Tiger theme by Jennifer Hoffman
Download: Tiger.p3t

(1 background)
| Tiger Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| A Bengal tigress in Kanha Tiger Reserve, India | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Subfamily: | Pantherinae |
| Genus: | Panthera |
| Species: | P. tigris
|
| Binomial name | |
| Panthera tigris | |
| Subspecies | |

| |
| Tiger distribution as of 2022 | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
The tiger (Panthera tigris) is a member of the genus Panthera and the largest living cat species native to Asia. It has a powerful, muscular body with a large head and paws, a long tail, and orange fur with black, mostly vertical stripes. It is traditionally classified into nine recent subspecies, though some recognise only two subspecies, mainland Asian tigers and island tigers of the Sunda Islands.
Throughout the tiger's range, it inhabits mainly forests, from coniferous and temperate broadleaf and mixed forests in the Russian Far East and Northeast China to tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests on the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. The tiger is an apex predator and preys mainly on ungulates such as deer and wild boar, which it takes by ambush. It lives a mostly solitary life and occupies home ranges, which it defends from individuals of the same sex. The range of a male tiger overlaps with that of multiple females with whom he mates. Females give birth to usually two or three cubs that stay with their mother for about two years. When becoming independent, they leave their mother's home range and establish their own.
Since the early 20th century, tiger populations have lost at least 93% of their historic range and are locally extinct in West and Central Asia, in large areas of China, and on the islands of Java and Bali. Today, the tiger's range is severely fragmented. It is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, as its range is thought to have declined by 53% to 68% since the late 1990s. Major reasons for this decline are habitat destruction and fragmentation due to deforestation, poaching for fur, and the illegal trade of tiger body parts for medicinal purposes. Tigers are also victims of human–wildlife conflict as they attack and prey on livestock in areas where natural prey is scarce.
The tiger is legally protected in all range countries. National conservation measures consist of action plans, anti-poaching patrols and schemes for monitoring tiger populations. In several range countries, wildlife corridors have been established and tiger reintroduction is planned..
The tiger is among the most popular of the world's charismatic megafauna. It has been kept in captivity since ancient times and has been trained to perform in circuses and other entertainment shows. The tiger featured prominently in the ancient mythology and folklore of cultures throughout its historic range and has continued to appear in culture worldwide.
Etymology[edit]
The Old English tigras derives from Old French tigre, from Latin tigris, which was a borrowing from Classical Greek τίγρις 'tigris'.[4] Since ancient times, the word tigris has been suggested to originate from the Armenian or Persian word for 'arrow', which may also be the origin of the name for the river Tigris.[5][6] However, today, the connection between the animal and the river is doubted, and they are likely to be homonyms.[6]
Taxonomy[edit]
In 1758, Carl Linnaeus described the tiger in his work Systema Naturae and gave it the scientific name Felis tigris, as the genus Felis was being used for all cats at the time. His scientific description was based on descriptions by earlier naturalists such as Conrad Gessner and Ulisse Aldrovandi.[2] In 1929, Reginald Innes Pocock subordinated the species under the genus Panthera using the scientific name Panthera tigris.[7][8]
Subspecies[edit]
Nine recent tiger subspecies have been proposed between the early 19th and early 21st centuries, the Bengal, Malayan, Indochinese, South China, Siberian, Caspian, Javan, Bali and Sumatran tigers.[9][10] The validity of several tiger subspecies was questioned in 1999 as most putative subspecies were distinguished on the basis of fur length and colouration, striping patterns and body size of specimens in natural history museum collections that are not necessarily representative for the entire population, it was proposed to recognise only two tiger subspecies as valid, namely P. t. tigris in mainland Asia and the smaller P. t. sondaica in the Greater Sunda Islands.[11]
This two-subspecies proposal was reaffirmed in 2015 through a comprehensive analysis of morphological, ecological, and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) traits of all putative tiger subspecies. The continental nominate subspecies P. t. tigris constitutes two clades: a northern clade composed of the Siberian and Caspian tiger populations, and a southern clade composed of all other mainland populations.[10] In 2017, the Cat Classification Task Force of the IUCN Cat Specialist Group revised felid taxonomy in accordance with the 2015 two-subspecies proposal and recognised only P. t. tigris and P. t. sondaica.[12] Results of a 2018 whole-genome sequencing study of 32 samples from the six living putative subspecies—the Bengal, Malayan, Indochinese, South China, Siberian and Sumatran tiger—found them to be distinct and separate clades.[13] These results were corroborated in 2021 and 2023.[14][15] The Cat Specialist Group states that "Given the varied interpretations of data, the [subspecific] taxonomy of this species is currently under review by the IUCN SSC Cat Specialist Group."[16]
The following tables are based on the classification of the tiger as of 2005,[9] and also reflect the classification recognised by the Cat Classification Task Force in 2017.[12]
| Population | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Bengal tiger formerly P. t. tigris (Linnaeus, 1758)[2] | This population inhabits the Indian subcontinent.[17] The Bengal tiger has shorter fur than tigers further north,[8] with a light tawny to orange-red colouration,[8][18] and relatively long and narrow nostrils.[19] | 
|
| †Caspian tiger formerly P. t. virgata (Illiger, 1815)[20] | This population occurred from Turkey to around the Caspian Sea.[17] It had bright rusty-red fur with thin and closely spaced brownish stripes,[21] and a broad occipital bone.[11] Genetic analysis revealed that it was closely related to the Siberian tiger.[22] It has been extinct since the 1970s.[23] | 
|
| Siberian tiger formerly P. t. altaica (Temminck, 1844)[24] | This population lives in the Russian Far East, Northeast China and possibly North Korea.[17] The Siberian tiger has long hair and dense fur.[24] Its ground colour varies widely from ochre-yellow in winter to more reddish and vibrant after moulting.[25] The skull is shorter and broader than the skulls of tigers further south.[19] | 
|
| South China tiger formerly P. t. amoyensis (Hilzheimer, 1905)[26] | This tiger historically lived in south-central China.[17] The skulls of the five type specimens had shorter carnassials and molars than tigers from India, a smaller cranium, orbits set closer together and larger postorbital processes; skins were yellowish with rhombus-like stripes.[26] It has a unique mtDNA haplotype due to interbreeding with ancient tiger lineages.[12][27][28] It is extinct in the wild as there has not been a confirmed sighting since the 1970s,[1] and survives only in captivity.[15] | 
|
| Indochinese tiger formerly P. t. corbetti (Mazák, 1968)[29] | This tiger population occurs on the Indochinese Peninsula.[17] Indochinese tiger specimens are smaller with smaller skulls than specimens from India and appear to have darker fur with slightly narrower stripes.[29][30] | 
|
| Malayan tiger formerly P. t. jacksoni (Luo et al., 2004)[31] | The Malayan tiger was proposed as a distinct subspecies on the basis of mtDNA and micro-satellite sequences that differ from the Indochinese tiger.[31] It does not differ significantly in fur colour or skull size from Indochinese tigers.[30] There is no clear geographical barrier between tiger populations in northern Malaysia and southern Thailand.[1] | 
|
| Population | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| †Javan tiger formerly P. t. sondaica (Temminck, 1944)[24] | This tiger was described based on an unspecified number of skins with short and smooth hair.[24] Tigers from Java were small compared to tigers of the Asian mainland, had relatively elongated skulls compared to the Sumatran tiger, and longer, thinner and more numerous stripes.[30] The Javan tiger is thought to have gone extinct by the 1980s.[23] | 
|
| †Bali tiger formerly P. t. balica (Schwarz, 1912)[32] | This tiger occurred on Bali and had brighter fur and a smaller skull than the Javan tiger.[32][33] A typical feature of Bali tiger skulls is the narrow occipital bone, which is similar to the Javan tiger's skull.[34] The tiger went extinct in the 1940s.[23] | 
