World theme by JackKing
Download: World_2.p3t

The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists.[1] The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts.
In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "[t]he totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, as identical to God or as the two being interdependent. In religions, there is a tendency to downgrade the material or sensory world in favor of a spiritual world to be sought through religious practice. A comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it, as is found in religions, is known as a worldview. Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world while eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world.
In various contexts, the term "world" takes a more restricted meaning associated, for example, with the Earth and all life on it, with humanity as a whole or with an international or intercontinental scope. In this sense, world history refers to the history of humanity as a whole and world politics is the discipline of political science studying issues that transcend nations and continents. Other examples include terms such as "world religion", "world language", "world government", "world war", "world population", "world economy", or "world championship".
Etymology[edit]
The English word world comes from the Old English weorold. The Old English is a reflex of the Common Germanic *weraldiz, a compound of weraz 'man' and aldiz 'age', thus literally meaning roughly 'age of man';[2] this word led to Old Frisian warld, Old Saxon werold, Old Dutch werolt, Old High German weralt, and Old Norse verǫld.[3]
The corresponding word in Latin is mundus, literally 'clean, elegant', itself a loan translation of Greek cosmos 'orderly arrangement'. While the Germanic word thus reflects a mythological notion of a "domain of Man" (compare Midgard), presumably as opposed to the divine sphere on the one hand and the chthonic sphere of the underworld on the other, the Greco-Latin term expresses a notion of creation as an act of establishing order out of chaos.[4]
Conceptions[edit]
Different fields often work with quite different conceptions of the essential features associated with the term "world".[5][6] Some conceptions see the world as unique: there can be no more than one world. Others talk of a "plurality of worlds".[4] Some see worlds as complex things composed of many substances as their parts while others hold that worlds are simple in the sense that there is only one substance: the world as a whole.[7] Some characterize worlds in terms of objective spacetime while others define them relative to the horizon present in each experience. These different characterizations are not always exclusive: it may be possible to combine some without leading to a contradiction. Most of them agree that worlds are unified totalities.[5][6]
Monism and pluralism[edit]
Monism is a thesis about oneness: that only one thing exists in a certain sense. The denial of monism is pluralism, the thesis that, in a certain sense, more than one thing exists.[7] There are many forms of monism and pluralism, but in relation to the world as a whole, two are of special interest: existence monism/pluralism and priority monism/pluralism. Existence monism states that the world is the only concrete object there is.[7][8][9] This means that all the concrete "objects" we encounter in our daily lives, including apples, cars and ourselves, are not truly objects in a strict sense. Instead, they are just dependent aspects of the world-object.[7] Such a world-object is simple in the sense that it does not have any genuine parts. For this reason, it has also been referred to as "blobject" since it lacks an internal structure like a blob.[10] Priority monism allows that there are other concrete objects besides the world.[7] But it holds that these objects do not have the most fundamental form of existence, that they somehow depend on the existence of the world.[9][11] The corresponding forms of pluralism state that the world is complex in the sense that it is made up of concrete, independent objects.[7]
Scientific cosmology[edit]
Scientific cosmology can be defined as the science of the universe as a whole. In it, the terms "universe" and "cosmos" are usually used as synonyms for the term "world".[12] One common definition of the world/universe found in this field is as "[t]he totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be".[13][5][6] Some definitions emphasize that there are two other aspects to the universe besides spacetime: forms of energy or matter, like stars and particles, and laws of nature.[14] World-conceptions in this field differ both concerning their notion of spacetime and of the contents of spacetime. The theory of relativity plays a central role in modern cosmology and its conception of space and time. A difference from its predecessors is that it conceives space and time not as distinct dimensions but as a single four-dimensional manifold called spacetime.[15] This can be seen in special relativity in relation to the Minkowski metric, which includes both spatial and temporal components in its definition of distance.[16] General relativity goes one step further by integrating the concept of mass into the concept of spacetime as its curvature.[16] Quantum cosmology uses a classical notion of spacetime and conceives the whole world as one big wave function expressing the probability of finding particles in a given location.[17]
Theories of modality[edit]
The world-concept plays a role in many modern theories of modality, sometimes in the form of possible worlds.[18] A possible world is a complete and consistent way how things could have been.[19] The actual world is a possible world since the way things are is a way things could have been. There are many other ways things could have been besides how they actually are. For example, Hillary Clinton did not win the 2016 US election, but she could have won them. So there is a possible world in which she did. There is a vast number of possible worlds, one corresponding to each such difference, no matter how small or big, as long as no outright contradictions are introduced this way.[19]
Possible worlds are often conceived as abstract objects, for example, in terms of non-obtaining states of affairs or as maximally consistent sets of propositions.[20][21] On such a view, they can even be seen as belonging to the actual world.[22] Another way to conceive possible worlds, made famous by David Lewis, is as concrete entities.[4] On this conception, there is no important difference between the actual world and possible worlds: both are conceived as concrete, inclusive and spatiotemporally connected.[19] The only difference is that the actual world is the world we live in, while other possible worlds are not inhabited by us but by our counterparts.[23] Everything within a world is spatiotemporally connected to everything else but the different worlds do not share a common spacetime: They are spatiotemporally isolated from each other.[19] This is what makes them separate worlds.[23]
