (for example, moving to or attacking a specific location). Orders may also be given by the team's commander. Squad leaders are able to issue requests for commander assets (such as artillery fire) and have a direct VoIP channel to the commander.
Members of a squad may spawn near their squad leader, provided that the leader is not dead (or incapacitated), and that the team holds at least one control point. This feature allows squads to more quickly regroup after taking casualties.
Commander[edit]
The commander position is an exclusive role played by one member of each team. Any member of a team may apply for the position, but priority is given to players of higher rank.
The commander alone has access to the "commander screen", an interface similar to that of a real-time strategy game. This allows the commander an overview of the battlefield as a whole, or zoom in and view parts of the map in real-time. The commander also has control of the various commander assets, which include artillery strikes, vehicle and supply drops, and UAV's. They can deploy them to assist their team. The commander can communicate with squads either by sending orders, or via VoIP voice communication. These tools allow the commander to strategically coordinate their forces on the battlefield.
A commander may resign at any point, freeing the position for other members of their team; they may also be forcibly removed by a successful mutiny vote conducted by their team (provided the server allows mutiny votes). Although the commander does not gain points by normal methods (kills, flag captures, etc.), their score is doubled at the end of the round if their team wins.
The commander position would be seen again in Battlefield 2142 and Battlefield 4.
Awards and unlockable weapons[edit]
Players can earn awards (ribbons, badges, and medals) for certain in-game accomplishments. Badges and ribbons are the easiest to obtain, while medals are usually much harder, requiring more extensive play. As players ascend through the ranks they will gain the ability to unlock certain weapons. Each time a player is promoted to an eligible rank, they are given the opportunity to unlock one of seven unlockable weapons, one for each class, which they may subsequently use in place of the standard weapon for the given class.
Battlefield recorder[edit]
A built-in game recorder records battles for subsequent replay. These files can be downloaded from a server which supports BattleRecorder directly after their respective game. Recorded battle files are around 1 to 8 megabytes in size and are played within the Battlefield 2 engine. Camera angles can be changed (free roaming & selected player), as well as the speed, though there is no rewind capability. Files can be exported to AVI format.[14] The Battlefield Recorder has facilitated the creation of various machinima. Usage of the PunkBuster service is mandatory for all official ranked Battlefield 2 servers, but optional for unranked servers.[15][16]
Maps[edit]

Battlefield 2 offers 15 maps for the players to play but shipped with 12.[17] These maps are diverse, ranging from swamps such as Songhua Stalemate, to urban areas such as Strike at Karkand, to an unfinished dam known as Kubra Dam. The USMC is present in all maps and faces against either the MEC or the PLA depending on the map. The PLA is present in Far East theaters such as Dragon Valley and Daqing Oilfields. MEC is present in Middle East theaters such as Gulf of Oman and Zatar Wetlands. The BF2 series including the expansion and booster packs puts the map count at 29 maps.
Battlefield 2 maps have 3 variations, each suited for a certain number of players. Each map has 16, 32, and 64 player-suggested variations in which the area of battlefield or playing field is relatively small, medium, and large, respectively. The only exceptions to this are Wake Island 2007, which is locked at 64-player size and the Euro Force maps, Operation Smokescreen, Great Wall, and Taraba Quarry, which have no 64-player size. 32 and 64 player maps are unavailable to offline players from retailers, but an option is given to download 64 Single player AI bot mods. Other contrasts between these variations other than the size are the number and position of control points and availability of vehicles. As a result, the gameplay of the map is different depending on the variation.[17][18]
Plot[edit]
The game is set in 2007 during a world war between various power blocs: the United States, aided by the European Union, is at war against Russia, China and the fictional Middle Eastern Coalition (MEC), aided by various insurgents.[19]
There is no given reason as to how or why the war broke out. In-game, the European Union and the United States fight China and the MEC. It is mentioned in-game that the US and EU are allies and the EU has negotiated a truce with Russia, but it is unknown if China and the MEC are allies. The game also takes place in different fronts, as the Middle East and China are being invaded by US and EU forces, and the United States is being invaded by Chinese and MEC forces.