|
| Sumatran tiger formerly P. t. sumatrae (Pocock, 1929)[35] | The type specimen from Sumatra had dark fur.[35] The Sumatran tiger has particularly long hair around the face,[17] thick body stripes,[30] and a broader and smaller nasal bone than other island tigers.[30][19] | 
|
Evolution[edit]
| Phylogeny of the Panthera based on nuclear DNA[36] |
The tiger shares the genus Panthera with the lion, leopard, jaguar and snow leopard. Results of genetic analyses indicate that the tiger and snow leopard are sister species whose lineages split from each other between 2.70 and 3.70 million years ago.[37] The tiger's whole genome sequencing shows repeated sequences that parallel those in other cat genomes.[38]
The fossil species Panthera palaeosinensis of early Pleistocene northern China was described as a possible tiger ancestor when it was discovered in 1924, but modern cladistics places it as basal to modern Panthera.[39][40] Panthera zdanskyi, which lived around the same time and place, was suggested to be a sister species of the modern tiger when it was examined in 2014.[40] However, as of 2023, at least two subsequent studies considered P. zdanskyi likely to be a synonym of P. palaeosinensis, noting that its proposed differences from that species fell within the range of individual variation.[41][42] The earliest appearance of the modern tiger species in the fossil record are jaw fragments from Lantion in China that are dated to the early Pleistocene.[40]
Middle- to late-Pleistocene tiger fossils have been found throughout China, Sumatra and Java. Prehistoric subspecies include Panthera tigris trinilensis and P. t. soloensis of Java and Sumatra, and P. t. acutidens of China; late Pleistocene and early Holocene fossils of tigers have also been found in
Blu-Attraction theme by tsoun-net Download: Blu-Attraction.p3t P3T Unpacker v0.12 This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit! Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip Instructions: Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme. The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract. The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following: Germany theme by Elliott Download: Germany.p3t
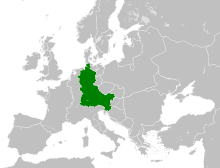
– in Europe (light green & dark grey) Germany,[e] officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),[f] is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its 16 constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of 357,600 km2 (138,100 sq mi). It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and Czechia to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr.
Settlement in what is now Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th century, northern German regions became the centre of the Protestant Reformation. Following the Napoleonic Wars and the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the German Confederation was formed in 1815.
Formal unification of Germany into the modern nation-state commenced on 18 August 1866 with the North German Confederation Treaty establishing the Prussia-led North German Confederation later transformed in 1871 into the German Empire. After World War I and the German Revolution of 1918–1919, the Empire was in turn transformed into the Weimar Republic. The Nazi seizure of power in 1933 led to the establishment of a totalitarian dictatorship, World War II, and the Holocaust. After the end of World War II in Europe and a period of Allied occupation, in 1949, Germany as a whole was organized into two separate polities with limited sovereignty: the Federal Republic of Germany, generally known as West Germany, and the German Democratic Republic, known as East Germany, while Berlin continued its de jure Four Power status. The Federal Republic of Germany was a founding member of the European Economic Community and the European Union, while the German Democratic Republic was a communist Eastern Bloc state and member of the Warsaw Pact. After the fall of the communist led-government in East Germany, German reunification saw the former East German states join the Federal Republic of Germany on 3 October 1990.
Germany has been described as a great power with a strong economy; it has the largest economy in Europe. As a global power in industrial, scientific and technological sectors, it is both the world's third-largest exporter and importer. As a developed country it offers social security, a universal health care system, and tuition-free university education. Germany is a member of the United Nations, Council of Europe, NATO, OECD and a founding member of the European Union, G7, and G20. It has the third-greatest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
The English word Germany derives from the Latin Germania, which came into use after Julius Caesar adopted it for the peoples east of the Rhine.[13] The German term Deutschland, originally diutisciu land ('the German lands') is derived from deutsch (cf. Dutch), descended from Old High German diutisc 'of the people' (from diot or diota 'people'), originally used to distinguish the language of the common people from Latin and its Romance descendants. This in turn descends from Proto-Germanic *þiudiskaz 'of the people' (see also the Latinised form Theodiscus), derived from *þeudō, descended from Proto-Indo-European *tewtéh₂- 'people', from which the word Teutons also originates.[14]
Pre-human ancestors, the Danuvius guggenmosi, who were present in Germany over 11 million years ago, are theorized to be among the earliest ones to walk on two legs.[15] Ancient humans were present in Germany at least 600,000 years ago.[16] The first non-modern human fossil (the Neanderthal) was discovered in the Neander Valley.[17] Similarly dated evidence of modern humans has been found in the Swabian Jura, including 42,000-year-old flutes which are the oldest musical instruments ever found,[18] the 40,000-year-old Lion Man,[19] and the 41,000-year-old Venus of Hohle Fels.[20][21] The Nebra sky disk, created during the European Bronze Age, has been attributed to a German site.[22]
The Germanic peoples are thought to date from the Nordic Bronze Age, early Iron Age, or the Jastorf culture.[23][24] From southern Scandinavia and northern Germany, they expanded south, east, and west, coming into contact with the Celtic, Iranian, Baltic, and Slavic tribes.[25]
Under Augustus, the Roman Empire began to invade lands inhabited by the Germanic tribes, creating a short-lived Roman province of Germania between the Rhine and Elbe rivers. In 9 AD, three Roman legions were defeated by Arminius in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest.[26] The outcome of this battle dissuaded the Romans from their ambition of conquering Germania, and is thus considered one of the most important events in European history.[27] By 100 AD, when Tacitus wrote Germania, Germanic tribes had settled along the Rhine and the Danube (the Limes Germanicus), occupying most of modern Germany. However, Baden-Württemberg, southern Bavaria, southern Hesse and the western Rhineland had been incorporated into Roman provinces.[28][29][30]
Around 260, Germanic peoples broke into Roman-controlled lands.[31] After the invasion of the Huns in 375, and with the decline of Rome from 395, Germanic tribes moved farther southwest: the Franks established the Frankish Kingdom and pushed east to subjugate Saxony and Bavaria, and areas of what is today eastern Germany were inhabited by Western Slavic tribes.[28]
City Views theme by Nvrends Download: CityViews.p3t P3T Unpacker v0.12 This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit! Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip Instructions: Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme. The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract. The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following: Summer Days theme by Rameez Yousefi (Dagobert) Download: SummerDays.p3t Summer Days is an erotic visual novel developed by 0verflow, released on June 23, 2006, for Microsoft Windows and later ported as a DVD game and for the PlayStation Portable (PSP). It is the second installation of School Days line of series, succeeding the visual novel of the same name and preceding Cross Days. Unlike the previous titles, that exist in the same continuity however, Summer Days is a spin-off of the original story retold from the perspective of Setsuna Kiyoura, a high school student out for summer vacation who finds herself attracted to Makoto Itou, a classmate and fellow patron of a restaurant she eventually comes to work at. The game retains the anime-like presentation familiar to the franchise, requiring little interaction from users, engaging players through a nonlinear plot they are given opportunities to change, and concluding with an ending specific to the choices made during play.