It has been suggested that, besides possible worlds, there are also impossible worlds. Possible worlds are ways things could have been, so impossible worlds are ways things could not have been.[24][25] Such worlds involve a contradiction, like a world in which Hillary Clinton both won and lost the 2016 US election. Both possible and impossible worlds have in common the idea that they are totalities of their constituents.[24][26]
Phenomenology[edit]
Within phenomenology, worlds are defined in terms of horizons of experiences.[5][6] When we perceive an object, like a house, we do not just experience this object at the center of our attention but also various other objects surrounding it, given in the periphery.[27] The term "horizon" refers to these co-given objects, which are usually experienced only in a vague, indeterminate manner.[28][29] The perception of a house involves various horizons, corresponding to the neighborhood, the city, the country, the Earth, etc. In this context, the world is the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons".[27][5][6] It is common among phenomenologists to understand the world not just as a spatiotemporal collection of objects but as additionally incorporating various other relations between these objects. These relations include, for example, indication-relations that help us anticipate one object given the appearances of another object and means-end-relations or functional involvements relevant for practical concerns.[27]
Philosophy of mind[edit]
In philosophy of mind, the term "world" is commonly used in contrast to the term "mind" as that which is represented by the mind. This is sometimes expressed by stating that there is a gap between mind and world and that this gap needs to be overcome for representation to be successful.[30][31][32] One problem in philosophy of mind is to explain how the mind is able to bridge this gap and to enter into genuine mind-world-relations, for example, in the form of perception, knowledge or action.[33][34] This is necessary for the world to be able to rationally constrain the activity of the mind.[30][35] According to a realist position, the world is something distinct and independent from the mind.[36] Idealists conceive of the world as partially or fully determined by the mind.[36][37] Immanuel Kant's transcendental idealism, for example, posits that the spatiotemporal structure of the world is imposed by the mind on reality but lacks independent existence otherwise.[38] A more radical idealist conception of the world can be found in Berkeley's subjective idealism, which holds that the world as a whole, including all everyday objects like tables, cats, trees and ourselves, "consists of nothing but minds and ideas".[39]
Theology[edit]
Different theological positions hold different conceptions of the world based on its relation to God. Classical theism states that God is wholly distinct from the world. But the world depends for its existence on God, both because God created the world and because He maintains or conserves it.[40][41][42] This is sometimes understood in analogy to how humans create and conserve ideas in their imagination, with the difference being that the divine mind is vastly more powerful.[40] On such a view, God has absolute, ultimate reality in contrast to the lower ontological status ascribed to the world.[42] God's involvement in the world is often understood along the lines of a personal, benevolent God who looks after and guides His creation.[41] Deists agree with theists that God created the world but deny any subsequent, personal involvement in it.[43] Pantheists reject the separation between God and world. Instead, they claim that the two are identical. This means that there is nothing to the world that does not belong to God and that there is nothing to God beyond what is found in the world.[42][44] Panentheism constitutes a middle ground between theism and pantheism. Against theism, it holds that God and the world are interrelated and depend on each other. Against pantheism, it holds that there is no outright identity between the two.[42][45]
History of philosophy[edit]
In philosophy, the term world has several possible meanings. In some contexts, it refers to everything that makes up reality or the physical universe. In others, it can mean have a specific ontological sense (see world disclosure). While clarifying the concept of world has arguably always been among the basic tasks of Western philosophy, this theme appears to have been raised explicitly only at the start of the twentieth century,[46]
Plato[edit]
Plato is well known for his theory of forms, which posits the existence of two different worlds: the sensible world and the intelligible world. The sensible world is the world we live in, filled with changing physical things we can see, touch and interact with. The intelligible world is the world of invisible, eternal, changeless forms like goodness, beauty, unity and sameness.[47][48][49] Plato ascribes a lower ontological status to the sensible world, which only imitates the world of forms. This is due to the fact that physical things exist only to the extent that they participate in the forms that characterize them, while the forms themselves have an independent manner of existence.[47][48][49] In this sense, the sensible world is a mere replication of the perfect exemplars found in the world of forms: it never lives up to the original. In the allegory of the cave, Plato compares the physical things we are familiar with to mere shadows of the real things. But not knowing the difference, the prisoners in the cave mistake the shadows for the real things.[50]
Wittgenstein[edit]
Two definitions that were both put forward in the 1920s, however, suggest the range of available opinion. "The world is everything that is the case", wrote Ludwig Wittgenstein in his influential Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus, first published in 1921.[51]
Heidegger[edit]
Martin Heidegger, meanwhile, argued that "the surrounding world is different for each of us, and notwithstanding that we move about in a common world".[52]
Eugen Fink[edit]