Additional content[edit]
Battlefield 2: Special Forces[edit]
| Battlefield 2: Special Forces | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Developer(s) | Digital Illusions Canada |
| Publisher(s) | Electronic Arts |
| Engine | Refractor 2 |
| Platform(s) | Microsoft Windows |
| Release |
|
| Genre(s) | First-person shooter |
| Mode(s) | Single-player, Multiplayer |
Battlefield 2's first expansion pack, Special Forces, first began its development sometime during or shortly before the release of the original Battlefield 2, and was worked on by DICE's Canadian division.[20] Battlefield producer, Mike Doran, commented in August 2005 that "The truth is that work on Battlefield 2: Special Forces began several months ago."[21] It was officially announced on July 14, 2005 and released on November 21 of the same year.[22][23] The focus of the development was infantry-based combat as opposed to vehicle-centric combat from the original. As such, most of the additional content in the expansion pack can only be used by or for infantry.
The expansion pack provides eight maps, 6 playable factions, and ten more vehicles such as the AH-64D Apache and Mi-35 Hind, though all jets have been removed. In addition to these new contents, players have access to new equipment such as night vision goggles, tear gas, gas masks, zip lines and grappling hooks which can alter gameplay. There are eight more small arms weapons available such as the G36K/E and FN SCAR L/H and several weapons from the original are replaced. The expansion offers more awards in the form of badges, ribbons, and medals that players can earn.[24] Finally, many of the weapons from the expansion may be used in the original Battlefield 2.
Booster packs[edit]
| Battlefield 2: Booster Pack Collection | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Developer(s) | Digital Illusions Canada |
| Publisher(s) | Electronic Arts |
| Engine | Refractor 2 |
| Platform(s) | Microsoft Windows |
| Release | November 20, 2006[citation needed] |
| Genre(s) | First-person shooter |
| Mode(s) | Single-player, Multiplayer |
Booster packs are additional content released for Battlefield 2 that are currently available for free download, and as with Special Forces, they were developed by DICE Canada.[25] The booster packs were later available in retail form as the Booster Pack Collection, containing a DVD which features these packs, as well as being included in "The Complete Collection", containing a DVD with both the original game and all of the expansions/booster packs.
Booster packs add a significant amount of content to the game, but are different from expansion packs because they are intended to add to the original gameplay and not stand on their own (such as Special Forces does). The booster packs include new maps, vehicles, and a new European Union faction.
The two booster packs were included free of charge in the 1.50 update released on September 1, 2009.
Euro Force[edit]
Battlefield 2: Euro Force is the first booster pack, and was released on March 14, 2006.[26] The booster pack allows players to play as a new European Union army, armed with new weapons and vehicles from the various countries of the EU. It is available for purchase online at the Electronic Arts download service, or as part of the retail Booster Pack Collection. It was scheduled for release in February, but was delayed due to a substantial number of new bugs caused by the release of patch 1.2. It features a whole new army, 4 new vehicles, 3 new maps, and 7 new weapons such as the L85A2 with AG36 GL, the FAMAS, the HK53, the HK21, and the Benelli M4. Some of the vehicles for the EU military include the Challenger 2, Eurocopter Tiger, Leopard 2A6 and the Eurofighter. The maps include 'The Great Wall of China', against the People's Liberation Army of China, where the EU army is trying to gain a strong foothold in northern China, to reinforce their American allies in the south later on. 'Operation Smoke Screen' features the EU army fighting the MEC in the Middle East for precious oil fields, and the third map, 'Taraba Quarry', where the EU army is trying to reinforce American positions in the south. Mindful of the European plans, the MEC tries to stall the EU, where the Europeans must confront their enemies because that route is the only possible path along that side of the Caspian Sea.