0verflow announced work on Summer Days in October 2005 and marketed it through a promotional campaign consisting of public screenings, sale of merchandise, and a celebratory event on the day of release. In spite of the game's positive performance during this time however, Summer Days was almost universally panned for its heavily bugged state that prompted a disorganized release of large, frustrating patches and an eventual recall. On August 26, 2011, 0verflow announced that the sale of Summer Days was being discontinued and that work on Shiny Days, a modern remake, was underway. The remake was released on April 27, 2012.
Though not as generous as its predecessor, Summer Days made transitions into other media following the game's release. A comics anthology of the series was published, as was two art books of character illustrations and a light novel. The game's soundtrack was also released by Lantis.
As a visual novel, Summer Days contains extremely minimal gameplay. The game's core onscreen presentation is composed of scenes that are viewed from a mostly third-person perspective. At predetermined intervals, the game brakes, and players are presented with one to two responses or actions relevant to the scene in progress to make, or not make, on behalf of characters. Each selection branches the game's progress up that point in an alternate direction, while also causing the player's love toward a character to blossom, plateau, or diminish,[1] thus providing for a nonlinear storytelling experience. As with its predecessor being an erotic title, relationships between characters may expectedly become sexual; scenes of this kind depict French kissing, masturbation, oral sex, anal sex, sexual intercourse, ejaculation, nudity (both female and male) or combination of the six, and pixelized censors over genitals[2] (The North America release did not censor the genitals). Each route the game takes does invariably conclude at some point with an ending specific to it, thus, players who wish to watch additional endings, and notably aforementioned sex scenes, will have to play through the game more than once.[1]
Much like the other games in the franchise, Summer Days is unusual in that instead of traditionally static characters with subtitled dialogue,[3] it incorporates motion and voice, making it reminiscent of an animated series. Cinamatics naturally play on their own, and players are afforded the ability to pause, fast-forward, and even skip those they've seen before; sex scenes, additionally, become unlockable from the main menu as they are reached in the game. Progress can be saved at any time and loaded from either the main menu or during play.[1]
Limited edition copies of Summer Days were also bundled with the standalone Flash mini-game Ahoge Battle (アホ毛 バトル, Ahoge Batoru),[4] a whimsical take on School Days ending "Bloody End". Choosing from three difficulties, the player controls Sekai, who attempts to fight off Kotonoha by pressing any two configurable keys in quick session. In the case of the highest difficulty, a third is also used. If the player is able to fend off their opponent long enough to fill their end of a progress bar, the game is won and a tally of how many times each key was pressed is recorded. If the player loses, they are given a chance to continue.[5] In an identical fashion, limited edition copies of Shiny Days are expected to come bundled with Strip Battle Days (ストリップバトルデイズ, Sutorippu Batoru Deizu), a rock-paper-scissors mini-game based around the disrobing of female characters.[6]
Setsuna Kiyoura is a high school student out of school for summer vacation, enjoying the break with family and peers. When her childhood friend Sekai is bedridden with mumps and unable to attend to her part-time waitressing job, Setsuna much to her chagrin, agrees to fill in for her. Though she finds the work almost thoroughly unpleasant, from the revealing uniforms to difficult customers, Setsuna manages to overcome the challenges of the job through the encouragement of friends, particularly that of Makoto Itōu, a classmate she likes.[7]
Set in the same universe as School Days, Summer Days retells the story of the first game had it occurred during the midst of summer vacation instead of at school[8] and from the perspective of another protagonist. The game takes place in a fictional, undisclosed prefecture of Japan that spans a range of cities, particularly a coastline called Haramihama, where the game's restaurant and center of activity, Radish, is established. As such Summer Days shares the same setting with a previous 0verflow game called Summer Radish Vaction!! as well as the same characters of Setsuna and Sekai's mothers.[9]
Summer Days incorporates all but a few of the recognized cast from School Days while introducing a handful of characters that would become new to the franchise. The game focuses on the life of Setsuna Kiyoura, a character remembered for her impassive personality in School Days,[10][11] repurposed as the thoroughly more open and emotional protagonist of its sequel. A first-year high school student out for summer vacation, Setsuna lives in the fictional city of Motehara[12][13] with her mother Mai,[11][14] a restaurateur who is frequently at work, and routinely visits Sekai Saionji, her childhood friend.[11][15]
In spite of the resentment she develops for the job she later takes, Setsuna finds the restaurant a wonderful social outlet. Besides reacquainting with Sekai's mother Youko, the owner,[11][16] and a couple of meddlesome co-workers, Noan and Oruha,[11][17][18] Setsuna meets a handful of new and familiar people on the job. Her first acquaintance is with Kokoro Katsura, a cheerful pre-teen who regularly stops in before piano lessons,[11][19] Itaru Itou, a contagiously sweet little girl visiting for the summer,[11][20] and Itaru's older brother Makoto,[11][21] a classmate whom Setsuna has a crush on.