"World" is one of the key terms in Eugen Fink's philosophy.[53] He thinks that there is a misguided tendency in western philosophy to understand the world as one enormously big thing containing all the small everyday things we are familiar with.[54] He sees this view as a form of forgetfulness of the world and tries to oppose it by what he calls the "cosmological difference": the difference between the world and the inner-worldly things it contains.[54] On his view, the world is the totality of the inner-worldly things that transcends them.[55] It is itself groundless but it provides a ground for things. It therefore cannot be identified with a mere container. Instead, the world gives appearance to inner-worldly things, it provides them with a place, a beginning and an end.[54] One difficulty in investigating the world is that we never encounter it since it is not just one more thing that appears to us. This is why Fink uses the notion of play or playing to elucidate the nature of the world.[54][55] He sees play as a symbol of the world that is both part of it and that represents it.[56] Play usually comes with a form of imaginary play-world involving various things relevant to the play. But just like the play is more than the imaginary realities appearing in it so the world is more than the actual things appearing in it.[54][56]
Goodman[edit]
The concept of worlds plays a central role in Nelson Goodman's late philosophy.[57] He argues that we need to posit different worlds in order to account for the fact that there are different incompatible truths found in reality.[58] Two truths are incompatible if they ascribe incompatible properties to the same thing.[57] This happens, for example, when we assert both that the earth moves and that the earth is at rest. These incompatible truths correspond to two different ways of describing the world: heliocentrism and geocentrism.[58] Goodman terms such descriptions "world versions". He holds a correspondence theory of truth: a world version is true if it corresponds to a world. Incompatible true world versions correspond to different worlds.[58] It is common for theories of modality to posit the existence of a plurality of possible worlds. But Goodman's theory is different since it posits a plurality not of possible but of actual worlds.[57][5] Such a position is in danger of involving a contradiction: there cannot be a plurality of actual worlds if worlds are defined as maximally inclusive wholes.[57][5] This danger may be avoided by interpreting Goodman's world-concept not as maximally inclusive wholes in the absolute sense but in relation to its corresponding world-version: a world contains all and only the entities that its world-version describes.[57][5]
Religion[edit]
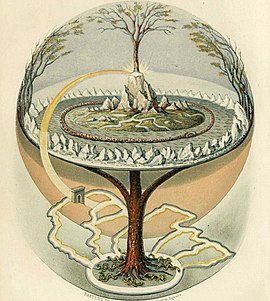
Mythological cosmologies depict the world as centered on an axis mundi and delimited by a boundary such as a world ocean, a world serpent or similar.[59][60]
Hinduism[edit]
Hinduism constitutes a family of religious-philosophical views.[61] These views present perspectives on the nature and role of the world. Samkhya philosophy, for example, is a metaphysical dualism that understands reality as comprising 2 parts: purusha and prakriti.[62] The term "purusha" stands for the individual conscious self that each of "us" possesses. Prakriti, on the other hand, is the 1 world inhabited by all these selves.[63] Samkhya understands this world as a world of matter governed by the law of cause and effect.[62] The term "matter" is understood in a sense in this tradition including physical and mental aspects.[64] This is reflected in the doctrine of tattvas, according to which prakriti is made up of 23 principles or elements of reality.[64] These principles include physical elements, like water or earth, and mental aspects, like intelligence or sense-impressions.[63] The relation between purusha and prakriti is conceived as 1 of observation: purusha is the conscious self aware of the world of prakriti and does not causally interact with it.[62]
A conception of the world is present in Advaita Vedanta, the monist school among the Vedanta schools.[61] Unlike the realist position defended in Samkhya philosophy, Advaita Vedanta sees the world of multiplicity as an illusion, referred to as Maya.[61] This illusion includes impression of existing as separate experiencing selfs called Jivas.[65] Instead, Advaita Vedanta teaches that on the most fundamental level of reality, referred to as Brahman, there exists no plurality or difference.[65] All there is is 1 all-encompassing self: Atman.[61] Ignorance is seen as the source of this illusion, which results in bondage to the world of mere appearances. Liberation is possible in the course of overcoming this illusion by acquiring the knowledge of Brahman, according to Advaita Vedanta.[65]
Christianity[edit]
Contemptus mundi is the name given to the belief that the world, in all its vanity, is nothing more than a futile attempt to hide from God by stifling our desire for the good and the holy.[66] This view has been criticised as a "pastoral of fear" by historian Jean Delumeau.[67]
Orbis Catholicus is a Latin phrase meaning 'Catholic world', per the expression Urbi et Orbi, and refers to that area of Christendom under papal supremacy.[68]
Islam[edit]
In Islam, the term "dunya" is used for the world. Its meaning is derived from the root word "dana", a term for "near".[69] It is associated with the temporal, sensory world and earthly concerns, i.e. with this world in contrast to the spiritual world.[70] Religious teachings warn of a tendency to seek happiness in this world and advise a more ascetic lifestyle concerned with the afterlife.[71] Other strands in Islam recommend a balanced approach.[70]
Mandaeism[edit]
In Mandaean cosmology, the world or earthly realm is known as Tibil. It is separated from the World of Light (alma d-nhūra) above and the World of Darkness (alma d-hšuka) below by aether (ayar).[72][73]
Related terms and problems[edit]
Worldviews[edit]

A worldview is a comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it.[74] As a representation, it is a subjective perspective of the world and thereby different from the world it represents.[75] All higher animals need to represent their environment in some way in order to navigate it. But it has been argued that only humans possess a representation encompassing enough to merit the term "worldview".[75] Philosophers of worldviews commonly hold that the understanding of any object depends on a worldview constituting the background on which this understanding can take place. This may affect not just our intellectual understanding of the object in question but the experience of it in general.[74] It is therefore impossible to assess one's worldview from a neutral perspective since this assessment already presupposes the worldview as its background. Some hold that each worldview is based on a single hypothesis that promises to solve all the problems of our existence we may encounter.[76] On this interpretation, the term is closely associated to the worldviews given by different religions.[76] Worldviews offer orientation not just in theoretical matters but also in practical matters. For this reason, they usually include answers to the question of the meaning of life and other evaluative components about what matters and how we should act.[77][78] A worldview can be unique to one individual but worldviews are usually shared by many people within a certain culture or religion.
