Kevin Harvick theme by ryanindy124
Download: KevinHarvick.p3t

(6 backgrounds)
Kevin Michael Harvick (born December 8, 1975) is an American semi-retired professional stock car racing driver and commentator for NASCAR on Fox.
He last competed full-time in the NASCAR Cup Series, driving the No. 4 Ford Mustang for Stewart–Haas Racing. Harvick won the Cup Series championship in 2014 as well as the 2001 and 2006 Xfinity Series championships, and the 2007 Daytona 500. Harvick holds the all-time record for Cup Series wins at Phoenix Raceway with nine wins. Harvick's 121 combined national series wins currently rank him third all-time in NASCAR history, behind Richard Petty and Kyle Busch, respectively, while his 60 Cup wins are tenth in series history. Harvick began his NASCAR career in 1992, he is the third of only six drivers that have won a championship in both the Cup Series and the Xfinity Series, and the fifth of 36 drivers to win a race in each of NASCAR's three national series. Harvick has worked as a broadcaster off-and-on for NASCAR on FOX since 2015, calling Xfinity Series races. Since retiring from NASCAR Cup Series competition, Harvick is signed to call Cup Series races for Fox starting in 2024.
Harvick is the owner of Kevin Harvick Incorporated, a race team that fielded cars in the Xfinity Series from 2004 to 2011 and the Truck Series between 2001 and 2011. The team's No. 29 late model is driven full-time in the CARS Tour by Brent Crews, alongside the No. 62 late model which is driven by several different drivers, including Harvick himself. In the media, he has sometimes been nicknamed "the Closer" and "Happy Harvick."
Early life[edit]
Harvick was born in 1975 in Bakersfield, California, to parents Mike and JoNell (Walker) Harvick, and has a younger sister, Amber. He began kart racing at an early age, after his parents bought him a go-kart as a kindergarten graduation gift.[1] Harvick grew up a fan of IndyCar driver and fellow Bakersfield native Rick Mears, and raced go-karts with Mears' son Clint.[2] He achieved considerable success on the go-kart racing circuit, earning seven national championships and two Grand National championships.[3]
While in high school, Harvick began racing late models part-time in 1992 in the NASCAR Featherlite Southwest Series.[4] During the racing offseason, he competed on the North High School wrestling team, qualifying for a CIF Central Section title in his weight class his senior year.[5] Harvick also played baseball, basketball, football, and soccer.[4] After graduation, he attended Bakersfield College with the intention of majoring in architecture,[4] but later dropped out in order to pursue a full-time racing career.[1]
NASCAR career[edit]
Early career[edit]
Harvick made his Craftsman Truck Series debut in 1995 at the Mesa Marin Raceway, in his hometown of Bakersfield, where he started and finished 27th in his family-owned No. 72. He drove four races in the No. 72 the next season, his best finish was 11th at Mesa Marin. In 1997, he signed to drive the No. 75 for Spears Motorsports mid-season, posting two eighth-place finishes. He ran a full schedule the next season, posting 3 top-fives and finishing 17th in points. Harvick also moved up to the NASCAR Grand National Division, AutoZone West Series in 1997, and in 1998 Harvick won five races on his way to the Winston West Series championship while driving for Spears. He received his first real national exposure during the winter of 1997/1998 on ESPN2's coverage of the NASCAR Winter Heat Series at Tucson Raceway Park. In 1999, he drove the No. 98 Porter Cable Ford for Liberty Racing, finishing 12th in points with six top-fives.
1999–2000: NASCAR Busch Series[edit]
On October 23, 1999, Harvick made his first NASCAR Busch Series start in the Kmart 200 at the Rockingham Speedway in the No. 2 Chevrolet. He would start 24th and finish 42nd due to engine failure. The race would be his only start in 1999. In 2000, Harvick would sign with Richard Childress Racing to drive the No. 2 Chevrolet for his first full Busch Series season. Despite failing to qualify for the second race of the season at Rockingham, Harvick would go on to win the NASCAR Busch Series Rookie of the Year with three wins, eight top-five finishes, and 16 top-tens as well as garnering third-place points finish.
2001: Cup Series debut, replacing Earnhardt[edit]

For 2001, Childress planned to run Harvick in the No. 2 Chevy in the Busch Series full-time again, while developing him into the Winston Cup Series with up to seven races in the No. 30 Chevy. He planned to race Harvick for a full schedule in 2002. The death of Dale Earnhardt on the last lap of the 2001 Daytona 500 changed Childress's plans, and Harvick began his first Cup race the following week in the Dura Lube 400 at Rockingham, filling the seat vacated by Earnhardt's passing in the renumbered No. 29 Chevrolet.
On March 11, 2001, in the Cracker Barrel Old Country Store 500 at Atlanta Motor Speedway, only three weeks after Earnhardt's death, Harvick won his first career Winston Cup race in just his third start by narrowly edging Jeff Gordon. He won the race by only six one-thousandths of a second (.006). After the win, he paid tribute to Earnhardt, driving on the track backward with three fingers held aloft outside the driver's window as a show of honor and respect.[6] At the time, this broke the record for earliest career start for a driver to win a race in the Modern Era, since surpassed by Jamie McMurray and Trevor Bayne, both of whom accomplished the feat in their second starts, and then by Shane van Gisbergen in 2023 in his debut.
He won his second career Cup race at Chicagoland Speedway in Joliet, Illinois.[7] At the end of the season, he finished with two victories, six Top 5s, and 16 Top 10s. Harvick was awarded the NASCAR Rookie of the Year Award and secured a ninth-place finish in the 2001 points standings. He also won the Busch Series championship, becoming the first driver to win the Busch Series championship while also driving full-time in the Winston Cup Series with a Top 10 finish. Harvick would end the season winning six pole positions, and making 69 starts: 35 in Cup Series, an appearance in the Winston, 33 in the Busch Series, and one in the Craftsman Truck Series at Richmond International Raceway for Rick Carelli.
2002[edit]
In 2002, Harvick spent the season concentrating on running the Cup Series and would only start four races in the Busch Series. Harvick began the 2002 season making his first Daytona 500 start on the outside pole next to Jimmie Johnson, but his day ended after triggering an 18-car crash on lap 148 while running second to Jeff Gordon, relegating him to a 36th-place finish. Later in the season, he was fined for a post-race incident with Greg Biffle at Bristol Motor Speedway. Harvick was also suspended for rough driving in a Truck race at Martinsville, in which he announced on his radio that he intentionally spun out driver Coy Gibbs, prompting NASCAR to immediately take him out of the race. Even though it was heard on the radio that he did, Harvick lied in a post-race interview saying that he did not purposely wreck Gibbs. Harvick was banned from the Cup Series race the next day, with Kenny Wallace replacing him; he was also fined $35,000 and placed into another probation (he was already on probation for the Biffle incident).[8] Harvick rebounded and scored his first career Winston Cup pole position in the Pepsi 400 at Daytona. Later in the season, he took his third Cup win at Chicagoland Speedway. This would prove to be one of the only bright spots in a disappointing season, as he finished 21st in the 2002 points standings with one win, one pole, five Top 5s, and eight Top 10s. Harvick became the 2002 IROC Champion in his first season in the Series, winning at California Speedway. In Trucks, Harvick began fielding his own No. 6 truck, driving himself in five races and winning at Phoenix.
2003[edit]