Through Makoto, Setsuna is further introduced to Otome Katou, Makoto's best friend and a member of the school's women's basketball team,[11][22] her younger sister Karen, a rambunctious antithesis with a comparatively larger bust,[11][23] and Karen's friends Futaba and Kazuha Nijou, a pair of identical twins.[11][24][25] Of the people Setsuna knows, Hikari Kuroda, a girl whose family owns a bakery known for its custard pie,[11][26] and Ai Yamagata, a bespectacled and soft-spoken classmate,[11][27] make occasional stopovers.
News about Summer Days arguably first appeared on October 1, 2005, when 0verflow posted a link to the game's then-live website on their official blog.[28] On April 1, 2006, 0verflow began a blog for the game, the first of which announced that Summer Days had been postponed from an original release in April to June 23.[29] Character profiles were added between April 9[29] to June 17.[30]
Promotion for the game began shortly after. 0verflow announced on April 26 that it would be attending Dream Party 2006, an anime convention, in Tokyo on May 4 and in Osaka on May 28,[29] selling retail copies of previous titles and Summer Days wall scrolls.[31] In addition to announcing its attendance, the company also began to sell costumes of the game's waitress uniform[32] on April 26.[33] On May 2,[30] 0verflow posted that the company would be visiting Akihabara, Osaka, Tokushima, Koriyama, Nagoya and Sapporo[34] showcasing the game and selling Summer Days phone cards.[35] Following a downloadable sample of the Summer Days limited edition DVD on May 12,[33] 0verflow released a teaser of the game on May 18.[33] The game's opening cinema was later posted for download on June 10.[36]
As Summer Days approached release, 0verflow announced on June 17[36] that it would host an autograph signing by the game's character artist, Junji Goto, from June 24 to 25 in Nagoya and Osaka respectively,[37] and that a celebratory event would be hosted at the Kyoto Kaikan Hall from 11:00am to 7:30pm on June 23.[38] Unfortunately for the company, Summer Days would not live up to its hype.
On December 1, 2006,[39] 0verflow posted that it would be attending Comic Exhibit 71, an anime convention, from December 29 to 30, selling Summer Days merchandise, such as phone cards and lanyards.[40] Following a short merchandise campaign from January 1 to January 9, 2007,[41] and the attendance of Dream Party 2007 in Osaka and Tokyo from April to May respectively,[42][43] active promotion for Summer Days effectively ended.
On June 22, 2006, the day before the game's release, 0verflow posted on their blog[36] that a patch called 1.01B, at 1.25 GB, was being distributed through file hosting sites and BitTorrent as a successor to a 1.01A[44] at 2.29GB.[45] Customers were encouraged to use BitComet and to seed the patch to others after download.[46] On June 28, having discovered that the game had been released in a heavily bugged condition, 0verflow issued an apology to its customers, stating that work on patches had begun and would be distributed to players through BitTorrent and retail outlets at no charge.[47] Players who had contacted the company would equally be sent copies of the patches in the mail.[47] Holyseal.net, a file hosting service that 0verflow had used for its patches, accounts that from June 24 to July 24, eleven additional patches, comprising 1.02B, 1.02, 1.03, 1.03B, 1.04, 1.04B, 1.05, 1.05B, 1.06, 1.07 and 1.09, totaling roughly 8.56GB, were released.[45] On October 30[48] 0verflow posted 2.01, the final patch necessary to bring the game to stable build.[49]
Two days after patch 1.06 had been posted on July 7, 2006,[50] 0verflow announced that limited edition copies of Summer Days were found to contain uncensored sex scenes, a violation of their game rating partner's policy[51] and Article 175 of the Penal Code of Japan.[52] As a result, 0verflow issued a recall of the affected games. Customers who had purchased limited edition copies were asked to contact the company via mail for replacements;[53] on October 11, 0verflow announced that renewals would be shipped out on October 27.[54] As a result of the game's unprofitable recall, a rumor surfaced that 0verflow was forced to lay off half of its company employees, reported on at least once by New-akiba.com, a Chiyoda-based online magazine for Akihabara.[55]
Summer Days was ported to two other platforms. AiCherry, an interactive movie developer, announced on January 17, 2008,[56] that it had picked up the game for development, releasing it as a DVD game on April 11.[57] PalaceGame, a UMD publisher, also published the game for the PlayStation Portable (PSP) on September 24, 2010.[58]
News alluding to a remake or sequel of Summer Days called Shiny Summer Days surfaced on August 26, 2011,[59] when 0verflow announced via their blog that support for Summer Days was being discontinued.[60] Days later on August 31,[59] the company began its first promotion for the new game, selling brand T-shirts[61] which reportedly sold out on September 16.[59] Promotions continued with the attendance of Dream Party 2011 in Tokyo on October 3, where 0verflow sold brand phone cards and ornaments, T-shirts and dakimakura cases.[62] The game's official website went live on December 1,[63] revealing the new story[64] and characters, two making first appearances.[65] A day later on December 2, 0verflow announced that retailers would begin accepting pre-orders on December 15,[63] followed by a public release of the game's opening on December 6 and a subsequent promo on December 16.[63]
On February 2, 2012, a public trial of Shiny Days was released for download.[66] Eight days later on February 10, 0verflow announced that the game had been postponed from its original launch date to sometime in late April.[67] The company followed up this announcement on March 12,[59] stating that a more specific date would be posted in the next couple of days.[68] The date change was announced on Nico Nico Douga as April 27.[69]
Shiny Days received a North American release on September 29, 2015 through JAST USA, with translation by former fan translation group Sekai Project. However, JAST USA announced that sex scenes involving the characters Kokoro and her classmate will be removed from the North American version of the game, due to the possibility of these scenes being considered child pornography, which is a federal crime in the United States.[citation needed] These scenes can be added back via a patch that was made available for download three months after the game's initial release, though. The game was JAST's first new release from the School Days franchise since their School Days HQ release in October 2012.