Paradox of many worlds[edit]
The idea that there exist many different worlds is found in various fields. For example, theories of modality talk about a plurality of possible worlds and the many-worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics carries this reference even in its name. Talk of different worlds is also common in everyday language, for example, with reference to the world of music, the world of business, the world of football, the world of experience or the Asian world. But at the same time, worlds are usually defined as all-inclusive totalities.[5][6][15][14] This seems to contradict the very idea of a plurality of worlds since if a world is total and all-inclusive then it cannot have anything outside itself. Understood this way, a world can neither have other worlds besides itself or be part of something bigger.[5][57] One way to resolve this paradox while holding onto the notion of a plurality of worlds is to restrict the sense in which worlds are totalities. On this view, worlds are not totalities in an absolute sense.[5] This might be even understood in the sense that, strictly speaking, there are no worlds at all.[57] Another approach understands worlds in a schematic sense: as context-dependent expressions that stand for the current domain of discourse. So in the expression "Around the World in Eighty Days", the term "world" refers to the earth while in the colonial[79] expression "the New World" it refers to the landmass of North and South America.[15]
Cosmogony[edit]
Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world. This includes both scientific cosmogony and creation myths found in various religions.[80][81] The dominant theory in scientific cosmogony is the Big Bang theory, according to which both space, time and matter have their origin in one initial singularity occurring about 13.8 billion years ago. This singularity was followed by an expansion that allowed the universe to sufficiently cool down for the formation of subatomic particles and later atoms. These initial elements formed giant clouds, which would then coalesce into stars and galaxies.[16] Non-scientific creation myths are found in many cultures and are often enacted in rituals expressing their symbolic meaning.[80] They can be categorized concerning their contents. Types often found include creation from nothing, from chaos or from a cosmic egg.[80]
Eschatology[edit]
Eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world. It is traditionally associated with religion, specifically with the Abrahamic religions.[82][83] In this form, it may include teachings both of the end of each individual human life and of the end of the world as a whole. But it has been applied to other fields as well, for example, in the form of physical eschatology, which includes scientifically based speculations about the far future of the universe.[84] According to some models, there will be a Big Crunch in which the whole universe collapses back into a singularity, possibly resulting in a second Big Bang afterward. But current astronomical evidence seems to suggest that our universe will continue to expand indefinitely.[84]
World history[edit]
World history studies the world from a historical perspective. Unlike other approaches to history, it employs a global viewpoint. It deals less with individual nations and civilizations, which it usually approaches at a high level of abstraction.[85] Instead, it concentrates on wider regions and zones of interaction, often interested in how people, goods and ideas move from one region to another.[86] It includes comparisons of different societies and civilizations as well as considering wide-ranging developments with a long-term global impact like the process of industrialization.[85] Contemporary world history is dominated by three mai
Shugo Chara
Shugo Chara theme by Momo123
Download: ShugoChara.p3t

Redirect to:
- From a modification: This is a redirect from a modification of the target's title or a closely related title. For example, the words may be rearranged.
- Please note that there are many more specific templates. Please use {{R from alternative spelling}}, {{R from alternative hyphenation}}, {{R from alternative punctuation}}, {{R from alternative spacing}} and {{R from misquotation}} where relevant; see subcategories of Category:Redirects from modifications for other options (capitals, abbreviations, diacritics, plurals, stylizations, transliteration, ligatures, different parts of speech, etc.). If you are unsure which to use, this template is fine; someone will make it more specific later if necessary.
- In cases of modification from distinctly longer or shorter names, please use {{R from long name}} or {{R from short name}}, respectively. An abbreviation should be tagged with {{R from initialism}} or, if it can be spoken like a word such as NASA and RADAR, use {{R from acronym}}.
- Use this rcat instead of {{R from other capitalisation}} and {{R from plural}} in namespaces other than mainspace for those types of modification. This may also apply to several other subcategories of modification; please check those templates' output before saving if using outside of mainspace.
Rushin
Rushin theme by Rushinobby
Download: Rushin.p3t
Rushin is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
- Bruce Rushin, British art teacher and coin designer
- Kate Rushin (born 1951), black lesbian poet
- Pat Rushin (born 1953), American screenwriter
- Steve Rushin (born 1966), American journalist, sportswriter, and novelist
Modern Warfare 2
Modern Warfare 2 theme by SAS_Sharpshooter
Download: ModernWarfare2_3.p3t

Redirect to:
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:
|
Vampire Hunter D: Bloodlust HD
Vampire Hunter D: Bloodlust HD theme by Jubei808
Download: VampireHunterDBloodlust.p3t

P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Batman Arkham Asylum
Batman Arkham Asylum theme by Momo
Download: BatmanArkhamAsylum.p3t

Redirect to:
- From a modification: This is a redirect from a modification of the target's title or a closely related title. For example, the words may be rearranged.
- Please note that there are many more specific templates. Please use {{R from alternative spelling}}, {{R from alternative hyphenation}}, {{R from alternative punctuation}}, {{R from alternative spacing}} and {{R from misquotation}} where relevant; see subcategories of Category:Redirects from modifications for other options (capitals, abbreviations, diacritics, plurals, stylizations, transliteration, ligatures, different parts of speech, etc.). If you are unsure which to use, this template is fine; someone will make it more specific later if necessary.
- In cases of modification from distinctly longer or shorter names, please use {{R from long name}} or {{R from short name}}, respectively. An abbreviation should be tagged with {{R from initialism}} or, if it can be spoken like a word such as NASA and RADAR, use {{R from acronym}}.
- Use this rcat instead of {{R from other capitalisation}} and {{R from plural}} in namespaces other than mainspace for those types of modification. This may also apply to several other subcategories of modification; please check those templates' output before saving if using outside of mainspace.