In the 2003 season, Harvick teamed with crew chief Todd Berrier in the Cup Series, with whom he had won the Busch championship in 2001. Together, they won the Brickyard 400 at Indianapolis. Harvick and his team jumped to fifth in the 2003 point standings, coming within 252 points of Matt Kenseth. In the Busch Series, Harvick was teamed with Johnny Sauter, driving the No. 21 Hershey's-sponsored PayDay car. The two would combine for three wins, 16 Top 5s, and 24 Top 10s, with Harvick posting all three wins. They would give Childress the NASCAR Busch Series owners' championship that season. Harvick competed in 19 of the 34 races, and Sauter competed in the other 15. Harvick also scored eight pole positions and finished 16th in the final drivers' standings.
2004: First winless season[edit]
On August 28 during the 2004 Sharpie 500 at Bristol Motor Speedway, Harvick had one of the most bizarre sequences of events happen to him. On lap 323, Harvick radioed to his crew that his right arm had fallen asleep on him and had gone numb which made it difficult for him to operate his race car properly and needed a backup driver. The caution came out 5 laps later and Harvick made his way onto pit road and was pulled out of the car. He was replaced by Kyle Petty, who was involved in an earlier wreck in the same race. Petty finished 24th 6 laps down for Harvick.[9] Harvick was still able to stay 8th in points but in the last 2 regular season races at California and Richmond, Harvick would fall from 8th to 15th in the standings missing out on the inaugural Chase for the Cup. Harvick's season was also known for his conflicts with Matt Kenseth at Pocono and rookie Kasey Kahne at Phoenix.[10][11] While winless in the 2004 Cup season, Harvick placed third in the voting for Most Popular Driver. He had fourteen Top 10 finishes and finished 14th in points. Harvick was paired with another driver in the Busch Series, rookie Clint Bowyer. They combined for one win, 13 Top 5s, and 20 Top 10s in the No. 21 car, with Reese's Peanut Butter Cups as a sponsor. Harvick drove the No. 29 Busch car in the final race of the season at Homestead–Miami Speedway in the Ford 300, which he would claim his second win of the season. He finished 14th in the final standings. The No. 21 car finished fourth in the owner's standings.
2005[edit]
In the 2005 season, Harvick's only Cup win came at the Food City 500 at Bristol Motor Speedway, despite starting towards the rear of the field. He won without the assistance of crew chief Todd Berrier, who was serving a four-week suspension for a rules violation. In the Busch Series, Harvick was paired with Brandon Miller. Harvick and Miller combined for 3 wins, 15 top-fives, and 19 top-tens to give the No. 21 its second fourth-place finish in the owner's standings. Harvick would win his first "sweep" of his career at Bristol, winning both the Sharpie Professional 250 Busch race and the Food City 500 Cup race, also giving him a record fourth Busch Series win at the track (tying with Morgan Shepherd). Harvick finished 14th in the Cup series standings and 18th in the Busch series driver's standings.
2006: Second Busch Championship and first Chase appearance[edit]

In 2006, Harvick decided to run both of NASCAR's Top 2 series full-time driving for Richard Childress. In the Busch Series, Harvick would be scheduled to run all 35 races, with three different cars. He ran four races for his team in the No. 33, the season opener at Daytona in Childress' No. 29, and the remaining 30 races for RCR's No. 21. He won his first Busch Series race of the 2006 season at Nashville Superspeedway. He followed the win with a weekend sweep of the Busch Series and Sprint Cup races at Phoenix International Raceway. Harvick had nine wins, 23 Top 5s, and 32 Top 10s in the Busch Series. He clinched the 2006 NASCAR Busch Series championship on October 13, 2006, at Lowe's Motor Speedway in the Dollar General 300. It was the earliest clinch of the championship ever in the Busch Series, locking up the title with four races to go. He ended the season with a record 824-point margin in the final standings.
In the Nextel Cup series, Harvick, along with teammate Jeff Burton, scored the first berths for Richard Childress Racing in the Chase for the Cup. Harvick would have 3 wins, 11 top-5's and 14 top-10s going into the chase.

After a dominant win at New Hampshire, Harvick would have a substandard Chase run. He fell to sixth place in the point standings until he finished third at Texas. Following that was another dominating performance in the Checker Auto Parts 500 at Phoenix International Raceway on November 12. Harvick would win that race, moving him up to third in points. At the season finale at Homestead-Miami Speedway, Harvick would finish fifth in the race and slip to fourth in the final standings to eventual 2006 NASCAR Sprint Cup Series champion Jimmie Johnson.
2007: Daytona 500 win[edit]
Harvick opened the 2007 Sprint Cup series with a dramatic final lap pass in the Daytona 500, beating Mark Martin by .020 seconds in a green-white-checkered finish, the closest margin at the 500 since electronic scoring started in 1993. He would become only the fourth NASCAR driver to sweep both the Nationwide and Cup races in the opening weekend at Daytona. With the win, Harvick also became the sixth of eight drivers to win both the Daytona 500 and the Brickyard 400, following Jeff Gordon, Dale Earnhardt, Dale Jarrett, Bill Elliott, Jimmie Johnson, and preceding Jamie McMurray and Ryan Newman.[12][13] Harvick would be quiet for the remainder of the season, his only other win coming in the Sprint All-Star Race and finishing 10th in points.
In 2007, Harvick started the Nationwide Series season by winning the Orbitz 300 at Daytona, claiming his first win in a restrictor-plate race, as well as the first win for new sponsor AutoZone in NASCAR's Nationwide Series. He also won at New Hampshire International Speedway, winning the Camping World 200 presented by RVs.com. He also ended up unexpectedly winning the inaugural race at Montreal in August, the NAPA Auto Parts 200, after with two laps to go, leader Robby Gordon was black-flagged for intentionally causing a crash involving rookie Marcos Ambrose. The win was considered a bit of an upset as many expected the road course ringers to dominate and Harvick had started 43rd in the race due to a driver change.[14]
2008: Second winless season[edit]