In a national sales ranking of bishōjo games in PCNEWS, a now-defunct online magazine, Summer Days ranked as the number one game sold for the second half of June 2006,[70] seventh most for the first half of July,[71] twenty-fifth for the second half of October,[72] before ending as the twenty-eighth and forty-eighth game for the first and second half of November.[72][73]
Getchu.com recorded similar sales. Summer Days for Windows was the number one game sold during the month of its release[74] but failed to chart any further thereafter, ranking eighth in the company for the overall year.[75]
Summer Days never transitioned into a serialized manga, though it did make it into other print. The first of these instances was a comics anthology by Junji Goto, fittingly titled Summer Days Comic Anthology, published by Comic XO on October 25, 2006.[76][77] Five days later, on October 30, Jive published two art books; The Summer Days & School Days Visual Collection and Summer Days Visual Guidebook.[76] The final publication to be made was a light novel written by Okada Ryuna, illustrated by Junji Goto, and published by Harvest Publishing under their Harvest Novels imprint on December 1.[76]
Like School Days, the original soundtrack of Summer Days was reproduced for distribution on June 23, 2006, by Lantis.[78][79] The album contains all the game's background music, all of which was composed by KIRIKO/HIKO Sound, and theme songs performed by YURIA, yozuca*, Minami Kuribayashi and Kanako Itō, totaling 31 tracks.[80]
Modern Nature theme by kriptex Download: ModernNature.p3t
Modern Nature is the 12th studio album by British rock band the Charlatans. It was released through BMG on 26 January 2015. After the release of the band's 11th studio album Who We Touch (2010), drummer Jon Brookes was diagnosed with brain cancer, and subsequently died in mid-2013. In early 2014, the band met up at their studio Big Mushroom with Jim Spencer, and began working on a new album. The sessions lasted seven months, and featured recordings from the drummers of the Verve, New Order, and Factory Floor. Described as a pop album, Modern Nature featured contributions from the High Llamas frontman Sean O'Hagan, as well as gospel vocals from Melanie Marshall and Sandra Marvin.
Preceded by the release of the singles "Talking in Tones" and "So Oh" in September and December 2014, respectively, Modern Nature was released with varying bonus tracks. The band promoted it with radio appearances, and in-store performances. To coincide with the release of the single "Come Home Baby" in February 2015, the band embarked on a UK headlining tour, their first since 2010. Over the course of the next year and a half, the band toured Japan, Europe, the United States, the UK, Australia, and at various UK festivals.
Modern Nature received generally positive reviews from music critics, some of whom commented on the album's throwback sound. The album charted at number 7 in the UK, and number 25 in Ireland.
Following the release of the Charlatans' 11th studio album Who We Touch (2010), drummer Jon Brookes was diagnosed with brain cancer while on tour in the United States; he was temporarily replaced by the Verve member Pete Salisbury, at the recommendation.[1][2][3] Brookes later re-joined the band towards the end of the year.[4] In February 2011, the band held a discussion for their next album, which they were aiming to release at some point in 2012.[5] Later in 2011, vocalist Tim Burgess started his own record label O Genesis; him and guitarist Mark Collins went on an acoustic tour; and Burgess worked on a solo album.[6][7] In mid-2012, the celebrated the 15th anniversary of their fifth studio album Tellin' Stories (1997) with two full-album performances, and a live album from one of the shows.[6] Brookes suffered from a relapse in September that same year.[4]
The band attempted to make an album, at the insistence of Brookes, however the effort was fruitless.[7] In July 2013, keyboardist Tony Rogers said the band were anticipating going into the studio to work on new songs.[8] In spite of Brookes receiving surgery that same month, Burgess announced Brookes' death in August.[4] A benefit show was held for him two months later.[9] Burgess and guitarist Mark Collins held a writing session Hastings, which resulted in several songs.[10] The band congregated at a beach house in Rye where the recorded ideas using a portable studio and drums courtesy of a mobile app.[11][12]
The band reconvened in early 2014 at their own studio Big Mushroom, and spurred on by the memories of Brookes, the band began recording in January that year.[13][3] The members intentionally wanted to make an uplifting record; some songs were worked on between Burgess and Collins, bassist Mark Blunt and Rogers, or the whole band.[14] Jim Spencer, who worked with them previously on their 2001–2008 albums, co-produced the proceedings.[9] Drummers from different bands participated in the recording sessions: Salisbury, New Order member Stephen Morris, and Factory Floor member Gabriel Gurnsey.[15] Morris and Gurnsey went into the studio to see how the band was progressing, only then to be asked to play on the recordings. Burgess expected the sessions to last three months, when in reality, they lasted seven.[3]
Musically, the sound of Modern Nature has been described as pop,[16] with elements of disco, funk, and soul.[17] Discussing the title, Burgess said he was visiting the band Grumbling Fur as they were recording song. They were in the middle of song when a book fell of a shelf and hit Burgess on the head.[3] The book turned out to be Derek Jarman's diaries, entitled Modern Nature.[7] Up to this point, they had already planned on calling it Nature as they had several songs with that as the working title.[18] Some of the upbeat songs, such as "So Oh" and "Let the Good Times Be Never Ending", were reminiscent of the pop nature of the band's seventh studio album Wonderland (2001).[19] Similarly, "So Oh" and "Come Home Baby" channel the band's early Madchester sound.[1] The High Llamas frontman Sean O'Hagan contributed orchestration throughout the album, alongside gospel vocal harmonies from Melanie Marshall and Sandra Marvin.[9][15] O'Hagan previously worked with Burgess for his solo album; Burgess made a mental note that if the Charlatans required strings, to ask O'Hagan.[3]