District 9
District 9 theme by Anon
Download: District9.p3t

| District 9 | |
|---|---|
 Theatrical release poster | |
| Directed by | Neill Blomkamp |
| Written by |
|
| Based on | Alive in Joburg[a] by Neill Blomkamp |
| Produced by | |
| Starring |
|
| Cinematography | Trent Opaloch |
| Edited by | Julian Clarke |
| Music by | Clinton Shorter[1][2] |
Production companies | |
| Distributed by | Sony Pictures Releasing (through Ster-Kinekor in South Africa[3]) |
Release dates |
|
Running time | 112 minutes[4] |
| Countries | |
| Language | English |
| Budget | $30 million[3] |
| Box office | $210.8 million[3] |
District 9 is a 2009 science fiction action film directed by Neill Blomkamp in his feature film debut, written by Blomkamp and Terri Tatchell, and produced by Peter Jackson and Carolynne Cunningham. It is a co-production of New Zealand, the United States, and South Africa. The film stars Sharlto Copley, Jason Cope, and David James, and was adapted from Blomkamp's 2006 short film Alive in Joburg.
The film is partially presented in a found footage format by featuring fictional interviews, news footage, and video from surveillance cameras. The story, which explores themes of humanity, xenophobia and social segregation, begins in an alternate 1982, when an alien spaceship appears over Johannesburg, South Africa. When a population of sick and malnourished insectoid aliens is discovered on the ship, the South African government confines them to an internment camp called District 9. Twenty years later, during the government's relocation of the aliens to another camp, one of the confined aliens named Christopher Johnson, who is about to try to escape from Earth with his son and return home, crosses paths with a bureaucrat named Wikus van de Merwe leading the relocation. The title and premise of District 9 were inspired by events in Cape Town's District Six, during the apartheid era.
A viral marketing campaign for the film began in 2008 at San Diego Comic-Con, while the theatrical trailer debuted in July 2009. District 9 had its World Premiere on 23 July 2009 at San Diego Comic-Con.[6][7] It was released by TriStar Pictures on 14 August 2009, in North America and became a financial success, earning over $210 million at the box office. It also received acclaim from critics and garnered numerous awards and nominations, including four Academy Award nominations for Best Picture, Best Adapted Screenplay, Best Visual Effects, and Best Film Editing.[8]
Plot[edit]
In 1982, a giant extraterrestrial spaceship arrives and hovers over the South African city of Johannesburg. An investigation team finds over a million malnourished aliens inside, and the South African government relocates them to a camp called District 9. However, over the years, it turns into a slum, and locals often complain that the aliens—derogatorily called "prawns"—are filthy, ignorant lawbreakers who bleed resources from humans.
Following unrest between the aliens and locals, the government hires Multinational United (MNU), a giant weapons manufacturer, to relocate the aliens to a new camp outside the city. Piet Smit, an MNU executive, appoints an MNU employee and his son-in-law, Wikus van de Merwe, to lead the relocation. Meanwhile, three aliens, Christopher Johnson, his young son CJ, and his friend Paul, search a District 9 garbage dump for alien fuel in Prawn technology, which Christopher has had them spend the last 20 years synthesizing enough of to enact his plan. They finally finish in Paul's shack as the relocation begins, but when Wikus comes to serve Paul a notice, he finds the hidden container with the fuel and accidentally sprays some of it in his face while confiscating it. Koobus Venter, a cruel MNU mercenary, kills Paul.
Wikus begins mutating into a Prawn, starting with his left arm injured after the fuel exposure. He is immediately taken to the brutal MNU lab, where researchers discover his chimeric DNA grants him the ability to operate Prawn weaponry, which is biologically restricted for them. Wanting to capture this human/alien hybridity before Wikus fully transforms, Smit orders Wikus' body to be vivisected and harvested for its profitable properties. Wikus, however, overpowers the lab personnel and escapes. While Venter's forces hunt for him, a smear story is broadcast, one that reaches Wikus' wife and Smit's daughter, Tania, claiming Wikus is a wanted fugitive who has contracted a contagious disease from copulating with aliens.
Wikus takes refuge in District 9, finding Christopher and the spaceship's concealed command module dropship underneath his house. Christopher explains to Wikus that the confiscated fuel is crucial to his plan of reactivating the dropship, and if he can get them in the dropship to the mothership, he can cure Wikus. Wikus attempts to acquire weapons from the District 9 Nigerian arms dealer, Obesandjo, who wants to eat Wikus's alien arm to gain alien abilities. Wikus, however, seizes an alien weapon and escapes.
Wikus and Christopher force themselves through MNU to the lab to retrieve the fuel. However, after seeing the brutal experiments MNU has performed on his people in the lab—including a dissected Paul—Christopher tells Wikus he must return home as fast as possible for help and cannot undo Wikus' mutation until he returns in 3 years due to the limited supply of fuel. Enraged, Wikus knocks Christopher down and attempts to fly the module to the mothership himself, but Venter's forces shoot it down. Venter captures Wikus and Christopher, but Obesandjo's gang ambushes the MNU convoy and seizes Wikus.
Meanwhile, CJ, remaining hidden in the dropship, remotely activates the mothership and a large robotic alien battle suit in Obesandjo's base. The suit guns down the Nigerians, and Wikus enters the suit and rescues Christopher from the mercenaries. Heading to the dropship, the two come under heavy fire, and Wikus decides to stay behind to fend off the mercenaries and buy time for Christopher to escape, who promises to return after 3 years and heal Wikus. After all of the other mercenaries are killed, Venter finally cripples the suit and is about to execute Wikus when slum Prawns attack and dismember him alive. Christopher makes it into the dropship with CJ, and the dropship is levitated via a tractor beam back into the mothership, which leaves Earth.