Harvick went winless in 2008, but he was still able to post a fourth-place ranking in the 2008 Chase for the Sprint Cup. The fourth-place finish in the 2008 standings tied 2006 for his highest points position at the end of the season. Harvick also went the entire season without a single DNF for the second straight year. In the Nationwide Series, he ran twenty-two races for his team with sponsorship from Camping World, Rheem, and RoadLoans. He did not win a race in this series either. His lone win came in a Truck race at Phoenix.
2009: Third winless season[
Chelsea FC
Chelsea FC theme by DeftoneUk
Download: ChelseaFC.p3t

(8 backgrounds)
Redirect to:
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:
|
Blackburn Rovers FC
Blackburn Rovers FC theme by DeftoneUk
Download: BlackburnRoversFC.p3t

(6 backgrounds)
Redirect to:
- From a modification: This is a redirect from a modification of the target's title or a closely related title. For example, the words may be rearranged.
- Please note that there are many more specific templates. Please use {{R from alternative spelling}}, {{R from alternative hyphenation}}, {{R from alternative punctuation}}, {{R from alternative spacing}} and {{R from misquotation}} where relevant; see subcategories of Category:Redirects from modifications for other options (capitals, abbreviations, diacritics, plurals, stylizations, transliteration, ligatures, different parts of speech, etc.). If you are unsure which to use, this template is fine; someone will make it more specific later if necessary.
- In cases of modification from distinctly longer or shorter names, please use {{R from long name}} or {{R from short name}}, respectively. An abbreviation should be tagged with {{R from initialism}} or, if it can be spoken like a word such as NASA and RADAR, use {{R from acronym}}.
- Use this rcat instead of {{R from other capitalisation}} and {{R from plural}} in namespaces other than mainspace for those types of modification. This may also apply to several other subcategories of modification; please check those templates' output before saving if using outside of mainspace.
Pittsburgh Steelers #2
Pittsburgh Steelers theme by Malus
Download: PittsburghSteelers_2.p3t

(4 backgrounds)
| Pittsburgh Steelers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Established July 8, 1933[1] First season: 1933 Play in Acrisure Stadium Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Headquartered in UPMC Rooney Sports Complex Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Training camp in Latrobe, Pennsylvania | |||||
| |||||
| League/conference affiliations | |||||
National Football League (1933–present)
| |||||
Current uniform | |||||
| Team colors | Black, gold[2][3] | ||||
| Mascot | Steely McBeam | ||||
| Website | steelers.com | ||||
| Personnel | |||||
| Owner(s) | Rooney family | ||||
| President | Art Rooney II[4] | ||||
| General manager | Omar Khan | ||||
| Head coach | Mike Tomlin | ||||
| Team history | |||||
| Team nicknames | |||||
| |||||
| Championships | |||||
| League championships (6) | |||||
| Conference championships (8) | |||||
| Division championships (24) | |||||
| Playoff appearances (34) | |||||
| Home fields | |||||
Temporary stadiums 1943 due to loss of players during World War II (temporary merger with Philadelphia Eagles):
1944 due to loss of players during World War II (temporary merger with Chicago Cardinals):
| |||||
| Team owner(s) | |||||
| |||||
| Team president(s) | |||||
| |||||
The Pittsburgh Steelers are a professional American football team based in Pittsburgh. The Steelers compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the American Football Conference (AFC) North Division. Founded in 1933, the Steelers are the seventh-oldest franchise in the NFL, and the oldest franchise in the AFC.[5]
In contrast with their status as perennial also-rans in the pre-merger NFL, where they were the oldest team never to have won a league championship, the Steelers of the post-merger (modern) era are among the most successful NFL franchises, especially during their dynasty in the 1970s.[6][7][8] The team is tied with the New England Patriots for the most Super Bowl titles at six, and they have both played in (16 times) and hosted (11 times) more conference championship games than any other team in the NFL. The Steelers have also won eight AFC championships, tied with the Denver Broncos, but behind the Patriots' record 11 AFC championships. The team is tied with the Broncos and Dallas Cowboys for the second-most Super Bowl appearances with eight.
The Steelers, whose history may be traced to a regional pro team that was established in the early 1920s, joined the NFL as the Pittsburgh Pirates on July 8, 1933. The team was owned by Art Rooney and took its original name from the baseball team of the same name, as was common practice for NFL teams at the time.[5] To distinguish them from the baseball team, local media took to calling the football team the Rooneymen, an unofficial nickname that persisted for decades after the team had adopted its current nickname. The ownership of the Steelers has remained within the Rooney family since the organization's founding.[9] Art Rooney's son, Dan Rooney, owned the team from 1988 until his death in 2017. Much control of the franchise has been given to Dan Rooney's son, Art Rooney II.
The Steelers enjoy a large, widespread fanbase nicknamed Steeler Nation.[10] They currently play their home games at Acrisure Stadium on Pittsburgh's North Side in the North Shore neighborhood, which also hosts the University of Pittsburgh Panthers. Built in 2001 as Heinz Field, the stadium replaced Three Rivers Stadium, which had hosted the Steelers for 31 seasons. Prior to Three Rivers, the Steelers had played their games in Pitt Stadium and at Forbes Field.
Franchise history[edit]
Rooney family era (1933–present)[edit]
The Pittsburgh Steelers of the NFL first took to the field as the Pittsburgh Pirates on September 20, 1933, losing 23–2 to the New York Giants.[5] Through the 1930s, the Pirates never finished higher than second place in their division, or with a record better than .500 (1936).[11] Pittsburgh did make history in 1938 by signing Byron White, a future Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court, to what was at the time the biggest contract in NFL history, but he played only one year with the Pirates before signing with the Detroit Lions.[5][12] Prior to the 1940 season, the Pirates renamed themselves the Steelers.
During World War II, the Steelers experienced player shortages. They twice merged with other NFL franchises to field a team. During the 1943 season, they merged with the Philadelphia Eagles forming the "Phil-Pitt Eagles" and were known as the "Steagles". This team went 5–4–1. In 1944, they merged with the Chicago Cardinals and were known as Card-Pitt (or, mockingly, as the "Carpets").[5] This team finished 0–10, marking the only winless team in franchise history.[13]
The Steelers made the playoffs for the first time in 1947, tying for first place in the division at 8–4 with the Philadelphia Eagles. This forced a tie-breaking playoff game at Forbes Field, which the Steelers lost 21–0.[14] That would be Pittsburgh's only playoff game in the pre-merger era; they did qualify for a "Playoff Bowl" in 1962 as the second-best team in their conference, but this was not considered an official playoff.[15]
In 1970, the year they moved into Three Rivers Stadium and the year of the AFL–NFL merger, the Pittsburgh Steelers were one of three old-guard NFL teams to switch to the newly formed American Football Conference (the others being the Cleveland Browns and the Baltimore Colts), in order to equalize the number of teams in the two conferences of the newly merged league. The Steelers also received a $3 million ($23.5 million today) relocation fee, which was a windfall for them; for years they rarely had enough to build a true contending team.[16]
Chuck Noll years (1969–1991)[edit]