The opening track "Talking in Tones" initially begins as a soundscape of glitch and electronica percussion loops, before shifting into 1960s beat music, with its chorus section being reminiscent of I'm a Man" (1967) by the Spencer Davis Group.[9][15] It was the result of a jam session between Collins, who was playing drums, and Burgess, who was playing guitar.[2] Burgess came up with the title while walking from Barclays bank on Upper Street, Islington to Flashback Records on Old Street.[18] The track discusses telepathic communication, and reminded Burgess of the Tellin' Stories opening song "With No Shoes".[3][2] Collins said "So Oh" was influenced by a Barry White song, while its bassline recalled the band's stand-alone single "The Only One I Know" (1990).[20][21] Burgess wrote the song's lyrics about being in a location, figuring out how you get there, and included a reference to David Bowie.[22][23]
"Come Home Baby" utilizes a gospel choir.[24] Rogers had the verse music for it for sometime, until Burgess had a melody part for it, which he dubbed "Baby Huey" after the person of the same name.[25] The soul track "Keep Enough" talks about mourning for an absent friend.[26][27] It was the first song the band wrote after becoming a four-piece.[2] "In the Tall Grass", alongside "Let the Good Times Be Never Ending", saw the band move into disco territory.[1] The keyboard parts in the former were compared to those played by the Doors member Ray Manzarek.[9] The song's overall sparse arrangement channelled the sound of the band's sixth studio album Us and Us Only (1999).[20] Rogers wrote the music for the song while he was in Ireland.[28] The vocals and plucked guitar parts in "Emilie" was compared to In Rainbows (2007)-era Radiohead.[29]
"Let the Good Times Be Never Ending" is a cross between the music of the Doors and the 5th Dimension, with brass parts from Dexys Midnight Runners member Jim Paterson.[2][26] The song was influenced by Little Anthony and the Imperials, and was initially scrapped on three occasions.[30][31] The first idea for the song was a six-minute-long bass part that Rogers turned into two iterations, one with a Rhodes piano, and the second with a Hammond organ. Burgess, Collins and Blunt liked both versions that Rogers made.[30] The final version was made after six months' worth of attempts, with a variety of additional instrumentation, such as drum machines and Chic-esque guitar playing.[32] "I Need You to Know", alongside "Lean In", use an organ sound in the style of Noel Gallagher's High Flying Birds.[33] "Lean In" features jangly guitarwork backing vocal harmonies recalled those hard in "Strawberry Wine" (1987) by My Bloody Valentine.[9] It was the last song written for the album, with Burgess, Collins and Blunt working on the guitar parts of it until the early hours of the morning.[34]
The piano-driven baggy song "Trouble Understanding" features several different dynamics and mood changes throughout it. Halfway through the song, a guitar line is heard, which builds towards a choral section.[2][33] It was initially titled "Nature #1", and was written by Burgess with Lou Reed in mind.[35] The closing track "Lot to Say" also evoked their Madchester sound, while incorporating elements of Motown.[15] Burgess purposely wanted to end the album with a quiet track; he wrote it after moving to Norfolk when his son was born.[36] "Walk with Me" was written by Brookes while laying in a hospital bed; it incorporates a back choir, which consisted of children from that that Brookes used to teach at.[2][37] Brookes had dictated the song's lyrics three weeks prior to his death.[7] "Honesty" is an acoustic instrumental rendition of "Emilie", with a string section, while "Marauder" is a drum and keyboard-based instrumental.[37]
The Charlatans' manager sent some songs out, which received attention from several labels.[7] One of the labels, BMG, was interested in the band. Their staff member Thomas was ecstatic about the four tracks he had been shown and asked for more.[3] The music video for "Talking in Tones" was released on 23 September 2014, directed by Nik Colk Void.[38] The track was released as a single six days later; the 7" vinyl version included a remix of the same song.[39][40] On 20 October, Modern Nature was scheduled for release later in December that year.[41] The music video for "So Oh" was released on 10 November, and was filmed in Santa Marinella, Italy.[42][43] The track was released a single on 1 December; the 7" vinyl version included a Brian Jonestown Massacre remix of the same song as the B-side.[44][45] The music video for "Come Home Baby" was released on 15 January 2015.[46]
Modern Nature was made available through The Guardian's website on 21 January 2015, and eventually released through BMG five days later.[47][48] The physical deluxe edition included a bonus disc which contained "We Sleep on Borrowed Time", "Walk with Me", "As Long as You Stick by Me", and the demo "I Will Never Leave You".[49] The digital deluxe edition featured "We Sleep on Borrowed Time", "Walk with Me", alongside "Honesty" and "Marauder" as bonus tracks.[50] The Japanese edition included all of the bonus track from the physical and digital deluxe editions, alongside remixes.[51] Some vinyl versions featured the physical deluxe edition bonus tracks, while other versions featured remixes.[52][53] The artwork sees the band on a beach with the sun in the background.[54]
The album was promoted with appearances on various radio stations, and performances at record stores.[39] "Come Home Baby" was released as a single on 2 February 2015, and featured a Simon Fisher Turner remix of the same song.[55] Later that month, the band played a show at the Brooklyn Bowl to coincide with the 2015 Brit Awards.[56] The following month, the band embarked on a UK tour with Salisbury acting as their drummer. The stint marked the band's first full tour of the UK since 2010.[41] Later in the month, Modern Nature was released in the US on 24 March.[54]
In April 2015, they toured across Japan; footage from the trek was later compiled into the music video for "Let the Good Times Be Never Ending", directed by Libby Burke Wilde.[57] On 28 April, the band performed "Let the Good Times Be Never Ending" on Later... with Jools Holland.[58] In June and July, the band performed at the Latitude, Isle of Wight, Truck and Glastonbury Festivals, and played at Castlefield Bowl.[59] In September, they toured Europe, before going on a US in November, with support from the Eyelids.[60] In December, the band toured the UK again; around this trek, Modern Nature was re-issued on vinyl.[61][62] In March 2016, the band went on a tour of Australia.[63] Norman Cook remixes of "Trouble Understanding" were released on a 12" vinyl single as part of Record Store Day 2016.[64]
Modern Nature was met with generally positive reviews from music critics. At Metacritic, the album received an average score of 80, based on 16 reviews.[66] Similarly, at AnyDecentMusic?, the album had an average rating of 7.6, based on 18 reviews.[65]