It was made free with patch 1.5.[27]
Armored Fury[edit]
Battlefield 2: Armored Fury is the second booster pack released for Battlefield 2 and was released on June 6, 2006.[citation needed] It added three new maps, as well as two new vehicle classes: attack jets for close air support and reconnaissance helicopters that operate as a mobile UAV. The booster pack has the USMC defending U.S. soil from invasions from the PLA and MEC. Operation Midnight Sun features the Chinese landing at the Alaskan port Valdez where they are trying to secure much needed fuel from the pipeline. Operation Road Rage is a MEC vs. USMC map, where the MEC are using US Highways to transport units to industrial areas. Operation Harvest sees the United States trying to stall the MEC en route to the capital of Washington D.C. from the northwest, being blocked in a Pennsylvania Dutch farm, while waiting for reinforcements. New vehicles include Attack or Close Air Support aircraft such as the A-10 Thunderbolt II, Su-39 and the Nanchang Q-5 as well as new light utility helicopters such as MH-6 Little Bird, EC-635 and the Z-11. As well as the addition of new helicopters and planes, DICE also added the Muscle Car and Semi Truck. However, the proposed AV-8B Harrier was cut from the add-on due to balancing issues.[28]
Like Euro Force, it was made free with patch 1.5.[27]
Soundtrack[edit]
The soundtrack of Battlefield 2 consists of 18 tracks composed and created by Fredrik Englund, David Tallroth, and Jonas Östholm.[29][30]
Reception[edit]
| Aggregator | Score |
|---|---|
| Metacritic | 91/100[31] |
| Publication | Score | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GameSpot | 9.3/10[4] | ||||||||||||||||||
| GameSpy | <
Outline 2Outline 2 theme by Barrie Download: outline2.p3t
P3T Unpacker v0.12 This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit! Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip Instructions: Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme. The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract. The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following: XBlueXBlue theme by wojnar Download: XBlue.p3t
P3T Unpacker v0.12 This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit! Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip Instructions: Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme. The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract. The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following: ChromeChrome theme by RaKooN Download: Chrome.p3t
Chrome may refer to: Materials[edit]
Computing[edit]
Gaming[edit]
Literature[edit]
Music[edit]
Albums[edit]
Songs[edit]
Places[edit]
Other uses[edit]
See also[edit]
Red BlackRed Black theme by LeX Download: RedBlack.p3t
P3T Unpacker v0.12 This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit! Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip Instructions: Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme. The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract. The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following: Grand Turismo HDGrand Turismo HD theme by MetalHaze Download: GTHD.p3t
P3T Unpacker v0.12 This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit! Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip Instructions: Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme. The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract. The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following: OutlineOutline theme by Barrie Download: outline.p3t
Look up outline in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Outline or outlining may refer to:
Media[edit]
See also[edit]
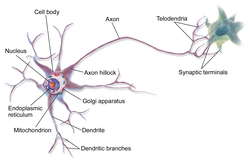
OniCrystalNeuronNeuron theme by opy01 Download: Neuron.p3t
Within a nervous system, a neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and Placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually gained new gene modules which enabled cells to create post-synaptic scaffolds and ion channels that generate fast electrical signals. The ability to generate electric signals was a key innovation in the evolution of the nervous system.[1] Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions[2] to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are functionally connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. Neurons are special cells which are made up of some structures that are common to all other eukaryotic cells such as the cell body (soma), a nucleus, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other cellular components.[3] Additionally, neurons have other unique structures such as dendrites, and a single axon.[3] The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dendrites are filaments extruding from the soma. Dendrites typically branch profusely and extend a few hundred micrometers from the soma. The axon leaves the soma at a swelling called the axon hillock and travels for as far as 1 meter in humans or more in other species. It branches but usually maintains a constant diameter. At the farthest tip of the axon's branches are axon terminals, where the neuron can transmit a signal across the synapse to another cell. Neurons may lack dendrites or have no axon. The term neurite is used to describe either a dendrite or an axon, particularly when the cell is undifferentiated. Most neurons receive signals via the dendrites and soma and send out signals down the axon. At the majority of synapses, signals cross from the axon of one neuron to a dendrite of another. However, synapses can connect an axon to another axon or a dendrite to another dendrite. The