The Steelers' history of bad luck changed with the hiring of coach Chuck Noll from the NFL champion Baltimore Colts for the 1969 season. Noll's most remarkable talent was in his draft selections, taking Hall of Famers "Mean" Joe Greene in 1969, Terry Bradshaw and Mel Blount in 1970, Jack Ham in 1971, Franco Harris in 1972,[17] and finally, in 1974, pulling off the incredible feat of selecting five Hall of Famers in one draft year, Lynn Swann, Jack Lambert, John Stallworth, Donnie Shell and Mike Webster.[18] The Pittsburgh Steelers' 1974 draft was their best ever; no other team has ever drafted five future Hall of Famers in one year, and only very few (including the 1970 Steelers) have drafted two or more in one year.
The players drafted in the early 1970s formed the base of an NFL dynasty, making the playoffs in eight seasons and becoming the only team in NFL history to win four Super Bowls in six years, as well as the first to win more than two. They also enjoyed a regular-season streak of 49 consecutive wins (1971–1979) against teams that would finish with a losing record that year.
The Steelers suffered a rash of injuries in the 1980 season and missed the playoffs with a 9–7 record. The 1981 season was no better, with an 8–8 showing. The team was then hit with the retirements of all their key players from the Super Bowl years. "Mean" Joe Greene retired after the 1981 season, Lynn Swann and Jack Ham after 1982's playoff berth, Terry Bradshaw and Mel Blount after 1983's divisional championship, and Jack Lambert after 1984's AFC Championship Game appearance.
After those retirements, the franchise skidded to its first losing seasons since 1971. Though still competitive, the Steelers would not finish above .500 in 1985, 1986, and 1988. In 1987, the year of the players' strike, the Steelers finished with a record of 8–7, but missed the playoffs. In 1989, they would reach the second round of the playoffs on the strength of Merrill Hoge and Rod Woodson before narrowly missing the playoffs in each of the next two seasons, Noll's last seasons.
Noll's career record with Pittsburgh was 209–156–1.
Bill Cowher years (1992–2006)[edit]
In 1992, Chuck Noll retired and was succeeded by Kansas City Chiefs defensive coordinator Bill Cowher, a native of the Pittsburgh suburb of Crafton.

Cowher led the Steelers to the playoffs in each of his first six seasons, a feat that had been accomplished only by legendary coach Paul Brown of the Cleveland Browns. In those first six seasons, Cowher coached them as deep as the AFC Championship Game three times and following the 1995 season an appearance in Super Bowl XXX on the strength of the "Blitzburgh" defense. However, the Steelers lost to the Dallas Cowboys in Super Bowl XXX, two weeks after a thrilling AFC Championship victory over the Indianapolis Colts. Cowher produced the franchise's record-tying fifth Super Bowl win in Super Bowl XL over the NFC champion Seattle Seahawks ten years later. With that victory, the Steelers became the third team to win five Super Bowls, and the first sixth-seeded playoff team to reach and win the Super Bowl since the NFL expanded to a 12-team post-season tournament in 1990. He coached through the 2006 season which ended with an 8–8 record, just short of the playoffs. Overall Cowher's teams reached the playoffs 10 of 15 seasons with six AFC Championship Games, two Super Bowl berths and a championship.
Cowher's career record with Pittsburgh was 149–90–1 in the regular season and 161–99–1 overall, including playoff games.[19]
Mike Tomlin years (2007–present)[edit]

On January 7, 2007, Cowher resigned from coaching the Steelers, citing a need to spend more time with his family. He did not use the term "retire", leaving open a possible return to the NFL as coach of another team. A three-man committee consisting of Art Rooney II, Dan Rooney, and Kevin Colbert was set up to conduct interviews for the head coaching vacancy.[20] On January 22, 2007, Minnesota Vikings defensive coordinator Mike Tomlin was announced as Cowher's successor as head coach. Tomlin is the first African-American to be named head coach of the team in its 75-year history. Tomlin became the third consecutive Steelers Head Coach to go to the Super Bowl, equaling the Dallas Cowboys (Tom Landry, Jimmy Johnson and Barry Switzer) in this achievement. He was named the Motorola 2008 Coach of the Year. On February 1, 2009, Tomlin led the Steelers to their second Super Bowl of this decade, and went on to win 27–23 against the Arizona Cardinals. At age 36, he was the youngest head coach to ever win the Super Bowl, and he is only the second African-American coach to ever win the Super Bowl (Tony Dungy was the first). The 2010 season made Tomlin the only coach to reach the Super Bowl twice before the age of 40 as he took the team to Super Bowl XLV on February 6, 2011. However, the Steelers were defeated by the Green Bay Packers, 31–25. The Steelers recorded their 400th victory in 2012 after defeating the Washington Redskins.[21]
Through the end of the 2021 season, Tomlin's record is 162–94–2 (.632), including playoffs. He is the first Pittsburgh coach to never post a losing season. The 2013–17 seasons were noted for record performances from the "Killer B's". This trio consisted of Antonio Brown, Ben Roethlisberger and Le'Veon Bell. Occasionally, the "Killer B's" has also included kicker Chris Boswell due to his ability to hit game-winning field goals.
Summary[edit]
Since the NFL merger in 1970, the Pittsburgh Steelers have compiled a regular-season record of 444–282–2 (.635) and an overall record of 480-305-2 (.635) including the playoffs, reached the playoffs 30 times, won their division 22 times, played in 16 AFC championship games, and won six of eight Super Bowls. They are also the only NFL team not to have a season with 12 or more losses since the league expanded to a 16-game schedule in 1978.[22]
Ownership[edit]