musicOMH contributor Graeme Marsh found Modern Nature "[q]uite simply stunning", calling it "a must-have." He added, it was "[w]holly unexpected and majestic," with "repeated plays" that "will reward tenfold".[2] AllMusic reviewer Stephen Thomas Erlewine praised the album's "soulful undercurrents," making it sound "more unified than Who We Touch and also contemplative". He said, a lot of the record's "haziness derives from the shimmering production".[1] The Guardian writer Lanre Bakare said that, "[f]rom the saddest of starting points, the Charlatans have made a joyful eulogy – and possibly the best album of their career."[26] Drowned in Sound's Dom Gourlay wrote that the album "fuses elements of the band's past glories with a vision firmly ensconced in the future." It acted as "another prized addition to The Charlatans' already wealthy canon."[9]
Hayley Scott of Loud and Quiet referred to it as "fragile, danceable and never void of idiosyncrasies."[69] London Evening Standard critic David Smyth wrote that the record "wears its sorrows lightly .. [with] no sense that the band are tossing out one more album for old time’s sake. Despite more troubles than most, they sound rejuvenated."[27] Daily Express writer Martin Townsend said the band "return with a record that has all the vibrancy of a debut."[67] Writing for Exclaim!, Lisa Sookraj described the album as "a fluid release, a chilled-out, soulful take on the Charlatans' psychedelic sound complemented by muted horns and jazzy keys."[29] Clash's Mat Smith found that "much of this album seems to hark back to the 1970s", while in other parts of it, "the addition of dense production," plant the tracks "in an era that only now seems to be appreciated for what it produced."[15]
Modern Nature reached number 7 in the UK; their highest in 14 years since Wonderland, which reached number 2.[70] It also reached number 25 in Ireland.[71]
Puerto Rico[i] (Spanish for 'rich port'; abbreviated PR),[15] officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico,[b][j] is a Caribbean island, Commonwealth, and unincorporated territory of the United States. It is located in the northeast Caribbean Sea, approximately 1,000 miles (1,600 km) southeast of Miami, Florida, between the Dominican Republic and the U.S. Virgin Islands, and includes the eponymous main island and several smaller islands, such as Mona, Culebra, and Vieques. With roughly 3.2 million residents, it is divided into 78 municipalities, of which the most populous is the capital municipality of San Juan.[15] Spanish and English are the official languages of the executive branch of government,[17] though Spanish predominates.[18]
Puerto Rico was settled by a succession of peoples beginning 2,000 to 4,000 years ago;[19] these included the Ortoiroid, Saladoid, and Taíno. It was then colonized by Spain in 1493 following the arrival of Christopher Columbus.[15] Puerto Rico was contested by other European powers, but remained a Spanish possession for the next four centuries. An influx of African slaves and settlers primarily from the Canary Islands and Andalusia vastly changed the cultural and demographic landscape of the island. Within the Spanish Empire, Puerto Rico played a secondary but strategic role compared to wealthier colonies like Peru and New Spain.[20][21] By the late 19th century, a distinct Puerto Rican identity began to emerge, centered around a fusion of indigenous, African, and European elements.[22][23] In 1898, following the Spanish–American War, Puerto Rico was acquired by the United States.[15][24]
Puerto Ricans have been U.S. citizens since 1917, and can move freely between the island and the mainland.[25] However, when resident in the unincorporated territory of Puerto Rico, Puerto Ricans are disenfranchised at the national level, do not vote for the president or vice president,[26] and generally do not pay federal income tax.[27][28][k] In common with four other territories, Puerto Rico sends a nonvoting representative to the U.S. Congress, called a Resident Commissioner, and participates in presidential primaries; as it is not a state, Puerto Rico does not have a vote in Congress, which governs it under the Puerto Rico Federal Relations Act of 1950. Congress approved a local constitution in 1952, allowing U.S. citizens residing on the island to elect a governor. Puerto Rico's current and future political status has consistently been a matter of significant debate.[29][30]
Beginning in the mid-20th century, the U.S. government, together with the Puerto Rico Industrial Development Company, launched a series of economic projects to develop Puerto Rico into an industrial high-income economy. It is classified by the International Monetary Fund as a developed jurisdiction with an advanced, high-income economy;[31] it ranks 40th on the Human Development Index. The major sectors of Puerto Rico's economy are manufacturing (primarily pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and electronics) followed by services (namely tourism and hospitality).[32]
Puerto Rico is Spanish for "rich port".[15] Puerto Ricans often call the island Borinquen, a derivation of Borikén, its indigenous Taíno name, which is popularly said to mean "Land of the Valiant Lord".[33][34][35] The terms boricua, borinqueño, and borincano are commonly used to identify someone of Puerto Rican heritage,[36][37] and derive from Borikén and Borinquen respectively.[38] The island is also popularly known in Spanish as La Isla del Encanto, meaning "the island of enchantment".[39]
Columbus named the island San Juan Bautista, in honor of Saint John the Baptist, while the capital city was named Ciudad de Puerto Rico ("Rich Port City").[15] Eventually traders and other maritime visitors came to refer to the entire island as Puerto Rico, while San Juan became the name used for the main trading/shipping port and the capital city.[l]
The island's name was changed to Porto Rico by the United States after the Treaty of Paris of 1898.[41] The anglicized name was used by the U.S. government and private enterprises. The name was changed back to Puerto Rico in 1931 by a joint resolution in Congress introduced by Félix Córdova Dávila.[42][m][47][48][49]
The official name of the entity in Spanish is Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico ("Free Associated State of Puerto Rico"), while its official English name is Commonwealth of Puerto Rico.[15]
The history of Puerto Rico began with the settlement of the Ortoiroid people before 430 BC. At the time of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1493, the dominant indigenous culture was that of the Taínos. The Taíno people's numbers went dangerously low during the later half of the 16th century because of new infectious diseases carried by Europeans, exploitation by Spanish settlers, and warfare.[51]