MNU's experiments are exposed, and the aliens are moved to the new camp named District 10. Tania finds a metal flower on her doorstep, giving her hope that Wikus is still alive. Wikus, now fully transformed into a Prawn, is shown in a junkyard crafting flowers for his wife.
Cast[edit]
- Sharlto Copley as Wikus van de Merwe, a mild-mannered, shy, bumbling, awkward bureaucrat at the MNU Department of Alien Affairs, who becomes infected with an alien fluid, slowly turning him into one of the "prawns". This was the first time acting professionally in a feature film for Copley, a friend of director Blomkamp.[9]
- Jason Cope as Christopher Johnson, a District 9 prawn who assists Wikus in fighting MNU.
- Cope also performed the role of Grey Bradnam, the UKNR Chief Correspondent and all the speaking aliens, as well as for the cameraman Trent[10]
- David James as Colonel Koobus Venter, an aggressive, sadistic, and xenophobic PMC mercenary-soldier sent to capture Wikus. He is shown as taking pleasure in killing the aliens and responding brutally to anyone who opposes him.
- Vanessa Haywood as Tania Smit-van de Merwe, Wikus's wife.
- Mandla Gaduka as Fundiswa Mhlanga, Wikus's assistant and trainee during the eviction
- Eugene Wanangwa Khumbanyiwa as Obesandjo, a paralyzed psychopathic Nigerian gang leader who believes that eating alien body parts will enable him to operate their weapons
- Louis Minnaar as Piet Smit, managing director of MNU South Africa and Wikus's father-in-law
- Kenneth Nkosi as Thomas, an MNU security guard and good friend of Wikus
- William Allen Young as Dirk Michaels, the CEO of MNU
- Nathalie Boltt as Sarah Livingstone, a sociologist at Kempton Park University
- Sylvaine Strike as Katrina McKenzie, a doctor from the Department of Social Assistance
- John Sumner as Les Feldman, a MIL engineer
- Nick Blake as Francois Moraneu, a member of the CIV Engineer Team
- Jed Brophy as James Hope, an officer with the SAPS Alien Crimes Unit
- Vittorio Leonardi as Michael Bloemstein, MNU Department of Alien Civil Affairs
- Johan van Schoor as Nicolaas van de Merwe, Wikus's father
- Marian Hooman as Sandra van de Merwe, Wikus's mother
- Jonathan Taylor as the Doctor
- Stella Steenkamp as Phyllis Sinderson, MNU Alien Relations
- Tim Gordon as Clive Henderson, an entomologist at WLG University
- Nick Boraine as Lieutenant Weldon, Colonel Venter's right-hand man
- Robert Hobbs as Ross Pienaar, an MNU mercenary
- Trevor Coppola as MNU Mercenary
- Morne Erasmus as MNU Medic
Themes[edit]
Like Alive in Joburg, the short film on which the feature film is based, the setting of District 9 is inspired by historical events during the apartheid era, particularly alluding to District Six, an inner-city residential area in Cape Town, declared a "whites only" area by the government in 1966, with 60,000 people forcibly removed to Cape Flats, 25 km (16 miles) away.[11] The film also refers to contemporary evictions and forced removals to suburban ghettos in post-apartheid South Africa, as well as the resistance of its residents.[12][13] This includes the high-profile attempted forced removal of the Joe Slovo informal settlement in Cape Town to temporary relocation areas in Delft, plus evictions in the shack settlement Chiawelo, where the film was actually shot.[10] Blikkiesdorp, a temporary relocation area in Cape Town, has also been compared with the District 9 camp, earning a front-page spread in the Daily Voice.[14][15]
Doctor Shohini Chauduri wrote that District 9 even echoes apartheid in its title, as it is reminiscent "of District 6 in Cape Town, declared a whites-only area under the Group Areas Act". She also discusses how the wide shots used in District 9 strongly emphasize the idea of exclusion under apartheid. The separation of people and "prawns" into human and non-human zones marks South Africa's social divisions.[16]
The film emphasizes the irony of Wikus and the impact of his experiences on his personality, which shows him becoming more humane as he becomes less biologically human. The film uses his story to pose the question of humanity as the "prawn" characters in the film are shown to be kinder to Wikus than the actual humans are as he undergoes his transformation. The film also features the portrayal of Nigerian Arms dealers, provoking thought on conflict between marginalized communities.[17] Chris Mikesell from the University of Hawaii newspaper Ka Leo writes that "Substitute 'black,' 'Asian,' 'Mexican,' 'illegal,' 'Jew,' 'white,' or any number of different labels for the word 'prawn' in this film and you will hear the hidden truth behind the dialogue".[18]
Themes of racism and xenophobia are shown in the form of speciesism. Used to describe the aliens, the word "prawn" is a reference to the Parktown prawn, a king cricket species considered a pest in South Africa.[19][20] Copley has said that the theme is not intended to be the main focus of the work, but can work at a subconscious level even if it is not noticed. The racism in the film is portrayed on an institutional level, as despite the brutality towards the aliens by MNU exposed to the public they are still relocated as originally planned.[21]
Duane Dudek of the Journal Sentinel wrote that "The result is an action film about xenophobia, in which all races of humans are united in their dislike and mistrust of an insect-like species".[22]
Another underlying theme in District 9 is states' reliance on multinational corporations (whose accountability is unclear and whose interests are not necessarily congruent with democratic principles) as a form of government-funded enforcement. As MNU represents the type of corporation which partners with governments, the negative portrayal of MNU in the film depicts the dangers of outsourcing militaries and bureaucracies to private contractors.[23][24]
Production[edit]