Since 2008, the Rooney family has brought in several investors for the team while retaining control of the team itself. This came about so that the team could comply with NFL ownership regulations.[23] Dan Rooney, and his son, Art Rooney II, president of the franchise, wanted to stay involved with the franchise, while two of the brothers – Timothy and Patrick – wanted to further pursue racetracks that they own in Florida and New York.[24] Since 2006, many of the racetracks have added video slot machines, causing them to violate "NFL policy that prohibits involvement with racetrack and gambling interests".[25]
Upon Dan Rooney's death in 2017, he and Art Rooney II retained control of the team with the league-minimum 30%, the following made up the other investors at the time:
- Several other members of the Rooney family, including Art Rooney Jr., John Rooney, and the McGinley family, who are cousins to the Rooneys.
- The Robert A. Paul family of Pittsburgh and Los Angeles, which is primarily involved with Pittsburgh-based Ampco Pittsburgh Corporation as well as Morton's Restaurant Group, Urban Active Fitness, Meyer Products and Harley Marine Services. Additionally, family members serve on numerous boards, including Cornell University, UPMC, University of Pittsburgh, the American Red Cross, Harvard Medical School and the Loomis Chaffee School.[26]
- Former Steelers wide receiver John Stallworth, a member of the Pro Football Hall of Fame.[27]
- Legendary Pictures president and CEO Thomas Tull.[26]
- GTCR chairman Bruce V. Rauner.[27]
Millonarios
Millonarios theme by Millos
Download: Millonarios.p3t

(3 backgrounds, wallpapers HD only)
Redirect to:
AFA Argentina Soccer (Fútbol)
AFA Argentina Soccer (Fútbol) theme by Stevn M Marín (xCiRRoSiSx)
Download: AFAArgentinaSoccer.p3t

(12 backgrounds)
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop MenonThis program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.Pittsburgh Penguins
Pittsburgh Penguins theme by Malus
Download: PittsburghPenguins.p3t

(1 background)
Pittsburgh Penguins  2024–25 Pittsburgh Penguins season
2024–25 Pittsburgh Penguins season
Conference Eastern Division Metropolitan Founded 1967 History Pittsburgh Penguins
1967–presentHome arena PPG Paints Arena City Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 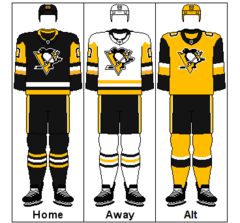
Team colors Black, Pittsburgh gold, white[1][2][3]
Media SportsNet Pittsburgh
The X (105.9 FM)
ESPN Pittsburgh (970 AM)
Pittsburgh Penguins Radio NetworkOwner(s) Fenway Sports Group
Mario Lemieux (minority)[4]General manager Kyle Dubas Head coach Mike Sullivan Captain Sidney Crosby Minor league affiliates Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Penguins (AHL)
Wheeling Nailers (ECHL)Stanley Cups 5 (1990–91, 1991–92, 2008–09, 2015–16, 2016–17) Conference championships 6 (1990–91, 1991–92, 2007–08, 2008–09, 2015–16, 2016–17) Presidents' Trophy 1 (1992–93) Division championships 9 (1990–91, 1992–93, 1993–94, 1995–96, 1997–98, 2007–08, 2012–13, 2013–14, 2020–21) Official website nhl .com /penguins The Pittsburgh Penguins (colloquially known as the Pens) are a professional ice hockey team based in Pittsburgh. The Penguins compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Metropolitan Division of the Eastern Conference, and have played their home games at PPG Paints Arena, originally known as Consol Energy Center, since 2010. The team previously played at the Civic Arena, which was also known as Mellon Arena from 1999 to 2010, and by its nickname "the Igloo". The Penguins are affiliated with two minor league teams – the Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Penguins of the American Hockey League (AHL) and the Wheeling Nailers of the ECHL.
Founded during the 1967 expansion, the Penguins have qualified for six Stanley Cup Finals, winning the Stanley Cup five times – in 1991, 1992, 2009, 2016, and 2017. Along with the Edmonton Oilers, the Penguins are tied for the most Stanley Cup championships among the non-Original Six teams and sixth overall. With their Stanley Cup wins in 2016 and 2017, the Penguins became the first back-to-back champions in the salary cap era. Several of the team's former members have been inducted into the Hockey Hall of Fame, including co-owner Mario Lemieux, who purchased the Penguins in 1999 and brought the club out of bankruptcy. Lemieux, Jaromir Jagr, Sidney Crosby, and Evgeni Malkin have won the Hart Memorial Trophy while playing for the franchise.
Team history[edit]
Early years (1967–1984)[edit]
Prior to the arrival of the Penguins, Pittsburgh had been the home of the NHL's Pittsburgh Pirates from 1925 to 1930 and of the American Hockey League's Pittsburgh Hornets franchise from 1936 to 1967 (with a short break from 1956 to 1961). In the spring of 1965, Jack McGregor, a state senator from Kittanning, Pennsylvania, began lobbying campaign contributors and community leaders to bring an NHL franchise back to Pittsburgh. The group focused on leveraging the NHL as an urban renewal tool for Pittsburgh. The senator formed a group of local investors that included H. J. Heinz Company heir H. J. Heinz III, Pittsburgh Steelers' owner Art Rooney and the Mellon family's Richard Mellon Scaife. The projected league expansion depended on securing votes from the then-current NHL owners; to ensure Pittsburgh would be selected as one of the expansion cities, McGregor enlisted Rooney to petition votes from James D. Norris, owner of the Chicago Black Hawks and his brother Bruce Norris, owner of the Detroit Red Wings. The effort was successful, and on February 8, 1966, the National Hockey League awarded an expansion team to Pittsburgh for the 1967–68 season. The Penguins paid $2.5 million ($23.8 million today) for their entry and $750,000 ($6.9 million today) more for start-up costs. The Civic Arena's capacity was boosted from 10,732 to 12,500 to meet the NHL requirements for expansion. The Pens also paid an indemnification bill to settle with the Detroit Red Wings, which owned the Pittsburgh Hornets franchise. The investor group named McGregor president and chief executive officer, and he represented Pittsburgh on the NHL's Board of Governors.[5][6]