Located in the northeastern Caribbean, Puerto Rico formed a key part of the Spanish Empire from the early years of the exploration, conquest and colonization of the New World. The island was a major military post during many wars between Spain and o Icicles theme by aznsushi41 Download: Icicles.p3t Redirect to:Blu-Attraction

(3 backgrounds)
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.Zen Garden
Germany

(1 background)
Anthem: "Das Lied der Deutschen"[a]
("The Song of the Germans")
– in the European Union (light green)Capital Berlin[b]
52°31′N 13°23′E / 52.517°N 13.383°EOfficial languages German[c] Demonym(s) German Government Federal parliamentary republic[4] Frank-Walter Steinmeier Olaf Scholz Legislature Bundestag, Bundesrat[d] Area 357,600 km2 (138,100 sq mi)[5] (63rd) 1.27[6] Population ![]() 84,669,326[7] (19th)
84,669,326[7] (19th)![]() 82,719,540[8]
82,719,540[8]236/km2 (611.2/sq mi) (58th) GDP (PPP) 2024 estimate ![]() $5.687 trillion[9] (5th)
$5.687 trillion[9] (5th)![]() $67,245[9] (18th)
$67,245[9] (18th)GDP (nominal) 2024 estimate ![]() $4.591 trillion[9] (3rd)
$4.591 trillion[9] (3rd)![]() $54,291[9] (19th)
$54,291[9] (19th)Gini (2022) ![]() 28.8[10]
28.8[10]
lowHDI (2022) ![]() 0.950[11]
0.950[11]
very high (7th)Currency Euro (€) (EUR) Time zone UTC+1 (CET) UTC+2 (CEST) Date format Driving side right Calling code +49 ISO 3166 code DE Internet TLD .de Etymology[edit]
History[edit]
Prehistory[edit]
Germanic tribes, Roman frontier and the Frankish Empire[edit]
East Francia and the Holy Roman Empire[edit]

City Views

(3 backgrounds)
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.Summer Days
(6 backgrounds)
Summer Days 
Genre Drama, eroge, harem Video game Developer 0verflow (Microsoft Windows)
AiCherry (DVD)
ixia (PSP)Publisher 0verflow (Windows)
AiCherry (DVD)
PalaceGame (PSP)Genre Visual novel Platform Released Light novel Written by Okada Ryuna Illustrated by Junji Goto Published by Harvest Publishing Imprint Harvest Novels Demographic Male Published December 1, 2006 Volumes 1 Gameplay[edit]

Plot[edit]
Setting[edit]
Characters[edit]
Development[edit]
Patches and recall[edit]
Ports[edit]
Remake[edit]

Sales[edit]
Media[edit]

Books and publications[edit]
Audio CD[edit]
No. Title Writer(s) Length 1. "SummerDays" Masaki Suzuki 4:20 2. "Dandelion Veil" (タンポポの綿帽子, Tanpopo no Men Boushi) Masaki Suzuki 4:16 3. "The Story Begins at the Sea" (海から始まる物語, Umi Kara Hajima Ru Monogatari) Masaki Suzuki 5:36 4. "It Clears Up After Cloudy Weather" (曇りのち晴れ, Kumori Nochi Hare) 1:45 5. "One Summer Day" 1:56 6. "One Summer Day ~Waiting for Your Call~" 1:24 7. "Sands of Twilight" (夕暮れの砂浜, Yuugure no Sunahama) 1:49 8. "Good Night" (おやすみ, Oyasumi) 1:50 9. "The Accent on Life" 1:29 10. "It's Show Time!" 1:30 11. "Festival Music" (お祭り囃子, Omatsuri Hayashi) 1:19 12. "Grove of the Village Shrine" (鎮守の森, Chinju no Mori) 2:03 13. "OBK Coming to Town" (OBK が街にやってきた, Obk ga Machi Niyattekita) 1:23 14. "Until the Day We Meet" (また会う日まで, Mata au Nichi Made) 2:24 15. "IAI Spirit" 1:33 16. "Road to Hope" (希望への道, Kibou Heno Michi) 2:13 17. "Saboritai!" (さぼりたい!) 2:06 18. "Self-righteousness" (唯我独尊, Yuigadokuson) 1:40 19. "Refuse" 1:56 20. "As Close As Possible" 2:43 21. "While Drifting..." (漂いながら..., Tadayoi Nagara...) 2:12 22. "In the Midst of Fumbling" (手探りの中で, Tesaguri no Naka de) 2:30 23. "Sweet Kiss" 1:33 24. "Surely Someday..." (きっといつか..., Kittoitsuka) 1:40 25. "Time of Trial" (試練の刻, Shiren no Koku) 1:59 26. "And Before" (そして前へ, Soshite Maehe) 1:55 27. "SummerDays ~piano arrange~" 1:52 28. "SummerDays ~music box arrange~" 1:52 29. "Knife or Saw? Part II" 2:09 30. "Knife or Saw? Part II ~Introduce~" 1:49 31. "Promise ~Girlhood's End~" (約束~Girlhood's End~, Yakusoku ~ Girlhood's End ~) HIKO 4:16 Total length: 69:02 References[edit]
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
Modern Nature

(2 backgrounds)
Modern Nature 
Studio album by Released 26 January 2015 Recorded 2014 Studio Big Mushroom Genre Pop Length 46:45 Label BMG Producer
The Charlatans chronology
Who We Touch
(2010)
Modern Nature
(2015)
Different Days
(2017)
Singles from Modern Nature
Released: 29 September 2014
Released: 1 December 2014
Released: 2 February 2015Background and production[edit]
Composition[edit]
Release[edit]
Reception[edit]
Aggregate scores Source Rating AnyDecentMusic? 7.6/10[65] Metacritic 80/100[66] Review scores Source Rating AllMusic ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() [1]
[1]Clash 7/10[15] Daily Express 4/5[67] The Daily Telegraph ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() [68]
[68]Drowned in Sound 8/10[9] Exclaim! 7/10[29] The Guardian ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() [26]
[26]London Evening Standard ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() [27]
[27]Loud and Quiet 8/10[69] musicOMH ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() [2]
[2]Track listing[edit]
![]()
Commonwealth of Puerto Rico[b]
Free Associated State of Puerto Rico
Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico (Spanish)
Nickname(s): Motto: Anthem: "La Borinqueña" (Spanish)
("The Song of Borinquen")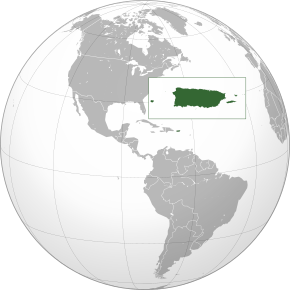
Sovereign state ![]() United States[a]
United States[a]Before annexation Captaincy General of Puerto Rico Cession from Spain 10 December 1898 Current constitution 25 July 1952 Capital San Juan
18°27′N 66°6′W / 18.450°N 66.100°WCommon languages 94.3% Spanish
5.5% English
0.2% other[2]Official languages Ethnic groups Demonym(s) Puerto Rican (Spanish: puertorriqueño -a)
boricua (neutral)[c]
borinqueño -a
borincano -a[5]
puertorro -a[d][6]Government Devolved presidential constitutional dependency Joe Biden (D) Pedro Pierluisi (PNP/D) Legislature Legislative Assembly Senate House of Representatives United States Congress Jenniffer González (PNP/R) Area 13,792 km2 (5,325 sq mi)[e][7] 8,868 km2 (3,424 sq mi) 4,924 km2 (1,901 sq mi) 35.6 Dimensions 178 km (111 mi) 65 km (40 mi) Highest elevation 1,338 m (4,390[g] ft) Population 3,205,691[h][9] (136th) 3,285,874[10] 361.4/km2 (936.0/sq mi) (41st) GDP (PPP) 2023 estimate ![]() $132.052 billion[11] (85th)
$132.052 billion[11] (85th)![]() $41,682[11] (40th)
$41,682[11] (40th)GDP (nominal) 2023 estimate ![]() $117.515 billion[11] (62nd)
$117.515 billion[11] (62nd)![]() $37,093[11] (28th)
$37,093[11] (28th)Gini (2011) 53.1[12]
highHDI (2015) 0.845[13]
very high · 40thCurrency United States dollar (US$) (USD) Time zone UTC-04:00 (AST) Date format dd/mm/yyyy
mm/dd/yyyyDriving side right Calling code +1 (787), +1 (939) USPS abbreviation ISO 3166 code Internet TLD .pr Etymology[edit]
History[edit]

Icicles

(3 backgrounds)
[[link]]s). However, do not replace these redirected links with a simpler link unless the page is updated for another reason (see WP:NOTBROKEN).