Development[edit]
Producer Peter Jackson planned to produce a film adaptation based on the Halo video game franchise with first-time director Neill Blomkamp. Due to a lack of financing, the Halo adaptation was placed on hold. Jackson and Blomkamp discussed pursuing alternative projects and eventually chose to produce and direct, respectively, District 9 featuring props and items originally made for the Halo film.[25] Blomkamp had previously directed commercials and short films, but District 9 was his first feature film. The director co-wrote the script with his wife, Terri Tatchell, and chose to film in South Africa, where he was born.[26][27]
In District 9, Tatchell and Blomkamp returned to the world explored in his short film Alive in Joburg, choosing characters, moments and concepts that they found interesting including the documentary-style filmmaking, staged interviews, alien designs, alien technology/mecha suits, and the parallels to racial conflict and segregation in South Africa, and fleshing out these elements for the feature film.[28]
QED International financed the negative cost. After the 2007 American Film Market, QED partnered with Sony's TriStar Pictures for distribution in several territories.[29][30]
Filming[edit]
The film was shot on location in Chiawelo, Soweto, during a time of violent unrest in Alexandra (Gauteng) and other South African townships involving clashes between native South Africans and Africans born in other countries.[31] The location that portrays District 9 is itself a real impoverished neighbourhood from which people were being forcibly relocated to government-subsidised housing.[10] Several scenes were shot at the Ponte building.[32]
Filming for District 9 took place during the winter in Johannesburg. According to director Neill Blomkamp, during the winter season, Johannesburg "actually looks like Chernobyl", a "nuclear apocalyptic wasteland". Blomkamp wanted to capture the deserted, bleak atmosphere and environment, so he and the crew had to film during the months of June through July. The film took a total of 60 days of shooting. Filming in December raised another issue in that there was much more rain. Due to the rain, there was a lot of greenery to work with, which Blomkamp did not want. Blomkamp had to cut some of the vegetation in the scenery to portray the setting as desolate and dark.
The film features many weapons and vehicles produced by the South African arms industry, including the R5 and Vektor CR-21 assault rifles, Denel NTW-20 20 mm anti-materiel rifle, Milkor BXP submachine gun, Casspir armoured personnel carrier, Ratel infantry fighting vehicle, Rooikat armoured fighting vehicle, Atlas Oryx helicopter and militarized Toyota Hilux "technical" pickup truck.[33][34]
Blomkamp said no single film influenced District 9, but cited the 1980s "hardcore sci-fi/action" films such as Alien, Aliens, The Terminator, Terminator 2: Judgment Day, Predator and RoboCop as subconscious influences. The director said, "I don't know whether the film has that feeling or not for the audience, but I wanted it to have that harsh 1980s kind of vibe—I didn't want it to feel glossy and slick."[28]
Because of the amount of hand-held shooting required for the film, the producers and crew decided to shoot using the digital Red One 4K camera. Cinematographer Trent Opaloch used nine digital Red Ones owned by Peter Jackson for primary filming.[35] According to HD Magazine, District 9 was shot on RED One cameras using build 15, Cooke S4 primes and Angenieux zooms. The documentary-style and CCTV-style cam footage was shot on the Sony EX1/EX3 XDCAM-HD. Additionally, the post-production team was warned that the most RED Camera footage they could handle a day was about an hour and a half. When that got to five hours a day additional resources were brought in, and 120 terabytes of data was filled.[36]
Creative background[edit]
This film is essentially an expanded version of director Neill Blomkamp's 2005 work. The original short film, titled "Alive in Joburg" was written and directed by Neill Blomkamp. It narrates the conflict between aliens and local residents in Johannesburg (referred to as Joburg). Sharlto Copley, who starred in "Alive in Joburg," also became the lead actor in "District 9." Interestingly, the movie was developed with six different endings, but only one was ultimately used.
During the same period, Peter Jackson was planning to produce a film adaptation of the Xbox game "Halo" and had chosen Neill Blomkamp as the director. However, due to the interests of major corporations, the project was indefinitely shelved. Believing in Blomkamp's talent, Peter Jackson decided to fund a new project, investing 30 million dollars for Blomkamp to direct a film of his own choosing. This led to the creation of "District 9."
Content mapping[edit]
The alien settlement depicted in the film was actually shot in an African slum, lending a gritty realism to the setting. Except for the main characters' dwelling and the alien protagonist Christopher's hut, which were temporarily constructed, all the slum shacks were real locations. The depiction of aliens dismembering wild beasts and their fondness for cat food draws a parallel to the desperate living conditions in slums, where inhabitants often rely on carrion or cat food for sustenance.
The idea of aliens eating cat food was inspired by a crew member who used cat food as bait for shrimp during the film's production. Additionally, the narrative of the aliens' relocation in the film mirrors a real event: the demolition of a Johannesburg slum and the subsequent forced relocation of its residents to a government-built settlement area.
This approach in the movie not only adds a layer of authenticity but also serves as a powerful metaphor for the socio-economic issues faced by marginalized communities.