The Civic Arena's capacity was increased to meet NHL requirements for a franchise. The arena served as the Penguins' home arena from 1967 to 2010. A contest was held where 700 of 26,000 entries picked "Penguins" as the team's nickname, sharing its nickname with the athletic department of the newly named Youngstown State University in nearby Youngstown, Ohio. (Youngstown is part of the Penguins' territorial rights to this day, though they did briefly share them with the Cleveland Barons in the mid-1970s.) Mark Peters had the winning entry (which was inspired because the team was to play in the "Igloo", the nickname of the Pittsburgh Civic Arena),[7][8] a logo was chosen that had a penguin in front of a triangle, which symbolized the "Golden Triangle" of downtown Pittsburgh.[7][9] The Penguins' first general manager, Jack Riley, opened the first pre-season camp for the franchise in Brantford, Ontario,[10] on September 13, 1967, playing the franchise's first exhibition match in Brantford against the Philadelphia Flyers on September 23, 1967. Restrictive rules which kept most major talent with the existing "Original Six" teams hampered the Pens, along with the rest of the expansion teams. Beyond aging sniper Andy Bathgate, all-star defenseman Leo Boivin (who had begun his professional career with the Hornets) and New York Rangers' veteran Earl Ingarfield, a cast of former minor leaguers largely manned the first Penguins' team. Several players played for the Hornets the previous season: Bathgate, wingers Val Fonteyne and Ab McDonald, and goaltenders Hank Bassen and Joe Daley. George Sullivan was named the head coach for the club's first two seasons, and McDonald was named the team's first captain.[11]
On October 11, 1967, league president Clarence Campbell and McGregor jointly dropped the ceremonial first puck of the Penguins' opening home game against the Montreal Canadiens.[5] On October 21, 1967, they became the first team from the expansion class to defeat an Original Six team, as they defeated the Chicago Black Hawks 4–2. However, the Penguins went 27–34–13 and finished in fifth place in the West Division, missing the playoffs and ending with the third-worst record in the league. The team's best player proved to be longtime Cleveland Barons AHL goaltender Les Binkley, who recorded a 2.88 goals-against average and was second in the league with six shutouts. Defensive winger Ken Schinkel won the team's sole league honor, being named to represent the Penguins in the NHL All-Star Game. Bathgate led the team in scoring with 59 points but retired at season's end. McDonald, who led the team in goals and was second in team scoring, was also gone at season's end, traded to the St. Louis Blues in exchange for center Lou Angotti.[6]
The next season saw the team slip in the standings amid a sharp drop in form by Binkley, into sixth place and with the league's worst record. Several changes were made to improve the team, resulting in Boivin and several others being traded, and new players—including longtime future Pens star Jean Pronovost—making their debuts. No captain was named to replace McDonald; the team went with four alternate captains.
Triumph of playoff berths and tragedy of Briere (1969–1974)[edit]

Michel Briere's number was taken out of circulation after his career-ending accident in 1970. It was later formally retired in 2001. In the 1969 draft the Penguins selected Michel Briere who, although being chosen 26th, was soon drawing comparisons to Phil Esposito and Bobby Clarke. Joining the team in November, he finished as the second-place rookie scorer in the NHL (behind Bobby Clarke) with 44 points (57th overall), and third on the Penguins. Briere placed second in Calder Memorial Trophy voting for Rookie of the Year honors behind Chicago goaltender Tony Esposito. Briere led Pittsburgh to its first NHL playoff berth since the 1928 Pirates. The Penguins defeated the Oakland Seals in a four-game sweep in the quarterfinals, with Briere scoring the series-clinching goal in overtime. In the semi-final round, defending conference champions St. Louis Blues got the best of the Penguins during six games. Briere led the team in playoff scoring, recording five goals (including three game-winners) and eight points. Tragedy struck the Penguins just days after their playoff heroics. On May 15, 1970, Briere was in a car crash in his native Quebec, suffering brain trauma and slipping into a coma from which he would never recover; he died a year later. His number 21 jersey was never reissued, remaining out of circulation until it was formally retired in 2001.[6]
In the 1970–71 season, the Penguins finished five games out of the playoffs with a 21–37–20 record, the fourth-worst record in the league. Pittsburgh achieved a playoff berth in 1972, only to be swept by the Chicago Black Hawks in the first round. Except for a handful of players like Ken Schinkel, Pronovost, Syl Apps Jr., Keith McCreary, agitator Bryan Watson and goaltender Les Binkley, talent was thin, but enough for the Penguins to reach the playoffs in both 1970 and 1972. The Penguins battled the California Golden Seals for the division cellar in 1974, when Riley was fired as general manager and replaced by Jack Button. Button obtained Steve Durbano, Ab DeMarco, Bob "Battleship" Kelly and Bob Paradise through trades. The personnel moves proved successful, and the team improved to a 28–41–9 record, although they remained nine points away from a playoff berth.
However, in early 1975, the Penguins' creditors demanded payment of back debts, forcing the team into bankruptcy. The doors to the team's offices were padlocked, and it looked like the Penguins would fold or relocate.[12] Around the same time, rumors began circulating that the Penguins and the California Golden Seals were to be relocated to Seattle and Denver respectively, the two cities that were to have been the sites of an expansion for the 1976–77 season.[13] Through the intervention of a group that included former Minnesota North Stars head coach Wren Blair, the team was prevented from folding and remained in Pittsburgh, eventually being bought by shopping mall magnate Edward J. DeBartolo, Sr.
Playoff runs and a uniform change (1974–1982)[edit]