signaling process is partly electrical and partly chemical. Neurons are electrically excitable, due to maintenance of voltage gradients across their membranes. If the voltage changes by a large enough amount over a short interval, the neuron generates an all-or-nothing electrochemical pulse called an action potential. This potential travels rapidly along the axon and activates synaptic connections as it reaches them. Synaptic signals may be excitatory or inhibitory, increasing or reducing the net voltage that reaches the soma. In most cases, neurons are generated by neural stem cells during brain development and childhood. Neurogenesis largely ceases during adulthood in most areas of the brain. Nervous system[edit]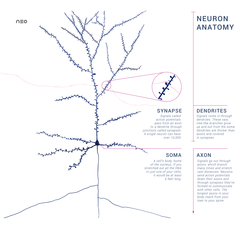 Neurons are the primary components of the nervous system, along with the glial cells that give them structural and metabolic support.[4] The nervous system is made up of the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which includes the autonomic, enteric and somatic nervous systems.[5] In vertebrates, the majority of neurons belong to the central nervous system, but some reside in peripheral ganglia, and many sensory neurons are situated in sensory organs such as the retina and cochlea. Axons may bundle into fascicles that make up the nerves in the peripheral nervous system (like strands of wire make up cables). Bundles of axons in the central nervous system are called tracts. Anatomy and histology[edit]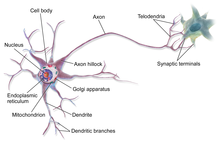 Neurons are highly specialized for the processing and transmission of cellular signals. Given their diversity of functions performed in different parts of the nervous system, there is a wide variety in their shape, size, and electrochemical properties. For instance, the soma of a neuron can vary from 4 to 100 micrometers in diameter.[6]
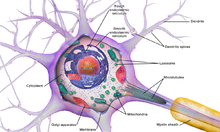 The accepted view of the neuron attributes dedicated functions to its various anatomical components; however, dendrites and axons often act in ways contrary to their so-called main function.[8] 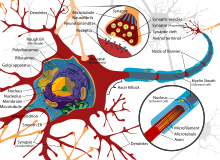 Axons and dendrites in the central nervous system are typically only about one micrometer thick, while some in the peripheral nervous system are much thicker. The soma is usually about 10–25 micrometers in diameter and often is not much larger than the cell nucleus it contains. The longest axon of a human motor neuron can be over a meter long, reaching from the base of the spine to the toes. Sensory neurons can have axons that run from the toes to the posterior column of the spinal cord, over 1.5 meters in adults. Giraffes have single axons several meters in length running along the entire length of their necks. Much of what is known about axonal function comes from studying the squid giant axon, an ideal experimental preparation because of its relatively immense size (0.5–1 millimeter thick, several centimeters long). Fully differentiated neurons are permanently postmitotic[9] however, stem cells present in the adult brain may regenerate functional neurons throughout the life of an organism (see neurogenesis). Astrocytes are star-shaped glial cells. They have been observed to turn into neurons by virtue of their stem cell-like characteristic of pluripotency. Membrane[edit]Like all animal cells, the cell body of every neuron is enclosed by a plasma membrane, a bilayer of lipid molecules with many types of protein structures embedded in it.[10] A lipid bilayer is a powerful electrical insulator, but in neurons, many of the protein structures embedded in the membrane are electrically active. These include ion channels that permit electrically charged ions to flow across the membrane and ion pumps that chemically transport ions from one side of the membrane to the other. Most ion channels are permeable only to specific types of ions. Some ion channels are voltage gated, meaning that they can be switched between open and closed states by altering the voltage difference across the membrane. Others are chemically gated, meaning that they can be switched between open and closed states by interactions with chemicals that diffuse through the extracellular fluid. The ion materials include sodium, potassium, chloride, and calcium. The interactions between ion channels and ion pumps produce a voltage difference across the membrane, typically a bit less than 1/10 of a volt at baseline. This voltage has two functions: first, it provides a power source for an assortment of voltage-dependent protein machinery that is embedded in the membrane; second, it provides a basis for electrical signal transmission between different parts of the membrane. Histology and internal structure[edit]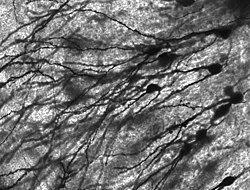  Numerous microscopic clumps called Nissl bodies (or Nissl substance) are seen when nerve cell bodies are stained with a basophilic ("base-loving") dye. These structures consist of rough endoplasmic reticulum and associated ribosomal RNA. Named after German psychiatrist and neuropathologist Franz Nissl (1860–1919), they are involved in protein synthesis and their prominence can be explained by the fact that nerve cells are very metabolically active. Basophilic dyes such as aniline or (weakly) haematoxylin[11] highlight negatively charged components, and so bind to the phosphate backbone of the ribosomal RNA. The cell body of a neuron is supported by a complex mesh of structural proteins called neurofilaments, which together with neurotubules (neuronal microtubules) are assembled into larger neurofibrils.