Visual effects[edit]
The aliens in District 9 were designed by Weta Workshop, and the design was executed by Image Engine.[citation needed]
Blomkamp wanted the aliens to maintain both humane and barbaric features in the design of the creatures. According to Terri Tatchell, the director's writing partner, "They are not appealing, they are not cute, and they don't tug at our heartstrings. He went for a scary, hard, warrior-looking alien, which is much more of a challenge."[37] The look of the alien, with its exoskeleton-crustacean hybrid and crab-like shells, was meant to initially evoke a sense of disgust from viewers but as the story progresses, the audience was meant to sympathize with these creatures who had such human-like emotions and characteristics. Blomkamp established criteria for the design of the aliens. He wanted the species to be insect-like but also bipedal. The director wanted the audience to relate to the aliens and said of the restriction on the creature design, "Unfortunately, they had to be human-esque because our psychology doesn't allow us to really empathize with something unless it has a face and an anthropomorphic shape. Like if you see something that's four-legged, you think it's a dog; that's just how we're wired ... If you make a film about an alien force, which is the oppressor or aggressor, and you don't want to empathize with them, you can go to town. So creatively that's what I wanted to do but story-wise, I just couldn't."[38]
Blomkamp originally sought to have Weta Digital design the creatures, but the company was busy with effects for Avatar. The director then decided to choose a Vancouver-based effects company because he anticipated making films there in the future and because British Columbia offered a tax credit. Blomkamp met with Image Engine and considered them "a bit of a gamble" since the company had not pursued a project as large as a feature film.[28] Aside from the aliens appearing on the operating table in the medical lab, all of them were created using CGI visual effects.[39]
Weta Digital designed the 21⁄2-kilometer-diameter mothership[40] and the drop ship, while the exo-suit and the little pets were designed by The Embassy Visual Effects. Zoic Studios performed overflow 2D work.[28] On-set live special effects were created by MXFX.[41] Some of the software used for the visual effects were Autodesk Softimage.[42]
Music[edit]
The music for District 9 was scored by Canadian composer Clinton Shorter, who spent three weeks preparing for the film. Director Neill Blomkamp wanted a "raw and dark" score, but one that maintained its South African roots. This was a challenge for Shorter, who found much of the South African music he worked with to be optimistic and joyful. Unable to get the African drums to sound dark and heavy, Shorter used a combination of taiko drums and synthesized instruments for the desired effects, with the core African elements of the score conveyed in the vocals and smaller percussion.[43] Both the score and soundtrack feature music and vocals from Kwaito artists.
Release[edit]
District 9 held its world premiere in 23 July 2009 at the Reading Gaslamp 15 at San Diego Comic-Con, with Copley, Blomkamp and Jackson in attendance.[44][45] It was released by TriStar Pictures on 14 August 2009.
Marketing[edit]
Sony Pictures launched a "Humans Only" marketing campaign to promote District 9. Sony's marketing team designed its promotional material to emulate the segregational billboards that appear throughout the film.[38] Billboards, banners, posters, and stickers were thus designed with the theme in mind, and the material was spread across public places such as bus stops in various cities, including "humans only" signs in certain locations and providing toll-free numbers to report "non-human" activity.[46][47] This marketing strategy was designed to provoke reactions in its target audience (namely, sci-fi fans and people concerned with discrimination), hence the use of obviously fake segregational propaganda.[48] According to Dwight Caines, Sony's president of digital marketing, an estimated 33,000 phone calls were made to the toll-free numbers during a two-week period with 2,500 of them leaving voicemails with reports of alien sightings.[49] Promotional material was also presented at the 2008 San Diego Comic-Con, advertising the website D-9.com,[50] which had an application presented by the fictional Multi-National United (MNU). The website had a local alert system for Johannesburg (the film's setting), news feeds, behavior recommendations, and rules and regulations. Other viral websites for the film were also launched, including an MNU website with a countdown timer for the film's release,[51] an anti-MNU blog run by fictional alien character Christopher Johnson,[52] and an MNU-sponsored educational website.[53][54] An online game for District 9 has also been made where players can choose to be a human or an alien. H
Momos Theme
Momos theme by Momo
Download: Momos.p3t
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Style Blue
Style Blue theme by Josh Bambrick
Download: StyleBlue.p3t
P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
Summer Glau 2.1
Summer Glau 2.1 theme by SC87
Download: SummerGlau21.p3t

P3T Unpacker v0.12
Copyright (c) 2007. Anoop Menon
This program unpacks Playstation 3 Theme files (.p3t) so that you can touch-up an existing theme to your likings or use a certain wallpaper from it (as many themes have multiple). But remember, if you use content from another theme and release it, be sure to give credit!
Download for Windows: p3textractor.zip
Instructions:
Download p3textractor.zip from above. Extract the files to a folder with a program such as WinZip or WinRAR. Now there are multiple ways to extract the theme.
The first way is to simply open the p3t file with p3textractor.exe. If you don’t know how to do this, right click the p3t file and select Open With. Alternatively, open the p3t file and it will ask you to select a program to open with. Click Browse and find p3textractor.exe from where you previously extracted it to. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename]. After that, all you need to do for any future p3t files is open them and it will extract.
The second way is very simple. Just drag the p3t file to p3textractor.exe. It will open CMD and extract the theme to extracted.[filename].
For the third way, first put the p3t file you want to extract into the same folder as p3textractor.exe. Open CMD and browse to the folder with p3extractor.exe. Enter the following:
p3textractor filename.p3t [destination path]Replace filename with the name of the p3t file, and replace [destination path] with the name of the folder you want the files to be extracted to. A destination path is not required. By default it will extract to extracted.filename.