During the mid-1970s, Lowell MacDonald was paired with Syl Apps Jr. and Jean Pronovost, forming the "Century Line". MacDonald played with the Penguins from 1970 to 1978. Beginning in the mid-1970s, Pittsburgh iced some powerful offensive clubs, led by the likes of the "Century Line" of Syl Apps, Lowell MacDonald and Jean Pronovost. They nearly reached the Stanley Cup semi-finals in 1975, but were ousted from the playoffs by the New York Islanders in one of the only four best-of-seven-game series in NHL history where a team came back from being down three games to none. As the 1970s wore on, a mediocre team defense neutralized the Penguins' success beyond the regular season. Baz Bastien, a former coach and general manager of the AHL's Hornets, later became general manager. The Penguins missed the playoffs in 1977–78. Bastien traded prime draft picks for several players whose best years were already behind them, and the team would suffer in the early 1980s as a result. The decade closed with a playoff appearance in 1979 and a rousing opening series win over the Buffalo Sabres before a second-round sweep at the hands of the Boston Bruins.[6]
The Penguins began the 1980s by changing their team colors; in January 1980, the team switched from wearing blue and white to their present-day scheme of black and gold to honor Pittsburgh's other sports teams, the Pittsburgh Pirates and the Pittsburgh Steelers, as well as the Flag of Pittsburgh. Both the Pirates and Steelers had worn black and gold for decades, and both had enjoyed world championship seasons. The Bruins protested this color change, claiming a monopoly on black and gold, but the Penguins defended their choice stating that the NHL Pirates also used black and gold as their team colors and that black and gold were Pittsburgh's traditional sporting colors. The NHL agreed, and Pittsburgh could use black and gold. The Penguins officially debuted the black and gold uniform in a game against the St. Louis Blues at the Civic Arena on January 30, 1980.[14] On the ice, the Penguins began the 1980s with defenseman Randy Carlyle, and prolific scorers Paul Gardner and Mike Bullard but little else.
During the early part of the decade, the Penguins made a habit of being a tough draw for higher-seeded opponents in the playoffs. In 1980, the 13th-seeded Penguins took the Bruins to the limit in their first-round playoff series. The following season, as the 15th seed, they lost the decisive game of their first-round series in overtime to the heavily favored St. Louis Blues. Then, in the 1982 playoffs, the Penguins held a 3–1 lead late in the fifth and final game of their playoff series against the reigning champions, the New York Islanders. However, the Islanders rallied to force overtime and won the series on a goal by John Tonelli, who had tied the game before.[15] It would be the Pens' final playoff appearance until 1989.
Lemieux–Jagr era (1984–2005)[edit]

Mario Lemieux played for the Penguins in three stints (1984–1994, 1995–1997, 2000–2006). The team had the league's worst record in both the 1982–83 and 1983–84 seasons. With the team suffering financial problems, it seemed the Penguins would either fold or relocate. Mario Lemieux, one of the most highly touted NHL draft picks in history, was due to be drafted in the 1984 NHL Entry Draft. Heading towards the end of the season ahead of the New Jersey Devils, who were placed last, the Penguins made several questionable moves that appeared to weaken the team in the short term. They posted three six-game winless streaks in the last 21 games of the season and earned the right to draft Lemieux amidst protests from Devils' management.[16] Pittsburgh head coach Lou Angotti later admitted that a conscious decision was made to finish the season as the team with the worst record, saying in an interview with the Pittsburgh Post-Gazette that a mid-season lunch prompted the plan, because there was a high chance of the franchise folding if Lemieux was not drafted.[17] Other teams offered substantial trade packages for the draft choice, but the Penguins kept the pick and drafted Lemieux first overall. Lemieux paid dividends right away, scoring on his first-ever shot of his first-ever NHL shift in his first NHL game. However, the team spent four more years out of the playoffs after his arrival. In the late 1980s, the Penguins finally gave Lemieux a strong supporting cast, trading for superstar defenseman Paul Coffey from the Edmonton Oilers (after the Oilers' 1987 Stanley Cup win) and bringing in young talent like scorers Kevin Stevens, Rob Brown and John Cullen from the minors. The team finally acquired a top-flight goaltender with the acquisition of Tom Barrasso from Buffalo. All this talent had an immediate impact in helping Lemieux lead the Pens; but the team struggled to make the playoffs. The 1985–86 Pens missed the playoffs on the final day of the season by one game. In 1986–87, they missed the playoffs by just two games and saw four teams with equal or worse records qualify. In 1987–88, for the second time in a row, the Penguins missed the playoffs by one game.[11]
In 1989, Pittsburgh finally broke through the barrier and made the playoffs on the back of Lemieux leading the league in goals, assists and points. On December 31, 1988, Lemieux became the only player in history to score a goal in all five possible game situations in the same game (even strength, shorthanded, penalty shot, power play, and empty net). The Pens shocked the New York Rangers in a four-game sweep in the first round; however, the Philadelphia Flyers halted their progress in the second round. The seven-game defeat featured Lemieux scoring five goals in the fifth game.[11]
Golden Age (1989–1997)[edit]
A herniated disc in Lemieux's back cut short his 1989–90 season, although he still amassed 123 points. However, the Penguins fell out of the playoff picture. They opted to strengthen their roster and support Lemieux in the 1990 off-season. Free-agent signings (Bryan Trottier) and trades (Joe Mullen, Larry Murphy, Ron Francis and Ulf Samuelsson) played a major part in this. Arguably no move was bigger during this time than when the Penguins drafted Jaromir Jagr with the fifth overall pick in the 1990 NHL Entry Draft. The first Czechoslovak player to be drafted into the NHL without first needing to defect to the West, Jagr became the Penguins' second franchise player, and quickly developed into a superstar offensive talent. The roster overhaul culminated in the Penguins winning their first Stanley Cup title by defeating the Minnesota North Stars in the Stanley Cup Finals in six games, punctuated by an 8–0 victory in the deciding game, the largest margin of victory in a final Stanley Cup game in over 80 years. After the 1991 Stanley Cup Finals, the Penguins met with President George H. W. Bush, the first NHL team ever to visit the White House.[18] The following season, the team lost coach Bob Johnson to cancer, and Scotty Bowman took over as coach. Under Bowman, they swept the Chicago Blackhawks to repeat as Stanley Cup champions in 1991–92.[6][11]
Cancer revisited the Penguins in 1993 when Lemieux was tragically diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma. Only two months after the diagnosis, missing 24 out of 84 games, he came back to win his fourth Art Ross Trophy as scoring champion with 160 points, edging out Pat LaFontaine and Adam Oates. Despite the off-ice difficulties, Pittsburgh finished with a 56–21–7 record, the franchise's best regular season ever, winning the Presidents' Trophy. After Lemieux's return, the team played better than it ever had before, winning an NHL-record 17 consecutive games. Despite all of this success, the New York Islanders eliminated them in the second round of Game 7 in overtime.[11][6]
The Penguins continued to be a formidable team throughout the 1990s. The stars of the Stanley Cup years were followed by the likes of forwards: Alexei Kovalev, Martin Straka, Aleksey Morozov, Robert Lang and Petr Nedved, and defensemen Sergei Zubov, Darius Kasparaitis and Kevin Hatcher. Despite the departure of many of the franchise's Stanley Cup-winning roster, the Penguins fielded enough talent to reach the first round of the playoffs in 1994 (where they lost to the Washington Capitals in six games), the second round in 1995 (where they lost to the New Jersey Devils in five games) and the conference finals in 1996 (where they lost to the Florida Panthers in seven games). The 1997 playoffs marked a turning point, as the Penguins suffered a first-round elimination at the hands of the rival Philadelphia Flyers in five games.[11]
Lemieux's retirement and return (1997–2001)[edit]