[12] Some neurons also contain pigment granules, such as neuromelanin (a brownish-black pigment that is byproduct of synthesis of catecholamines), and lipofuscin (a yellowish-brown pigment), both of which accumulate with age.[13][14][15] Other structural proteins that are important for neuronal function are actin and the tubulin of microtubules. Class III β-tubulin is found almost exclusively in neurons. Actin is predominately found at the tips of axons and dendrites during neuronal development. There the actin dynamics can be modulated via an interplay with microtubule.[16] There are different internal structural characteristics between axons and dendrites. Typical axons almost never contain ribosomes, except some in the initial segment. Dendrites contain granular endoplasmic reticulum or ribosomes, in diminishing amounts as the distance from the cell body increases. Classification[edit]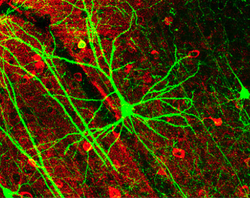 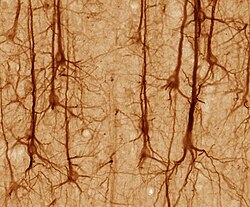 Neurons vary in shape and size and can be classified by their morphology and function.[18] The anatomist Camillo Golgi grouped neurons into two types; type I with long axons used to move signals over long distances and type II with short axons, which can often be confused with dendrites. Type I cells can be further classified by the location of the soma. The basic morphology of type I neurons, represented by spinal motor neurons, consists of a cell body called the soma and a long thin axon covered by a myelin sheath. The dendritic tree wraps around the cell body and receives signals from other neurons. The end of the axon has branching axon terminals that release neurotransmitters into a gap called the synaptic cleft between the terminals and the dendrites of the next neuron.[citation needed] Structural classification[edit]Polarity[edit]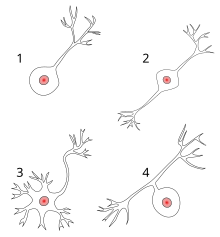 1 Unipolar neuron 2 Bipolar neuron 3 Multipolar neuron 4 Pseudounipolar neuron Most neurons can be anatomically characterized as:[19]
Other[edit]Some unique neuronal types can be identified according to their location in the nervous system and distinct shape. Some examples are:[citation needed]
Functional classification[edit]Direction[edit]
Afferent and efferent also refer generally to neurons that, respectively, bring information to or send information from the brain. Action on other neurons[edit]A neuron affects other neurons by releasing a neurotransmitter that binds to chemical receptors. The effect upon the postsynaptic neuron is determined by the type of receptor that is activated, not by the presynaptic neuron or by the neurotransmitter. A neurotransmitter can be thought of as a key, and a receptor as a lock: the same neurotransmitter can activate multiple types of receptors. Receptors can be classified broadly as excitatory (causing an increase in firing rate), inhibitory (causing a decrease in firing rate), or modulatory (causing long-lasting effects not directly related to firing rate).[citation needed] The two most common (90%+) neurotransmitters in the brain, glutamate and GABA, have largely consistent actions. Glutamate acts on several types of receptors, and has effects that are excitatory at ionotropic receptors and a modulatory effect at metabotropic receptors. Similarly, GABA acts on several types of receptors, but all of them have inhibitory effects (in adult animals, at least). Because of this consistency, it is common for neuroscientists to refer to cells that release glutamate as "excitatory neurons", and cells that release GABA as "inhibitory neurons". Some other types of neurons have consistent effects, for example, "excitatory" motor neurons in the spinal cord that release acetylcholine, and "inhibitory" spinal neurons that release glycine.[citation needed] The distinction between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters is not absolute. Rather, it depends on the class of chemical receptors present on the postsynaptic neuron. In principle, a single neuron, releasing a single neurotransmitter, can have excitatory effects on some targets, inhibitory effects on others, and modulatory effects on others still. For example, photoreceptor cells in the retina constantly release the neurotransmitter glutamate in the absence of light. So-called OFF bipolar cells are, like most neurons, excited by the released glutamate. However, neighboring target neurons called ON bipolar cells are instead inhibited by glutamate, because they lack typical ionotropic glutamate receptors and instead express a class of inhibitory metabotropic glutamate receptors.[20] When light is present, the photoreceptors cease releasing glutamate, which relieves the ON bipolar cells from inhibition, activating them; this simultaneously removes the excitation from the OFF bipolar cells, silencing them.[citation needed] It is possible to identify the type of inhibitory effect a presynaptic neuron will have on a postsynaptic neuron, based on the proteins the presynaptic neuron expresses. Parvalbumin-expressing neurons typically dampen the output signal of the postsynaptic neuron in the visual cortex, whereas somatostatin-expressing neurons typically block dendritic inputs to the postsynaptic neuron.[21] Discharge patterns[edit]Neurons have intrinsic electroresponsive properties like intrinsic transmembrane voltage oscillatory patterns.[22] So neurons can be classified according to their electrophysiological characteristics:
Neurotransmitter[edit]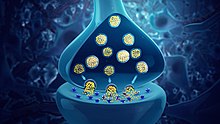 Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers passed from one neuron to another neuron or to a muscle cell or gland cell.
RAWR | ||||||||||||||||||