Lemieux with the Penguins during the 2000–01 season, his first season after coming out of retirement. On April 6, 1997, the franchise was rocked when Mario Lemieux, citing ongoing health concerns and his disapproval with the way NHL hockey was being officiated, announced he would retire at the conclusion of the 1997 playoffs. Lemieux was so respected in the NHL, and his achievements over the course of his career were so great, that he was inducted into the Hockey Hall of Fame in the year he retired, the three-year waiting period being waived. His departure was the first in a series of events that would once again lead the Penguins into regular season stagnation, and to the brink of financial ruin.
The Montreal Canadiens eliminated the team in the first round of the playoffs in 1998, despite being the second-seeded team in the East. The following year, their playoff run ended in the second round when they lost to the Toronto Maple Leafs in six games. In 2000, the Penguins stunned the highly touted Washington Capitals 4–1 in the first round, only to fall to the Philadelphia Flyers 4–2 in the second round.
By this time, the lofty contracts handed out during the early 1990s were catching up with the Penguins. At one point, the team owed over $90 million to numerous creditors, leading then-owners Howard Baldwin and Morris Belzberg (who bought the Penguins after their first Stanley Cup win) to ask the players to defer their salaries to help pay the bills. When the deferred salaries finally came due, combined with other financial pressures, the Penguins were forced to file for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in November 1998.
Lemieux then stepped in with an unusual proposal to buy the team out of bankruptcy. The Penguins owed Lemieux $32.5 million in deferred salary, making him the team's largest individual creditor. He proposed recovering this money by converting it into equity—enough to give him controlling interest. He also vowed to keep the team in Pittsburgh. The NHL and the courts agreed, and Lemieux (with help from supermarket tycoon Ronald Burkle) assumed control on September 3, 1999, saving the franchise for the second time.[6]
Lemieux again shocked the hockey world by announcing at a press conference on December 8, 2000, his intentions to return to the Penguins as an active player. On December 27, 2000, Lemieux stepped onto NHL ice for the first time in 44 months, officially becoming the first player–owner in NHL history. Lemieux helped lead the Penguins deep into the 2001 playoffs, highlighted by an overtime victory against the Buffalo Sabres in Game 7 of the second round. Darius Kasparaitis scored the series-clinching goal to advance the Penguins to the Eastern Conference Finals, where they lost in five games to the New Jersey Devils.[6]
Rebuilding (2001–2005)[edit]
Marc-Andre Fleury was drafted first overall in 2003 by the Penguins. The Penguins' attendance had dwindled in the late 1990s. In 19
2007 Green Bay Packers
2007 Green Bay Packers theme by Fully Rendered
Download: 2007GreenBayPackers.p3t
(3 backgrounds, HD only)
Redirect to:
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:When appropriate, protection levels are automatically sensed, described and categorized.- From a short name: This is a redirect from a title that is a shortened form of a more complete page title, such as a person's full name or the unbroken title of a written work.
- Use this rcat (not {{R from initialism}} nor {{R from abbreviation}}) to tag redirects that are the initials of a person's name.
Celtic FC
Celtic FC theme by Michael Dorrian
Download: CelticFC.p3t

(3 backgrounds)
Redirect to:
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:When appropriate, protection levels are automatically sensed, described and categorized.- From a modification: This is a redirect from a modification of the target's title or a closely related title. For example, the words may be rearranged.
- Please note that there are many more specific templates. Please use {{R from alternative spelling}}, {{R from alternative hyphenation}}, {{R from alternative punctuation}}, {{R from alternative spacing}} and {{R from misquotation}} where relevant; see subcategories of Category:Redirects from modifications for other options (capitals, abbreviations, diacritics, plurals, stylizations, transliteration, ligatures, different parts of speech, etc.). If you are unsure which to use, this template is fine; someone will make it more specific later if necessary.
- In cases of modification from distinctly longer or shorter names, please use {{R from long name}} or {{R from short name}}, respectively. An abbreviation should be tagged with {{R from initialism}} or, if it can be spoken like a word such as NASA and RADAR, use {{R from acronym}}.
- Use this rcat instead of {{R from other capitalisation}} and {{R from plural}} in namespaces other than mainspace for those types of modification. This may also apply to several other subcategories of modification; please check those templates' output before saving if using outside of mainspace.
Sporting Lisbon
- From a short name: This is a redirect from a title that is a shortened form of a more complete page title, such as a person's full name or the unbroken title of a written work.
















